Transformed Plant And Method For Producing Exudate Containing Sugar Using Transformed Plant
OHTO; Chikara ; et al.
U.S. patent application number 16/684760 was filed with the patent office on 2020-03-05 for transformed plant and method for producing exudate containing sugar using transformed plant. This patent application is currently assigned to TOYOTA JIDOSHA KABUSHIKI KAISHA. The applicant listed for this patent is Naohiro AOKI, Tatsuro HIROSE, Ryu OHSUGI, Chikara OHTO, Madoka YONEKURA. Invention is credited to Naohiro AOKI, Tatsuro HIROSE, Ryu OHSUGI, Chikara OHTO, Madoka YONEKURA.
| Application Number | 20200071715 16/684760 |
| Document ID | / |
| Family ID | 53478887 |
| Filed Date | 2020-03-05 |










View All Diagrams
| United States Patent Application | 20200071715 |
| Kind Code | A1 |
| OHTO; Chikara ; et al. | March 5, 2020 |
TRANSFORMED PLANT AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING EXUDATE CONTAINING SUGAR USING TRANSFORMED PLANT
Abstract
The production of exudate containing sugar from a plant at a high concentration is provided. A nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation having a certain consensus sequence derived from the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins classified in the clade III is introduced and/or expression of the protein is enhanced.
| Inventors: | OHTO; Chikara; (Toyota-shi, JP) ; YONEKURA; Madoka; (Nagoya-shi, JP) ; AOKI; Naohiro; (Tokyo, JP) ; OHSUGI; Ryu; (Tokyo, JP) ; HIROSE; Tatsuro; (Joetsu-shi, JP) | ||||||||||
| Applicant: |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assignee: | TOYOTA JIDOSHA KABUSHIKI
KAISHA Toyota-shi JP THE UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO Tokyo JP NATIONAL AGRICULTURE AND FOOD RESEARCH ORGANIZATION Tsukuba-shi JP |
||||||||||
| Family ID: | 53478887 | ||||||||||
| Appl. No.: | 16/684760 | ||||||||||
| Filed: | November 15, 2019 |
Related U.S. Patent Documents
| Application Number | Filing Date | Patent Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15107998 | Jun 24, 2016 | 10494641 | ||
| PCT/JP2014/084316 | Dec 25, 2014 | |||
| 16684760 | ||||
| Current U.S. Class: | 1/1 |
| Current CPC Class: | C12N 15/8245 20130101; C07K 14/415 20130101 |
| International Class: | C12N 15/82 20060101 C12N015/82; C07K 14/415 20060101 C07K014/415 |
Foreign Application Data
| Date | Code | Application Number |
|---|---|---|
| Dec 27, 2013 | JP | 2013-273128 |
Claims
1. A method for producing an exudate, comprising the steps of cultivating a transformed plant in which a nucleic acid encoding a transporter protein having a consensus sequence comprising the following amino acid sequence: (L/I/V/M/F)x(G/A)xx(I/L/V/M/F)xxxx(L/I/V/F)(A/S)(P/S) [SEQ ID NO: 1] (1-3aa) (P/S/T/A)T (F/L)xx(I/V)xxxKxxxxxxxxPYxxx(L/I)xxxx(L/I)x(I/L/M/V/F)xY(A/S/G) [SEQ ID NO: 2] (7-13aa)(I/L/V/M)(1-2aa)(I/V)Nxxxxxx(E/Q)xxYxxx(Y/F)xx(Y/F)(A/G/S) [SEQ ID NO: 3] (35-36aa)(R/Q/H)xxxxGx(V/I/L)xxxxx(V/M/L/I/F)xxxx(A/S/T)P(L/M)x(I/V)(I/M/- V/L) [SEQ ID NO: 4] (2-7aa) (V/I) (V/I/M)x(T/S)x(S/N)xx(F/Y) (M/L) (P/S) (F/I/V/L)xLSxx(L/I) (T/V)xx(A/G)xx W(F/L)xYGxxxxDxx(V/I)xxPNxxGxx(F/L) (G/S)xxQ(M/I)x(L/M/I/V/F) (Y/H/F) [SEQ ID NO: 5] and being involved in sugar transportation is introduced and/or expression of the protein is enhanced; and collecting an exudate from the transformed plant.
2. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the transformed plant is cultivated under conditions at a relative humidity of 80% RH or more.
3. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the exudate is guttation.
4. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the transporter protein is a protein in the clade III among the clades I to V of taxonomic groups based on the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins.
5. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): (a) a protein comprising any of the amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 137; (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 137 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
6. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1 wherein the consensus sequence comprises the following amino acid sequence: TABLE-US-00030 [SEQ ID NO: 6] G(L/I/V/F/M)xGx(I/V/L)(I/V/L)(S/T)xxxxL(A/S)P(L/ V/I/M)(P/S/T/A)TFxx(I/V)x(K/R)xK(S/T)xxx(F/Y)x(S/ A)xPYxx(A/S/T)LxSxxLx(L/I/M/V)(Y/F)Y(A/G) [SEQ ID NO: 7] (7-9 aa)(L/I)(I/V/L)(T/S)INxx(G/A)xx(I/V/M)(E/Q) xxYxxx(F/Y)(L/I/V/F)x(Y/F)Ax(K/R/N)xxxxx(T/A) [SEQ ID NO: 8] (7-8 aa)(V/F/L/I/M)(18-19 aa)(R/Q/H)xxxxGx(I/V) xxxxx(V/I/L/M)x(V/M)F(A/V)(A/S/T)PLx(I/V)(I/M/V/L) xxV(I/V)(K/R/Q)(T/S)(K/R)S(V/A)x(F/Y)MP(F/I/L)xLS (L/F/V)xL(T/V)(L/I)xAxxW(F/L)xYG(L/F)xxxDxx(V/I) xxPNxxGxx(L/F)(G/S)xxQMx(L/V/I)(Y/F)xx(Y/F).
7. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 6, wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): (a) a protein comprising any of the amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 35; (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 35 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
8. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the consensus sequence comprises the following amino acid sequence: TABLE-US-00031 [SEQ ID NO: 9] (A/V)xxxG(I/L/V)xGN(I/L/V)(I/L/V)S(F/L)x(V/T)xL (A/S)P(V/L/I)(P/A)TFxx(I/V)x(K/R)xK(S/T)xx(G/S) (F/Y)(Q/S/E)SxPYxx(A/S/T)LxS(A/C/S)xLx(L/I/M)(Y/F) Y(A/G)xx(K/T) [SEQ ID NO: 10] (3-5 aa)(L/M/P)(L/I)(I/L/V)(T/S)INxx(G/A)xx(I/V) (E/Q)xxY(I/L)x(L/M/V/I)(F/Y)(L/I/V/F)x(Y/F)Ax(K/R) xxxxx(T/A)xx(L/M/F/V/I)(L/F/V/I)xxx(N/D)(F/V/I/L) xx(F/L)xx(I/L/V)xxxxxx(L/I/V) [SEQ ID NO: 11] (5-6 aa)(R/Q)xxxxGx(I/V)xxxx(S/A)(V/L/M)(C/S/A)VF (A/V)(A/S)P Lx(I/V)(I/M/V)xxV(I/V)(K/R/Q)(T/S)(K/ R)S(V/A)E(F/Y)MP(F/I)xLS(L/F/V)xL(T/V)(L/I)(S/N)A (V/I)xW(F/L)xYGLxx(K/N)Dxx(V/I)xxPN(V/I)xGxx(F/L) (G/S)xxQMxL(Y/F)xx(Y/F).
9. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 8, wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): (a) a protein comprising any of the amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 26; (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 26 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
10. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the consensus sequence comprises the following amino acid sequence: TABLE-US-00032 [SEQ ID NO: 12] (M/L/V)xx(T/K/N/S)xxxxAxxFG(L/I/V)LGN(I/L/V)(I/V) SFxVxL(S/A)P(V/I)PTFxxIxK(K/R)K(S/T)x(E/K)(G/S)(F/ Y)(Q/E)S(I/L)PYxx(A/S)LxS(A/C)xLx(L/I/M)YY(A/G)xxK [SEQ ID NO: 13] (4-5 aa)(L/M)(L/I)(I/V)(T/S)IN(A/S/T)(F/V)(G/A)x (F/V)(I/V)(E/Q)xxY(I/L)x(L/M/I)(F/Y)(F/V/I/L)x(Y/ F)Ax(K/R)xx(R/K)xx(T/A)(L/V/M)K(V/L/M/F)(L/I/V/F) xxx(N/D)(F/V/I)xx(F/L)xx(I/L)(L/I/V/F)(L/M/V)(L/V) xx(F/L)(L/I/V) [SEQ ID NO: 14] (5-6 aa)(R/Q)x(K/S/Q)x(L/I/V)Gx(I/V)Cxxx(S/A)(V/L) (S/C/A)VF(A/V)(A/S)PLx(I/V)(M/I/V)xxV(I/V)(K/R)T (K/R)S(V/A)E(Y/F)MPFxLS(L/F)xLT(I/L)(S/N)A(V/I)xW (L/F)xYGLx(L/I)(K/N)Dxx(V/I)A(L/F/I/M)PN(V/I)(L/ I/V)Gxx(L/F)GxxQM(I/V)L(Y/F)(V/L/I/M)(V/L/I/M)(Y/ F)(K/R/Q).
11. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 10, wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): (a) a protein comprising any of the amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 21; (b) a protein comprising an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 21.
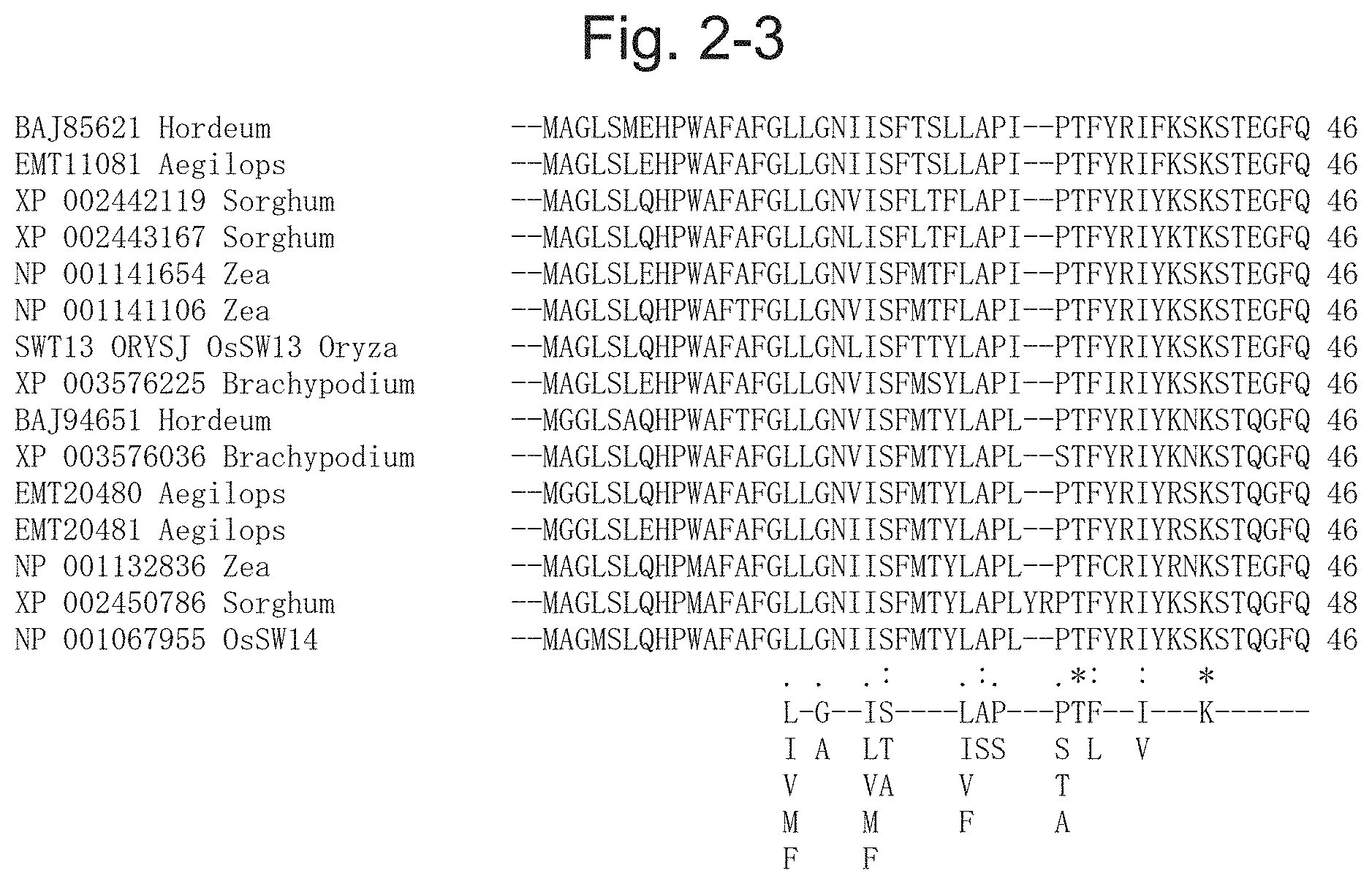
12. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 1, wherein the transformed plant is a phanerogam.
13. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 12, wherein the phanerogam is an angiosperm.
14. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 13, wherein the angiosperm is a monocot.
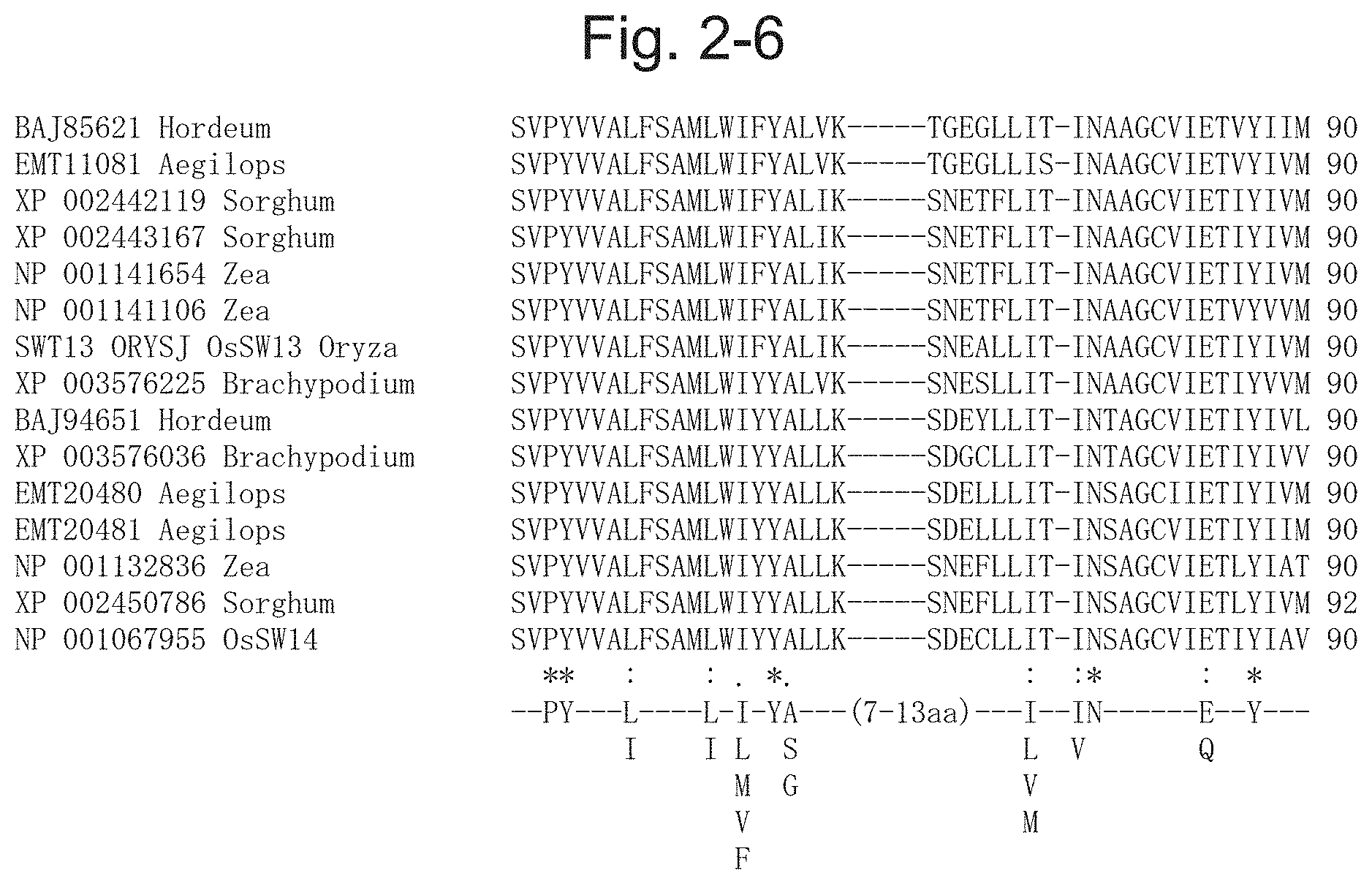
15. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 14, wherein the monocot is a plant of the family Poaceae.
16. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 15, wherein the plant of the family Poaceae is a plant of the genus Oryza.
17. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 13, wherein the angiosperm is a dicot.
18. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 17, wherein the dicot is a plant of the family Brassicaceae.
19. The method for producing an exudate according to claim 18, wherein the plant of the family Brassicaceae is a plant of the genus Arabidopsis.
Description
CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application is a Divisional of U.S. application Ser. No. 15/107,998 filed Jun. 24, 2016, which is a National Stage of International Application No. PCT/JP2014/084316 filed Dec. 25, 2014, claiming priority based on Japanese Patent Application No. 2013-273128 filed Dec. 27, 2013, the contents of all of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety.
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0002] The present invention relates to a transformed plant that has gained an excellent trait by introduction of a given gene and a method for producing an exudate containing sugar using the transformed plant.
BACKGROUND ART
[0003] For stable production of biofuel or bioplastics, low cost and stable supply of their raw material sugar is desired. The representative example of the raw material sugar is sugar accumulated in sugarcane. Extraction of sugar from sugarcane generally requires processes such as cutting down of sugarcane at a predetermined harvest time, crushing, pressing, concentration, and purification. Moreover, after harvest, the farmland requires management work such as maintenance of farm for new cultivation, planting, and spraying herbicides and insecticides. The production of the raw material sugar with plants such as sugarcane has been conventionally a process requiring a great deal of cost such as that for the production process and the cultivation, as described above.
[0004] Patent Literature 1 discloses a method for recovering a heterologous protein encoded by a heterologous gene from a plant transformed to express the heterologous gene. The method disclosed in Patent Literature 1 comprises collecting an exudate from a plant transformed to express a heterologous gene and recovering the heterologous protein from the collected exudate. Examples of the exudate in Patent Literature 1 include exudate from the rhizome and the guttation exuded from a plant as an exudate through the hydathode of the leaf
[0005] Patent Literature 2 and Non Patent Literature 1 disclose transporter proteins involved in sugar transport in plant in Arabidopsis thaliana and rice (Oryza sativa). The transporter proteins disclosed in Patent Literature 2 and Non Patent Literature 1 are known as GLUE proteins or SWEET proteins. Introduction of a nucleic acid encoding a transporter protein disclosed in Patent Literature 2 and Non Patent Literature 1 into a plant may improve the amount of sugar transport to root.
[0006] Non Patent Literature 2 describes the confirmation of function of a cell membrane small molecule transporter by artificially localizing the cell membrane transporter on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and measuring the small molecule transporter activity of the ER. In particular, the glucose transporters GLUTs and SGLTs were localized on the ER and their original functions were speculated using FRET (Forster resonance energy transfer or fluorescence resonance energy transfer).
CITATION LIST
Patent Literature
Patent Literature 1
[0007] JP Patent Publication (Kohyou) No. 2002-501755 A
Patent Literature 2
[0008] JP Patent Publication (Kohyou) No. 2012-525845 A
Non Patent Literature
Non Patent Literature 1
[0009] Nature (2010) 468, 527-534
Non Patent Literature 2
[0010] FASEB J. (2010) 24, 2849-2858
SUMMARY OF INVENTION
Technical Problem
[0011] As described in the foregoing, large cost of producing sugar using plants has been a big problem. The aforementioned problem may be however solved by including sugar at a high concentration in the exudate derived from a plant and collecting the exudate. Patent Literature 1 discloses the collection of a heterologous protein from exudate, but no technique to collect sugar from the exudate. Patent Literature 2 and Non Patent Literature 1 disclose the transporter proteins, designated as SWEETs, involved in sugar transportation and nucleic acids encoding them, but no relation between these transporter proteins or nucleic acids encoding them and the sugar content in the exudate.
[0012] Accordingly, in view of the circumstances described above, an object of the present invention is to provide a transformed plant that produces an exudate containing sugar at a high concentration and a method for producing sugar using the transformed plant.
Solution to Problem
[0013] As a result of diligent studies to achieve the purpose described above, the present inventors have found that high sugar contents in exudate are achieved in the transformed plant in which a nucleic acid encoding a SWEET protein in a certain group (clade) is introduced and expression of the protein is enhanced, thereby completing the present invention.
[0014] The present invention encompasses the following:
[0015] (1) A transformed plant or a transformed plant cell in which a nucleic acid encoding a transporter protein having a consensus sequence comprising the following amino acid sequence: (L/V/M/M/F)x(G/A)xx(I/L/V/M/F)xxxx(L/V/M/F)(A/S)(P/S) [SEQ ID NO: 1] (1-3aa)(P/S/T/A)T(F/L)xx(I/V)xxxKxxxxxxxxPYxxx(L/I)xxxx(L/I)x(I/L/M/V/F)x- Y(A/S/G) [SEQ ID NO: 2] (7-13aa)(I/L/V/M)(1-2aa)(I/V)Nxxxxxx(E/Q)xxYxxx(Y/F)xx(Y/F)(A/G/S) [SEQ ID NO: 3] (35-36aa)(R/Q/H)xxxxGx(V/I/L)xxxxx(V/M/L/I/F)xxxx(A/S/T)P(L/M)x- (I/V)(I/MN/L) [SEQ ID NO: 4] (2-7aa)(V/I)(V/I/M)x(T/S)x(S/N)xx(F/Y)(M/L)(P/S)(F/I/V/L)xLSxx(L/I)(T/V)x- x(A/G)xxW(F/L) xYGxxxxDxx(V/I)xxPNxxGxx(F/L)(G/S)xxQ(M/I)x(L/M/I/V/F)(Y/H/F) [SEQ ID NO: 5] and being involved in sugar transportation is introduced and/or expression of the protein is enhanced.
[0016] (2) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (1), wherein the transporter protein is a protein in the clade III among the clades I to V of taxonomic groups based on the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins.
[0017] (3) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (1), wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): [0018] (a) a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 137; [0019] (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 137 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
[0020] (4) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (1), wherein the consensus sequence comprises the following amino acid sequence:
TABLE-US-00001 [SEQ ID NO: 6] G(L/I/V/F/M)xGx(I/V/L)(I/V/L)(S/T)xxxxL(A/S)P(L/ V/I/M)(P/S/T/A)TFxx(I/V)x(K/R)xK(S/T)xxx(F/Y)x (S/A)xPYxx(A/S/T)LxSxxLx(L/I/M/V)(Y/F)Y(A/G) [SEQ ID NO: 7] (7-9 aa)(L/I)(I/V/L)(T/S)INxx(G/A)xx(I/V/M)(E/Q) xxYxxx(F/Y)(L/I/V/F)x(Y/F)Ax(K/R/N)xxxxx(T/A) (7-8 aa) [SEQ ID NO: 8] (V/F/L/I/M)(18-19 aa)(R/Q/H)xxxxGx(I/V)xxxxx(V/I/ L/M)x(V/M)F(A/V)(A/S/T)PLx(I/V)(I/M/V/L)xxV(I/V) (K/R/Q)(T/S)(K/R)S (V/A)x(F/Y)MP(F/I/L)xLS(L/F/V) xL(T/V)(L/I)xAxxW(F/L)xYG(L/F)xxxDxx(V/I)xxPNxxGxx (L/F)(G/S)xxQMx(L/V/I)(Y/F)xx(Y/F).
[0021] (5) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (4), wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): [0022] (a) a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 35; [0023] (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 35 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
[0024] (6) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (1), wherein the consensus sequence comprises the following amino acid sequence:
TABLE-US-00002 [SEQ ID NO: 9] (A/V)xxxG(I/L/V)xGN(I/L/V)(I/L/V)S(F/L)x(V/T)xL(A/ S)P(V/L/I)(P/A)TFxx(I/V)x(K/R)xK(S/T)xx(G/S)(F/Y) (Q/S/E)SxPYxx(A/S/T)LxS(A/C/S)xLx(L/I/M)(Y/F)Y (A/G)xx(K/T) [SEQ ID NO: 10] (3-5 aa)(L/M/P)(L/I)(I/L/V)(T/S)INxx(G/A)xx(I/V) (E/Q)xxY(I/L)x(L/M/V/I)(F/Y)(L/I/V/F)x(Y/F)Ax(K/R) xxxxx(T/A)xx(L/M/F/V/I)(L/F/V/I)xxx(N/D)(F/V/I/L) xx(F/L)xx(I/L/V)xxxxxx(L/I/V) [SEQ ID NO: 11] (5-6 aa)(R/Q)xxxxGx(I/V)xxxx(S/A)(V/L/M)(C/S/A)VF (A/V)(A/S)PLx(I/V)(I/M/V)xxV(I/V)(K/R/Q)(T/S)(K/R) S(V/A)E(F/Y)MP(F/I)xL S(L/F/V)xL(T/V)(L/I)(S/N)A (V/I)xW(F/L)xYGLxx(K/N)Dxx(V/I)xxPN(V/I)xGxx(F/L) (G/S)xxQMxL(Y/F)xx(Y/F).
[0025] (7) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (6), wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): [0026] (a) a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 26; [0027] (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 26 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
[0028] (8) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (1), wherein the consensus sequence comprises the following amino acid sequence:
TABLE-US-00003 [SEQ ID NO: 12] (M/L/V)xx(T/K/N/S)xxxxAxxFG(L/I/V)LGN(I/L/V)(I/V) SFxVxL(S/A)P(V/I)PTFxxIxK(K/R)K(S/T)x(E/K)(G/S)(F/ Y)(Q/E)S(I/L)PYxx(A/S)LxS(A/C)xLx(L/I/M)YY(A/G)xxK [SEQ ID NO: 13] (4-5 aa)(L/M)(L/I)(I/V)(T/S)IN(A/S/T)(F/V)(G/A)x (F/V)(I/V)(E/Q)xxY(I/L)x(L/M/I)(F/Y)(F/V/I/L)x(Y/ F)Ax(K/R)xx(R/K)xx(T/A)(L/V/M)K(V/L/M/F)(L/I/V/F) xxx(N/D)(F/V/I)xx(F/L)xx(I/L)(L/I/V/F)(L/M/V)(L/V) xx(F/L)(L/I/V) [SEQ ID NO: 14] (5-6 aa)(R/Q)x(K/S/Q)x(L/I/V)Gx(I/V)Cxxx(S/A)(V/L) (S/C/A)VF(A/V)(A/S)PLx(I/V)(M/I/V)xxV(I/V)(K/R)T (K/R)S(V/A)E(Y/F)MPFxLS(L/F)xLT(I/L)(S/N)A(V/I)xW (L/F)xYGLx(L/I)(K/N)Dxx(V/I)A(L/F/I/M)PN(V/I)(L/ I/V)Gxx(L/F)GxxQM(I/V)L(Y/F)(V/L/I/M)(V/L/I/M)(Y/ F)(K/R/Q).
[0029] (9) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (8), wherein the transporter protein is a protein of any of the following (a) and (b): [0030] (a) a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 21; [0031] (b) a protein having an amino acid sequence having an identity of 90% or more to an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 21 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation.
[0032] (10) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (1), wherein the transformed plant is a phanerogam.
[0033] (11) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (10), wherein the phanerogam is an angiosperm.
[0034] (12) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (11), wherein the angiosperm is a monocot.
[0035] (13) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (12), wherein the monocot is a plant of the family Poaceae.
[0036] (14) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (13), wherein the plant of the family Poaceae is a plant of the genus Oryza.
[0037] (15) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (11), wherein the angiosperm is a dicot.
[0038] (16) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (15), wherein the dicot is a plant of the family Brassicaceae.
[0039] (17) The transformed plant or transformed plant cell according to (16), wherein the plant of the family Brassicaceae is a plant of the genus Arabidopsis.
[0040] (18) A method for producing an exudate, comprising the steps of cultivating a transformed plant according to any of the above (1) to (17); and collecting an exudate from the transformed plant.
[0041] (19) A method for producing an exudate according to (18), wherein the transformed plant is cultivated under conditions at a relative humidity of 80% RH or more.
[0042] (20) The method for producing an exudate according to (18), wherein the exudate is guttation.
[0043] The description of the present application encompasses the contents described in the description and/or the drawings of JP patent application No. 2013-273128, which is the basics of the priority of the present application.
Advantageous Effects of Invention
[0044] According to the present invention, the sugar content in the exudate derived from plants can be greatly increased. Accordingly, transformed plants according to the present invention can produce exudate having a property such as high sugar content by introducing a nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation and/or enhancing expression of the protein. Also, the method for producing an exudate according to the present invention can produce an exudate with a high sugar content by using a transformed plant in which a nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation is introduced and/or expression of the protein is enhanced. Furthermore, the exudate collected from the transformed plant can be used as a raw material for producing alcohol, organic acid, alkane, and terpenoids because of its high sugar content.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
[0045] FIG. 1-1 is a schematic view of a phylogenetic tree made based on the information of amino acid sequences of SWEET proteins in the clade III defined in Non-Patent Literature 1 (Nature (2010) 468, 527-532) collected from the GenBank database provided at National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).
[0046] FIG. 1-2 is an extended view of a part of the phylogenetic tree shown in FIG. 1-1.
[0047] FIG. 1-3 is an extended view of a part of the phylogenetic tree shown in FIG. 1-1.
[0048] FIG. 2-1 illustrates a result of multiple alignment analysis of the proteins contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1[XP 004235326 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 117), XP 004235334 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 119), ACV71016 Capsicum (SEQ ID NO: 36), XP 004235333 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 118), XP 004235342 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 122), XP 004235339 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 120), XP 004241452 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 124), XP 004235340 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 121), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 004503778 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 131), AFK48645 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 38), NP 001241307 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 75), NP 001242732 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 76), XP 003523161 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 99), NP 001237418 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 73), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), XP 004138032 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 109), EMJ10621 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 49), XP 004297512 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 127), XP 002284244 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 79), EOA14646 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 61), NP 199892 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), XP 002321731 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 82), XP 002322281 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 83), XP 002321730 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 81), XP 002511127 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 93), XP 002511128 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 94), CBI32263 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 46), EMJ01437 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 48), XP 002520679 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 96), XP 004247459 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 125), EOA28959 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 67), NP 181439 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), XP 002333315 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 84), NEC1 PETHY Petunia (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 002267792 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 78), XP 004138978 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 111), XP 004138979 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 112), XP 003518628 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 98), XP 004489106 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 130), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), XP 004302124 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 129), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), NP 001239695 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 74), AFK39311 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 37), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), XP 003530901 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 101), XP 003524088 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 100), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003547573 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 102)].
[0049] FIG. 2-2 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following below FIG. 2-1 [XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), EOA22072 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 65), NP 196821 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), EMJ23678 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 50), XP 004301046 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 128), XP 002299333 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 80), XP 002514863 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 95), XP 004140547 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 113), XP 002264875 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 77), NP 199893 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), XP 002862913 Arabiopsis (SEQ ID NO: 97), EOA14916 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 62), EOA17919 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 63), NP 194231 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), EOA21276 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 64), NP 197755 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), EOA24501 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 66), NP 190443 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), XP 002511126 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 92), XP 004297511 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 126), XP 004153501 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 115), XP 004161952 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 116), XP 004145146 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 114), XP 004138250 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 110), XP 004235470 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 123), CBI15715 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 45), AFW71563 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 39), NP 001149028 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 72), XP 002453892 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 89), EMT09236 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 54), XP 003575028 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 105), NP 001046944 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), EMS46194 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 52), AFW88409 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 40), XP 002465280 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 91), BAJ99068 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 43), EMT31030 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 59), XP 003561640 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 103), NP 001050099 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), BAK07340 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 44), EMS45810 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 51), XP 003578398 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 108), XP 002462642 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 90), EAZ09693 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 47), NP 001148964 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 71), XP 002444688 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 87), XP 003572455 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 104), NP 001062354 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22), EMT31640 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 60), EMS51422 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 53), EMT20808 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 58)].
[0050] FIG. 2-3 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following below FIG. 2-2 [BAJ85621 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 41), EMT11081 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 55), XP 002442119 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 85), XP 002443167 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 86), NP 001141654 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 70), NP 001141106 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 69), SWT13 ORYSJ OsSW13 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 24), XP 003576225 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 107), BAJ94651 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 42), XP 003576036 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 106), EMT20480 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 56), EMT20481 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 57), NP 001132836 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 68), XP 002450786 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 88), NP 001067955 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25)].
[0051] FIG. 2-4 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-1 [XP 004235326 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 117), XP 004235334 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 119), ACV71016 Capsicum (SEQ ID NO: 36), XP 004235333 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 118), XP 004235342 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 122), XP 004235339 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 120), XP 004241452 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 124), XP 004235340 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 121), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 004503778 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 131), AFK48645 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 38), NP 001241307 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 75), NP 001242732 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 76), XP 003523161 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 99), NP 001237418 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 73), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), XP 004138032 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 109), EMJ10621 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 49), XP 004297512 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 127), XP 002284244 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 79), EOA14646 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 61), NP 199892 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), XP 002321731 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 82), XP 002322281 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 83), XP 002321730 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 81), XP 002511127 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 93), XP 002511128 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 94), CBI32263 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 46), EMJ01437 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 48), XP 002520679 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 96), XP 004247459 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 125), EOA28959 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 67), NP 181439 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), XP 002333315 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 84), NEC1 PETHY Petunia (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 002267792 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 78), XP 004138978 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 111), XP 004138979 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 112), XP 003518628 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 98), XP 004489106 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 130), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), XP 004302124 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 129), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), NP 001239695 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 74), AFK39311 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 37), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), XP 003530901 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 101), XP 003524088 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 100), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003547573 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 102)].
[0052] FIG. 2-5 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-2 [XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), EOA22072 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 65), NP 196821 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), EMJ23678 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 50), XP 004301046 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 128), XP 002299333 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 80), XP 002514863 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 95), XP 004140547 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 113), XP 002264875 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 77), NP 199893 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), XP 002862913 Arabiopsis (SEQ ID NO: 97), EOA14916 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 62), EOA17919 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 63), NP 194231 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), EOA21276 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 64), NP 197755 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), EOA24501 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 66), NP 190443 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), XP 002511126 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 92), XP 004297511 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 126), XP 004153501 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 115), XP 004161952 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 116), XP 004145146 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 114), XP 004138250 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 110), XP 004235470 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 123), CBI15715 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 45), AFW71563 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 39), NP 001149028 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 72), XP 002453892 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 89), EMT09236 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 54), XP 003575028 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 105), NP 001046944 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), EMS46194 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 52), AFW88409 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 40), XP 002465280 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 91), BAJ99068 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 43), EMT31030 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 59), XP 003561640 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 103), NP 001050099 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), BAK07340 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 44), EMS45810 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 51), XP 003578398 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 108), XP 002462642 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 90), EAZ09693 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 47), NP 001148964 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 71), XP 002444688 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 87), XP 003572455 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 104), NP 001062354 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22), EMT31640 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 60), EMS51422 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 53), EMT20808 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 58)].
[0053] FIG. 2-6 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-3[BAJ85621 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 41), EMT11081 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 55), XP 002442119 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 85), XP 002443167 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 86), NP 001141654 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 70), NP 001141106 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 69), SWT13 ORYSJ OsSW13 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 24), XP 003576225 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 107), BAJ94651 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 42), XP 003576036 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 106), EMT20480 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 56), EMT20481 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 57), NP 001132836 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 68), XP 002450786 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 88), NP 001067955 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25)].
[0054] FIG. 2-7 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-4 [XP 004235326 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 117), XP 004235334 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 119), ACV71016 Capsicum (SEQ ID NO: 36), XP 004235333 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 118), XP 004235342 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 122), XP 004235339 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 120), XP 004241452 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 124), XP 004235340 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 121), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 004503778 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 131), AFK48645 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 38), NP 001241307 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 75), NP 001242732 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 76), XP 003523161 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 99), NP 001237418 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 73), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), XP 004138032 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 109), EMJ10621 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 49), XP 004297512 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 127), XP 002284244 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 79), EOA14646 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 61), NP 199892 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), XP 002321731 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 82), XP 002322281 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 83), XP 002321730 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 81), XP 002511127 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 93), XP 002511128 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 94), CBI32263 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 46), EMJ01437 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 48), XP 002520679 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 96), XP 004247459 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 125), EOA28959 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 67), NP 181439 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), XP 002333315 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 84), NEC1 PETHY Petunia (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 002267792 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 78), XP 004138978 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 111), XP 004138979 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 112), XP 003518628 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 98), XP 004489106 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 130), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), XP 004302124 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 129), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), NP 001239695 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 74), AFK39311 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 37), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), XP 003530901 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 101), XP 003524088 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 100), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003547573 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 102)].
[0055] FIG. 2-8 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-5 [XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), EOA22072 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 65), NP 196821 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), EMJ23678 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 50), XP 004301046 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 128), XP 002299333 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 80), XP 002514863 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 95), XP 004140547 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 113), XP 002264875 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 77), NP 199893 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), XP 002862913 Arabiopsis (SEQ ID NO: 97), EOA14916 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 62), EOA17919 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 63), NP 194231 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), EOA21276 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 64), NP 197755 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), EOA24501 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 66), NP 190443 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), XP 002511126 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 92), XP 004297511 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 126), XP 004153501 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 115), XP 004161952 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 116), XP 004145146 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 114), XP 004138250 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 110), XP 004235470 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 123), CBI15715 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 45), AFW71563 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 39), NP 001149028 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 72), XP 002453892 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 89), EMT09236 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 54), XP 003575028 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 105), NP 001046944 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), EMS46194 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 52), AFW88409 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 40), XP 002465280 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 91), BAJ99068 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 43), EMT31030 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 59), XP 003561640 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 103), NP 001050099 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), BAK07340 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 44), EMS45810 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 51), XP 003578398 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 108), XP 002462642 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 90), EAZ09693 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 47), NP 001148964 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 71), XP 002444688 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 87), XP 003572455 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 104), NP 001062354 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22), EMT31640 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 60), EMS51422 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 53), EMT20808 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 58)].
[0056] FIG. 2-9 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-6 [BAJ85621 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 41), EMT11081 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 55), XP 002442119 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 85), XP 002443167 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 86), NP 001141654 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 70), NP 001141106 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 69), SWT13 ORYSJ OsSW13 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 24), XP 003576225 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 107), BAJ94651 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 42), XP 003576036 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 106), EMT20480 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 56), EMT20481 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 57), NP 001132836 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 68), XP 002450786 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 88), NP 001067955 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25)].
[0057] FIG. 2-10 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-7[XP 004235326 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 117), XP 004235334 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 119), ACV71016 Capsicum (SEQ ID NO: 36), XP 004235333 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 118), XP 004235342 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 122), XP 004235339 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 120), XP 004241452 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 124), XP 004235340 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 121), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 004503778 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 131), AFK48645 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 38), NP 001241307 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 75), NP 001242732 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 76), XP 003523161 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 99), NP 001237418 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 73), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), XP 004138032 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 109), EMJ10621 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 49), XP 004297512 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 127), XP 002284244 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 79), EOA14646 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 61), NP 199892 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), XP 002321731 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 82), XP 002322281 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 83), XP 002321730 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 81), XP 002511127 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 93), XP 002511128 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 94), CBI32263 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 46), EMJ01437 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 48), XP 002520679 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 96), XP 004247459 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 125), EOA28959 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 67), NP 181439 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), XP 002333315 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 84), NEC1 PETHY Petunia (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 002267792 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 78), XP 004138978 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 111), XP 004138979 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 112), XP 003518628 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 98), XP 004489106 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 130), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), XP 004302124 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 129), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), NP 001239695 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 74), AFK39311 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 37), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), XP 003530901 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 101), XP 003524088 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 100), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003547573 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 102)].
[0058] FIG. 2-11 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-8 [XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), EOA22072 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 65), NP 196821 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), EMJ23678 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 50), XP 004301046 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 128), XP 002299333 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 80), XP 002514863 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 95), XP 004140547 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 113), XP 002264875 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 77), NP 199893 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), XP 002862913 Arabiopsis (SEQ ID NO: 97), EOA14916 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 62), EOA17919 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 63), NP 194231 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), EOA21276 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 64), NP 197755 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), EOA24501 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 66), NP 190443 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), XP 002511126 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 92), XP 004297511 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 126), XP 004153501 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 115), XP 004161952 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 116), XP 004145146 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 114), XP 004138250 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 110), XP 004235470 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 123), CBI15715 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 45), AFW71563 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 39), NP 001149028 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 72), XP 002453892 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 89), EMT09236 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 54), XP 003575028 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 105), NP 001046944 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), EMS46194 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 52), AFW88409 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 40), XP 002465280 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 91), BAJ99068 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 43), EMT31030 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 59), XP 003561640 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 103), NP 001050099 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), BAK07340 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 44), EMS45810 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 51), XP 003578398 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 108), XP 002462642 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 90), EAZ09693 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 47), NP 001148964 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 71), XP 002444688 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 87), XP 003572455 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 104), NP 001062354 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22), EMT31640 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 60), EMS51422 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 53), EMT20808 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 58)].
[0059] FIG. 2-12 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-9 [BAJ85621 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 41), EMT11081 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 55), XP 002442119 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 85), XP 002443167 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 86), NP 001141654 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 70), NP 001141106 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 69), SWT13 ORYSJ OsSW13 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 24), XP 003576225 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 107), BAJ94651 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 42), XP 003576036 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 106), EMT20480 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 56), EMT20481 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 57), NP 001132836 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 68), XP 002450786 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 88), NP 001067955 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25)].
[0060] FIG. 2-13 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-10 [XP 004235326 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 117), XP 004235334 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 119), ACV71016 Capsicum (SEQ ID NO: 36), XP 004235333 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 118), XP 004235342 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 122), XP 004235339 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 120), XP 004241452 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 124), XP 004235340 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 121), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 004503778 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 131), AFK48645 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 38), NP 001241307 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 75), NP 001242732 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 76), XP 003523161 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 99), NP 001237418 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 73), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), XP 004138032 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 109), EMJ10621 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 49), XP 004297512 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 127), XP 002284244 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 79), EOA14646 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 61), NP 199892 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), XP 002321731 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 82), XP 002322281 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 83), XP 002321730 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 81), XP 002511127 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 93), XP 002511128 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 94), CBI32263 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 46), EMJ01437 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 48), XP 002520679 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 96), XP 004247459 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 125), EOA28959 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 67), NP 181439 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), XP 002333315 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 84), NEC1 PETHY Petunia (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 002267792 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 78), XP 004138978 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 111), XP 004138979 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 112), XP 003518628 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 98), XP 004489106 Cicer (SEQ ID NO: 130), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), XP 004302124 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 129), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), NP 001239695 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 74), AFK39311 Lotus (SEQ ID NO: 37), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), XP 003530901 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 101), XP 003524088 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 100), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003547573 Glycine (SEQ ID NO: 102)].
[0061] FIG. 2-14 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-11 [XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), EOA22072 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 65), NP 196821 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), EMJ23678 Prunus (SEQ ID NO: 50), XP 004301046 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 128), XP 002299333 Populus (SEQ ID NO: 80), XP 002514863 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 95), XP 004140547 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 113), XP 002264875 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 77), NP 199893 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), XP 002862913 Arabiopsis (SEQ ID NO: 97), EOA14916 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 62), EOA17919 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 63), NP 194231 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), EOA21276 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 64), NP 197755 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), EOA24501 Capsella (SEQ ID NO: 66), NP 190443 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), XP 002511126 Ricinus (SEQ ID NO: 92), XP 004297511 Fragaria (SEQ ID NO: 126), XP 004153501 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 115), XP 004161952 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 116), XP 004145146 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 114), XP 004138250 Cucumis (SEQ ID NO: 110), XP 004235470 Solanum (SEQ ID NO: 123), CBI15715 Vitis (SEQ ID NO: 45), AFW71563 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 39), NP 001149028 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 72), XP 002453892 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 89), EMT09236 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 54), XP 003575028 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 105), NP 001046944 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), EMS46194 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 52), AFW88409 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 40), XP 002465280 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 91), BAJ99068 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 43), EMT31030 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 59), XP 003561640 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 103), NP 001050099 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), BAK07340 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 44), EMS45810 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 51), XP 003578398 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 108), XP 002462642 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 90), EAZ09693 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 47), NP 001148964 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 71), XP 002444688 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 87), XP 003572455 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 104), NP 001062354 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22), EMT31640 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 60), EMS51422 Triticum (SEQ ID NO: 53), EMT20808 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 58)].
[0062] FIG. 2-15 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the protein contained in the phylogenetic tree illustrated in FIG. 1-1, and following the right of FIG. 2-12 [BAJ85621 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 41), EMT11081 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 55), XP 002442119 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 85), XP 002443167 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 86), NP 001141654 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 70), NP 001141106 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 69), SWT13 ORYSJ OsSW13 Oryza (SEQ ID NO: 24), XP 003576225 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 107), BAJ94651 Hordeum (SEQ ID NO: 42), XP 003576036 Brachypodium (SEQ ID NO: 106), EMT20480 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 56), EMT20481 Aegilops (SEQ ID NO: 57), NP 001132836 Zea (SEQ ID NO: 68), XP 002450786 Sorghum (SEQ ID NO: 88), NP 001067955 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25)].
[0063] FIG. 3-1 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins classified in the clade III in Non-Patent Literature 1 (Nature (2010) 468, 527-532) [AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), PhNEC1 (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), OsSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 24), OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25), OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22)].
[0064] FIG. 3-2 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins classified in the clade III in Non-Patent Literature 1 (Nature (2010) 468, 527-532), and following below FIG. 3-1 [AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), PhNEC1 (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), OsSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 24), OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25), OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22)].
[0065] FIG. 3-3 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins classified in the clade III in Non-Patent Literature 1 (Nature (2010) 468, 527-532), and following below FIG. 3-2 [AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), PhNEC1 (SEQ ID NO: 35), XP 003617528 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 27), NOD3 MEDTR Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 31), XP 003620983 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 32), AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), XP 003615405 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 33), XP 003593107 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 34), AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), OsSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 24), OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25), OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), AFK35161 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 29), CAC44123 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 30), XP 003602780 Medicago (SEQ ID NO: 28), AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22)].
[0066] FIG. 4-1 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of SWEET proteins derived from Arabidopsis thaliana and SWEET proteins derived from Oryza sativa in the clade III [At5g50790.1 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), At5g13170.1 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), At3g48740.1 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), At5g23660.1 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), At5g50800.1 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), At4g25010.1 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), 0512g0476200 OsSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 24), 0511g0508600 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25), 0502g0513100 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), At2g39060.1 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), 0503g0347500 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), 0508g0535200 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22)].
[0067] FIG. 4-2 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of SWEET proteins derived from Arabidopsis thaliana and SWEET proteins derived from Oryza sativa in the clade III, and following below FIG. 4-1 [At5g50790.1 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), At5g13170.1 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), At3g48740.1 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), At5g23660.1 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), At5g50800.1 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), At4g25010.1 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), 0512g0476200 OsSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 24), 0511g0508600 OsSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 25), 0502g0513100 OsSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 26), At2g39060.1 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15), 0503g0347500 OsSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 23), 0508g0535200 OsSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 22)].
[0068] FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a result of multiple alignment analysis of SWEET proteins derived from Arabidopsis thaliana in the clade III [At5g50790.1 AtSW10 (SEQ ID NO: 16), At5g13170.1 AtSW15 (SEQ ID NO: 21), At3g48740.1 AtSW11 (SEQ ID NO: 17), At5g23660.1 AtSW12 (SEQ ID NO: 18), At5g50800.1 AtSW13 (SEQ ID NO: 19), At4g25010.1 AtSW14 (SEQ ID NO: 20), At2g39060.1 AtSW09 (SEQ ID NO: 15)].
[0069] FIG. 6 is a configuration diagram schematically illustrating a physical map of the nucleic acid AtSWEET/pRI201AN prepared in Examples.
[0070] FIG. 7 is a photograph of the part producing guttation in Arabidopsis under conditions described in Examples.
[0071] FIG. 8 is a configuration diagram schematically illustrating a physical map of the nucleic acids pZH2B_GWOx_AtSWEET11 and pZH2B_GWOx_AtSWEET12 prepared in Examples.
[0072] FIG. 9 is a photograph of the part producing guttation under conditions described in Examples in rice.
DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS
[0073] The present invention will be described in detail below. The present invention involves introduction of a nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation and/or enhancement of expression of the protein. In this way, exudates with high sugar concentrations can be collected from transformed plants in which the nucleic acid is introduced into cells and/or the expression of the protein is enhanced. As used herein, the exudate refers to a liquid oozed out of tissue in plant, including, for example, root exudate, seed exudate, guttation-liquid oozed out of the hydathode. The phenomenon in which a liquid is oozed out of the hydathode is referred to as guttation. Therefore, guttation-liquid is synonymous with guttation. In particular, the transformed plant in which a nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation is introduced into cells and/or the expression of the protein is enhanced can produce guttation with high sugar concentrations.
[0074] As used herein, the meaning of nucleic acid includes naturally occurring nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA, artificial nucleic acids such as peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and nucleic acid molecules in which a base, sugar, or phosphodiester moiety is chemically modified. The meaning of the nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation includes both of the gene in the genome and the transcription product of the gene.
[0075] As used herein, the sugar refers to a substance represented by the chemical formula C.sub.n(H.sub.2O).sub.m, including polysaccharides, oligosaccharides, disaccharides, and monosaccharides, including aldehyde and ketone derivatives of polyol and derivatives and condensation products related thereto. Glucosides in which aglycone such as alcohol, phenol, saponin, or pigment is bound to reduced group of sugar are also included. The monosaccharides may be classified into triose, tetrose, hexose, or pentose based on the number of carbon atoms and they may be classified into aldose, which has an aldehyde group, ketose, which has a ketone group, or the like based on a functional group in the molecule. The sugar may be divided into D-form and L-form according to the conformation at the asymmetric carbon most apart from the aldehyde or ketone group. Specific examples of the monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, galactose, mannose, xylose, xylulose, ribose, erythrose, threose, erythrulose, glyceraldehyde, dihydroxyacetone, etc. and specific examples of the disaccharides include sucrose (saccharose), lactose, maltose, trehalose, cellobiose, etc.
[0076] The plants according to the present invention have significantly increased amounts of sugar contained in exudate such as guttation in comparison with the wild type by introducing a nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation into cells and/or enhancing expression of the protein. The protein may be expressed at the all cells in the plant tissue or it may be expressed in at least a part of the cells in the plant tissue. As used herein, the meaning of the plant tissue includes the plant organs such as leaf, stem, seed, root, and flower. In the present invention, introducing a nucleic acid means significantly increasing the molecular number per cell of the nucleic acid encoding a transporter protein in comparison with the molecular number in the wild type. In the present invention, enhancing expression of a transporter protein means increasing the expression of its transcription product and/or its translation product by modifying an expression regulatory region of a nucleic acid encoding the transporter protein and/or injecting the nucleic acid itself into a cell.
Transporter Protein Gene Involved in Sugar Transportation
[0077] The aforementioned "nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation" encodes a transporter protein having a consensus sequence 1 comprising the following amino acid sequence:
TABLE-US-00004 [SEQ ID NO: 1] (L/I/V/M/F)x(G/A)xx(I/L/V/M/F)xxxx(L/I/V/F)(A/S) (P/S) [SEQ ID NO: 2] (1-3 aa)(P/S/T/A)T(F/L)xx(I/V)xxxKxxxxxxxxPYxxx (L/I)xxxx(L/I)x(I/L/M/V/F)xY(A/S/G) [SEQ ID NO: 3] (7-13 aa)(I/L/V/M)(1-2aa)(I/V)Nxxxxxx(E/Q)xxYxxx (Y/F)xx(Y/F)(A/G/S) [SEQ ID NO: 4] (35-36 aa)(R/Q/H)xxxxGx(V/I/L)xxxxx(V/M/L/I/F)xxxx (A/S/T)P(L/M)x(I/V)(I/M/V/L) [SEQ ID NO: 5] (2-7 aa)(V/I)(V/I/M)x(T/S)x(S/N)xx(F/Y)(M/L)(P/S) (F/I/V/L)xLSxx(L/I)(T/V)xx(A/G)xxW(F/L)xYGxxxxDxx (V/I)xxPNxxGxx(F/L)(G/S)xxQ(M/I)x(L/M/I/V/F)(Y/ H/F)
and being involved in sugar transportation.
[0078] In the amino acid sequence above, x denotes an arbitrary amino acid residue. In the amino acid sequence, the notations with 2 numbers connected by - and the following "aa" indicate that there is a sequence of arbitrary amino acids at the position and that the sequence consists of a number of amino acid residues, where the number is in the range between the 2 numbers. In the amino acid sequence, the notations with plural amino acids separated by/in a parenthesis indicate that there is one of the plural amino acids at the position. This way of notation is adopted in the description of the amino acid sequences herein.
[0079] The amino acid sequence shown above can be in other words an amino acid sequence in which the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, 1 to 3 arbitrary amino acid residues, the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 2, 7 to 13 arbitrary amino acid residues, the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 3, any amino acid residue of I/L/V/M, 1 to 2 amino acid residues, the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 4, 2 to 7 amino acid residues, and the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 5 are connected in this order from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
[0080] Supplementary FIG. 8 in Nature (2010) 468, 527-534 discloses a phylogenetic tree of SWEETs, transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation, based on the amino acid sequences. The document discloses SWEET proteins from thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), SWEET proteins from rice (Oryza sativa), SWEET proteins from bur clover (Medicago truncatula), SWEET proteins from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, SWEET proteins from Physcomitrella patens, SWEET proteins from Petunia hybrida, SWEET proteins from Caenorhabditis elegans, and SWEET proteins from mammals. According to this phylogenetic tree, it is understood that SWEETs, transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation, are classified into five clades of I to V based on the similarity of the amino acid sequence.
[0081] Table 1 below shows corresponding GenBank ID numbers, indexes of the protein coding regions calculated from the genome data (Index in the Genome), gene names, protein names, abbreviations of the proteins, SWEET protein clade numbers, and species of the organisms of origin of SWEET proteins from Arabidopsis thaliana, SWEET proteins from Oryza sativa, and Medicago truncatula SWEET proteins and a Petunia hybrida SWEET protein among the transporter proteins SWEETs involved in sugar transportation disclosed in the document.
TABLE-US-00005 TABLE 1 Abbreviation GenBank GenBank Index in the Encoded of Encoded (NCBI) ID No. #1 (NCBI) ID No. #2 Genome Gene Name Protein Protein SWEET Clade Organism NP_564140 SWET1_ARATH At1g21460 AtSWEET1 AtSWEET1 AtSW01 I Arabidopsis thaliana NP_566493 SWET2_ARATH At3g14770 AtSWEET2 AtSWEET2 AtSW02 I Arabidopsis thaliana NP_200131 SWET3_ARATH At5g53190 AtSWEET3 AtSWEET3 AtSW03 I Arabidopsis thaliana NP_566829 SWET4_ARATH At3g28007 AtSWEET4 AtSWEET4 AtSW04 II Arabidopsis thaliana NP_201091 SWET5_ARATH At5g62850 AtSWEET5 AtSWEET5 AtSW05 II Arabidopsis thaliana NP_176849 SWET6_ARATH At1g66770 AtSWEET6 AtSWEET6 AtSW06 II Arabidopsis thaliana NP_587386 SWET7_ARATH At4g10850 AtSWEET7 AtSWEET7 AtSW07 II Arabidopsis thaliana NP_588579 SWET8_ARATH At5g40260 AtSWEET8 AtSWEET8 AtSW08 II Arabidopsis thaliana NP_181439 AAM63257 At2g39060 AtSWEET9 AtSWEET9 AtSW09 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_199892 AED95992 At5g50790 AtSWEET10 AtSWEET10 AtSW10 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_190443 AEE78451 At3g48740 AtSWEET11 AtSWEET11 AtSW11 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_197755 AED93195 At5g23660 AtSWEET12 AtSWEET12 AtSW12 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_199893 AED95993 At5g50800 AtSWEET13 AtSWEET13 AtSW13 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_194231 AEE84991 At4g25010 AtSWEET14 AtSWEET14 AtSW14 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_196821 AED91859 At5g13170 AtSWEET15 AtSWEET15 AtSW15 III Arabidopsis thaliana NP_188291 SWT16_ARATH At3g16690 AtSWEET16 AtSWEET16 AtSW16 IV Arabidopsis thaliana NP_193327 SWT17_ARATH At4g15920 AtSWEET17 AtSWEET17 AtSW17 IV Arabidopsis thaliana NP_001044998 SWT1A_ORYSJ Os01g0881300 OsSWEET1a OsSWEET1a OsSW01a I Oryza sativa NP_001055599 SWT1B_ORYSJ Os05g0426000 OsSWEET1b OsSWEET1b OsSW01b I Oryza sativa NP_001043270 SWT2A_ORYSJ Os01g0541800 OsSWEET2a OsSWEET2a OsSW02a I Oryza sativa NP_001043983 SWT2B_ORYSJ Os01g0700100 OsSWEET2b OsSWEET2b OsSW02b I Oryza sativa NP_001054926 SWT3A_ORYSJ Os05g0214300 OsSWEET3a OsSWEET3a OsSW03a I Oryza sativa NP_001042428 SWT3B_ORYSJ Os01g0220700 OsSWEET3b OsSWEET3b OsSW03b I Oryza sativa NP_001046621 SWET4_ORYSJ Os02g0301100 OsSWEET4 OsSWEET4 OsSW04 II Oryza sativa NP_001056475 SWET5_ORYSJ Os05g0588500 OsSWEET5 OsSWEET5 OsSW05 II Oryza sativa NP_001043523 SWT6A_ORYSJ Os01g0608000 OsSWEET6a OsSWEET6a OsSW06a II Oryza sativa NP_001043522 SWT6B_ORYSJ Os01g0805700 OsSWEET6b OsSWEET6b OsSW06b II Oryza sativa NP_001062690 SWT7A_ORYSJ Os09g0254600 OsSWEET7a OsSWEET7a OsSW07a II Oryza sativa NP_001062702 SWT7B_ORYSJ Os09g0258700 OsSWEET7b OsSWEET7b OsSW07b II Oryza sativa SWT7C_ORYSJ Os12g0178500 OsSWEET7c OsSWEET7c OsSW07c II Oryza sativa NP_001062354 -- Os08g0535200 OsSWEET11 OsSWEET11 OsSW11 III Oryza sativa NP_001050099 -- Os03g0347500 OsSWEET12 OsSWEET12 OsSW12 III Oryza sativa SWT13_ORYSJ -- Os12g0476200 OsSWEET13 OsSWEET13 OsSW13 III Oryza sativa NP_001067955 -- Os11g0508600 OsSWEET14 OsSWEET14 OsSW14 III Oryza sativa NP_001046944 -- Os02g0513100 OsSWEET15 OsSWEET15 OsSW15 III Oryza sativa NP_001050071 SWT16_ORYSJ Os03g0341300 OsSWEET16 OsSWEET16 OsSW16 IV Oryza sativa XP_003617528 -- Medtr5g092600 MtSWEET9 MtSWEET9 MtSW09 III Medicago truncatula XP_003602780 -- Medtr3g098930 MtSWEET10a MtSWEET10a MtSW10a III Medicago truncatula AFK35161 -- -- MtSWEET10b MtSWEET10b MtSW10b III Medicago truncatula CAC44123 -- -- MtSWEET10c MtSWEET10c MtSW10c III Medicago truncatula NOD3_MEDTR -- -- NOD3 MtSWEET15a MtSW15a III Medicago truncatula XP_003620983 -- Medtr7g005690 MtSWEET15b MtSWEET15b MtSW15b III Medicago truncatula XP_003615405 -- Medtr5g067530 MtSWEET15c MtSWEET15c MtSW15c III Medicago truncatula XP_003593107 -- Medtr2g007890 MtSWEET15d MtSWEET15d MtSW15d III Medicago truncatula NEC1_PETHY -- -- NEC1 PhNEC1 PhNEC1 III Petunia hybrida
[0082] As used herein, the word AtSWEET refers to AtSWEET1, AtSWEET2, AtSWEET3, AtSWEET4, AtSWEET5, AtSWEET6, AtSWEET7, AtSWEET8, AtSWEET9, AtSWEET10, AtSWEET11, AtSWEET12, AtSWEET13, AtSWEET14, AtSWEET15, AtSWEET16, and AtSWEETT17 in Table 1 and the word OsSWEET refers to OsSWEET1a, OsSWEET1b, OsSWEET2a, OsSWEET2b, OsSWEET3a, OsSWEET3b, OsSWEET4, OsSWEET5, OsSWEET6a, OsSWEET6b, OsSWEET7a, OsSWEET7b, OsSWEET7c, OsSWEET11, OsSWEET12, OsSWEET13, OsSWEET14, OsSWEET15, and OsSWEET16 in Table 1.
[0083] Consensus Sequence 1 described above is an amino acid sequence generated from a phylogenetic tree (FIG. 1-1 to FIG. 1-3) by ClustalW and multiple alignment (FIG. 2-1 to FIG. 2-15) made based on the information on amino acid sequences of SWEET proteins in the clade III defined in the aforementioned document collected from the GenBank database. Accordingly, the aforementioned transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation having Consensus Sequence 1 include the SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned document, but no SWEET proteins classified in any of clades I, II, IV, and V in the aforementioned document. In other words, Consensus Sequence 1 described above is a sequence that is characteristic of the SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned document and the SWEET proteins collected from the GenBank database and classified in clade III and that is a criterion for the clear distinction from those in clades I, II, IV, and V according to the aforementioned document.
[0084] FIG. 1-1 illustrates a whole picture of the phylogenetic tree and FIGS. 1-2 to 1-3 illustrate the enlargement of partial areas of the whole picture shown in FIG. 1-1. The whole picture shown in FIG. 1-1 contains neither GenBank ID nor protein names. The partial areas shown in FIGS. 1-2 to 1-3 contain GenBank IDs and protein names.
[0085] Specific examples of clade III include SWEET proteins derived from, in addition to besides thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), rice (Oryza sativa), bur clover (Medicago denticulata), and petunia (Petunia hybrida) listed in Table 1, soybean (Glycine max), bird's-foot trefoil (Lotus japonicus), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), red pepper (Capsicum annuum), chick-pea (Cicer arietinum), cucumber (Cucumis sativus), peach (Prunus persica), strawberry (Fragaria vesca), grape (Vitisvinifera), Capsella rubella, poplar (Populus trichocarpa), castorbean (Ricinus communis), corn (Zea mays), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor), Tausch's goatgrass (Aegilops tauschii), purple false brome (Brachypodium distachyon), red wild einkorn (Triticumurartu), barley (Hordeum vulgare), etc., as shown in FIGS. 1-1 to 1-3.
[0086] Table 2 below shows corresponding GenBank ID numbers, gene names, species of the organisms of origin, and SEQ ID NOs of amino acid sequence of the SWEET proteins derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Medicago denticulata, and Petunia hybrida listed in Table 1 among these SWEET proteins included in clade III.
TABLE-US-00006 TABLE 2 SEQ ID NO of GenBank ID Gene Name Species of organism of origin amino acid sequence NP_181439 AtSWEET9 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 15 NP_199892 AtSWEET10 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 16 NP_190443 AtSWEET11 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 17 NP_197755 AtSWEET12 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 18 NP_199893 AtSWEET13 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 19 NP_194231 AtSWEET14 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 20 NP_196821 AtSWEET15 Arabidopsis thaliana SEQ ID NO: 21 NP_001062354 OsSWEET11 Oryza sativa SEQ ID NO: 22 NP_001050099 OsSWEET12 Oryza sativa SEQ ID NO: 23 SWT13_ORYSJ OsSWEET13 Oryza sativa SEQ ID NO: 24 NP_001067955 OsSWEET14 Oryza sativa SEQ ID NO: 25 NP_003602780 OsSWEET15 Oryza sative SEQ ID NO: 26 XP_003617528 MtSWEET9 Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 27 XP_003602780 MtSWEET10a Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 28 AFK35161 MtSWEET10b Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 29 CAC44123 MtSWEET10c Medicago trancatula SEQ ID NO: 30 NOD3_MEDTR NODS Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 31 XP_003620983 MtSWEET15b Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 32 XP_003515405 MtSWEET15c Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 33 XP_003593107 MtSWEET15d Medicago truncatula SEQ ID NO: 34 NEC1_PETHY NEC1 Petunia hydriba SEQ ID NO: 35
[0087] Tables 3, 4, and 5 below show corresponding GenBank ID numbers, species of the organisms of origin, and SEQ ID NOs of amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins shown in FIGS. 1-1 to 1-3 derived from organisms of species other than Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Medicago denticulata, and Petunia hybrida.
TABLE-US-00007 TABLE 3 SEQ ID NO of GenBank ID Species of organism of origin amino acid sequence ACV71016 Capsicum annuum SEQ ID NO: 36 AFK39311 Lotus japonicus SEQ ID NO: 37 AFK48645 Lotus japonicus SEQ ID NO: 38 AFW71563 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 39 ARW88409 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 40 BAJ65621 Hordeum vulgare SEQ ID NO: 41 BAJ94561 Hordeum vulgare SEQ ID NO: 42 BAJ99068 Hordeum vulgare SEQ ID NO: 43 BAK07340 Hordeum vulgare SEQ ID NO: 44 CBI15715 Vitis vinifera SEQ ID NO: 45 CBI32263 Vitis vinifera SEQ ID NO: 46 EAZ09693 Oryza sativa indica SEQ ID NO: 47 EMJ01437 Prunus persica SEQ ID NO: 48 EMJ10621 Prunus persica SEQ ID NO: 49 EMJ23678 Prunus persica SEQ ID NO: 60 EMS45810 Triticum urartu SEQ ID NO: 51 EMS46194 Triticum urartu SEQ ID NO: 52 EMS51422 Triticum urartu SEQ ID NO: 53 EMT09236 Aegilops tauschii SEQ ID NO: 54 EMT11081 Aegilops tauschii SEQ ID NO: 55 EMT20480 Aegilops tauschii SEQ ID NO: 56 EMT20481 Aegilops tauschii SEQ ID NO: 57 EMT20808 Aegilops tauschii SEQ ID NO: 58 EMT31030 Aegilops tauschii SEQ ID NO: 59 EMT31640 Aegilops tauschli SEQ ID NO: 60 EOA14646 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 61 EOA14916 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 62 EOA17919 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 63 EOA21276 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 64 EOA22072 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 65 EOA24501 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 66 EOA28959 Capsella rubella SEQ ID NO: 67 NP_001132836 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 68 NP_001141106 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 69 NP_001141654 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 70 NP_001148964 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 71
TABLE-US-00008 TABLE 4 SEQ ID NO of GenBank ID Species of organism of origin amino acid sequence NP_001149028 Zea mays SEQ ID NO: 72 NP_001237418 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 73 NP_001239695 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 74 NP_001241307 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 75 NP_001242732 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 76 XP_002264875 Vitis vinifera SEQ ID NO: 77 XP_002267792 Vitis vinifera SEQ ID NO: 78 XP_002284244 Vitis vinifera SEQ ID NO: 79 XP_002299333 Populus trichocarpa SEQ ID NO: 80 XP_002321730 Populus trichocarpa SEQ ID NO: 81 XP_002321731 Populus trichocarpa SEQ ID NO: 82 XP_002322281 Populus trichocarpa SEQ ID NO: 83 XP_002333315 Populus trichocarpa SEQ ID NO: 84 XP_002442119 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 85 XP_002443167 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 86 XP_002444688 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 87 XP_002450786 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 88 XP_002453892 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 89 XP_002462642 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 90 XP_002465280 Sorghum bicolor SEQ ID NO: 91 XP_002511126 Ricinus communis SEQ ID NO: 92 XP_002511127 Ricinus communis SEQ ID NO: 93 XP_002511128 Ricinus communis SEQ ID NO: 94 XP_002514863 Ricinus communis SEQ ID NO: 95 XP_002520679 Ricinus communis SEQ ID NO: 96 XP_002862913 Arabiopsis lyrata SEQ ID NO: 97 XP_003518628 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 98 XP_003523161 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 99 XP_003524088 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 100 XP_003530901 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 101 XP_003547573 Glycine max SEQ ID NO: 102 XP_003561640 Brachypodium distachyon SEQ ID NO: 103 XP_003572455 Brachypodium distachyon SEQ ID NO: 104 XP_003575028 Brachypodium distachyon SEQ ID NO: 105 XP_003576036 Brachypodium distachyon SEQ ID NO: 106 XP_003576225 Brachypodium distachyon SEQ ID NO: 107
TABLE-US-00009 TABLE 5 SEQ ID NO of GenBank ID Species of organism of origin amino acid sequence XP_003578398 Brachypodium distachyon SEQ ID NO: 108 XP_004138032 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 109 XP_004138250 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 110 XP_004138978 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 111 XP_004138979 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 112 XP_004140547 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 113 XP_004145146 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 114 XP_004153501 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 115 XP_004161952 Cucumis sativus SEQ ID NO: 116 XP_004235326 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 117 XP_004235333 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 118 XP_004235334 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 119 XP_004235339 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 120 XP_004235340 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 121 XP_004235342 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 122 XP_004235470 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 123 XP_004241452 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 124 XP_004247459 Solanum lycopersicum SEQ ID NO: 125 XP_004297511 Fragaria vesca SEQ ID NO: 126 XP_004297512 Fragaria vesca SEQ ID NO: 127 XP_004301046 Fragaria vesca SEQ ID NO: 128 XP_004302124 Fragaria vesca SEQ ID NO: 129 XP_004489106 Cicer arietinum SEQ ID NO: 130 XP_004503778 Cicer arietinum SEQ ID NO: 131
[0088] FIGS. 2-1 to 2-15 illustrate a result of analysis of alignment of the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins derived from various organisms listed in Tables 2 to 5 using ClustalW multiple sequence alignment program (available in DDBJ at National Institute of Genetics). The version and various parameters used in the analysis are shown below.
ClustalW Version, 2.1
[0089] Pairwise Alignment Parameters [0090] Alignment Type, Slow [0091] Slow Pairwise Alignment Options [0092] Protein Weight Matrix, Gonnet [0093] Gap Open, 10 [0094] Gap Extension, 0.1
Multiple Sequence Alignment Parameters
[0094] [0095] Protein Weight Matrix, Gonnet [0096] Gap Open, 10 [0097] Gap Extension, 0.20 [0098] Gap Distances, 5 [0099] No End Gaps, no [0100] Iteration, none [0101] Numiter, 1 [0102] Clustering, NJ
Output Options
[0102] [0103] Format, Aln w/numbers [0104] Order, Aligned
[0105] The aforementioned SWEET proteins classified in clade III of the SWEET protein are found to have Consensus sequence 1 described above, as shown in FIGS. 2-1 to 2-15. The variations of amino acid residues that can occur at the certain positions in Consensus Sequence 1 shown above are based on the following reasons. It is well known that the amino acids are classified according to their side chains of similar properties (chemical properties and the physical size) as described in Reference (1) ("McKee's Biochemistry," 3rd edition, Chapter 5 Amino acid, peptide, protein, 5.1 Amino acid, Japanese Edition supervised by Atsushi Ichikawa, translation supervised by Shinnichi Fukuoka, published by Ryosuke Sone, from Kagaku-Dojin Publishing Company, inc., ISBN4-7598-0944-9). Also, it is well known that substitution process in molecular evolution occurs frequently between amino acid residues classified in a certain group while maintaining the activity of protein. Based on this idea, a score matrix (BLOSUM) for the amino acid residue substitution is proposed in FIG. 2 in References (2): Henikoff S., Henikoff J. G., Amino-acid substitution matrices from protein blocks, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 10915-10919 (1992) and used widely. Reference (2) is based on the findings that the substitution between amino acids having side chains of similar chemical properties has a less impact on the structure and function of the whole protein. According to References (1) and (2) mentioned above, the groups of side chains of amino acids to be considered in the multiple alignment may be those based on indexes for chemical properties, the physical size, etc. These are shown as the groups of amino acids having scores of 0 or more, or preferably amino acids having 1 or more in the score matrix (BLOSUM) disclosed in References (2). Representative groups include the following 8 groups. Another sub-grouping may be the groups of amino acids having scores of 0 or more, preferably the groups of amino acids having scores of 1 or more, or more preferably the groups of amino acids having scores of 2 or more.
1) Aliphatic Hydrophobic Amino Acid Group (ILMV Group)
[0106] This group is a group of the amino acids having an aliphatic hydrophobic side chain among the neutral non-polar amino acids shown in Reference (1) mentioned above and constituted of valine (V, Val), leucine (L, Leu), isoleucine (I, Ile), and methionine (M, Met). Among the amino acids classified as neutral non-polar amino acids in Reference (1), FGACWP are not included in this "aliphatic hydrophobic amino acid group" for the following reasons. Glycine (G, Gly) and alanine (A, Ala) have weak effects of the nonpolar groups because the sizes are not larger than the methyl group. Cysteine (C, Cys) may play an important role in S-S bonding and also have a property of forming hydrogen bonding with the oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom in nature. Phenylalanine (F, Phe) and tryptophan (W, Trp) have a side chain having a high molecular weight and a strong effect of the aromatic group. Proline (P, Pro) has a strong effect of the imino acid group, and fixes the angle of the main chain of polypeptide.
2) Group Having Hydroxy Methylene Group (ST Group)
[0107] This group is a group of amino acids having a hydroxy methylene group in the side chain among the neutral polar amino acids, and constituted of serine (S, Ser) and threonine (T, Thr). Because the hydroxyl group in the side chains of S and T is a sugar-binding site, they are often important sites for a particular activity of a certain polypeptide (protein).
3) Acidic Amino Acid (DE Group)
[0108] This group is a group of amino acids having an acidic carboxyl group in the side chain, and constituted of aspartic acid (D, Asp) and glutamic acid (E, Glu).
4) Basic Amino Acid (KR Group)
[0109] This group is a group of the basic amino acids, and constituted of lysine (K, Lys) and arginine (R, Arg). These K and R are positively charged and display basic characteristics in a wide range of pH. On the other hand, histidine (H, His), which is classified as a basic amino acid, is not classified in this group because it is hardly ionized at pH 7
5) Methylene Group=Polar Group (DHN Group)
[0110] In this group, all amino acids characteristically have, as a side chain, a methylene group bound to the .alpha. carbon atom and a polar group attached to the methylene group. They are characterized by having a methylene group, which is a nonpolar group, similar in physical size, and the group is constituted of asparagine (N, Asn, the polar group is the amido group), aspartic acid (D, Asp, the polar group is the carboxyl group), and histidine (H, His, the polar group is the imidazole group).
6) Dimethylene Group=Polar Group (EKQR Group)
[0111] In this group, all amino acids characteristically have, as a side chain, a linear hydrocarbon equal to or longer than the dimethylene group bound to the .alpha. carbon atom and a polar group attached to the hydrocarbon. They are characterized by having a dimethylene group, which is a nonpolar group, similar in physical size. The group is constituted of glutamic acid (E, Glu, the polar group is the carboxyl group), lysine (K, Lys, the polar group is the amino group), glutamine (Q, Gln, the polar group is the amido group), and arginine (R, Arg, the polar groups are the imino group and the amino group).
7) Aromatic (FYW Group)
[0112] This group is a group of aromatic amino acids, which have a benzene nucleus in the side chain and characterized by chemical properties unique to aromatic groups. The group consists of phenylalanine (F, Phe), tyrosine (Y, Tyr), and tryptophan (W, Trp).
8) Cyclic & Polar (HY Group)
[0113] This group is a group of amino acids that has a ring structure and polarity in the side chain, and constituted of histidine (H, His, the ring structure and the polar group are both the imidazole group), tyrosine (Y, Tyr, the ring structure is the benzene nucleus and the polar group is the hydroxyl group).
[0114] Based on the aforementioned amino acid groups, substitution of an amino acid residue in the amino acid sequence of a protein having a certain function with an amino acid residue in the same group can be easily expected to result in a novel protein having a similar function. For example, based on the aforementioned "1) Aliphatic hydrophobic amino acid group (ILMV group)," substitution of an isoleucine residue in the amino acid sequence of a protein having a certain function with a leucine residue can be easily expected to result in a novel protein having a similar function. If there are multiple proteins having a certain function, their amino acid sequences may be expressed as a consensus sequence. Also in such a case, substitution of an amino acid residue with an amino acid residue in the same group can be easily expected to result in a novel protein having a similar function. For example, if there are multiple proteins having a certain function and an amino acid residue in the consensus sequence calculated from them is isoleucine or leucine (L/I), based on the aforementioned "1) Aliphatic hydrophobic amino acid group (ILMV group)", substitution of the isoleucine or leucine residue with a methionine or valine residue can be easily expected to result in a novel protein having a similar function.
[0115] The aforementioned "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" can be defined as a protein that has Consensus Sequence 2 consisting of an amino acid sequence in which certain amino acid residues are added at the N-terminal side and the C-terminal side of Consensus Sequence 1 described above and the variation of amino acids that can be present at certain positions are limited. The amino acid sequence of Consensus Sequence 2 is as follows.
TABLE-US-00010 [SEQ ID NO: 6] G(L/I/V/F/M)xGx(I/V/L)(I/V/L)(S/T)xxxxL(A/S)P(L/ V/I/M)(P/S/T/A)TFxx(I/V)x(K/R)xK(S/T)xxx(F/Y)x(S/ A)xPYxx(A/S/T)LxSxxLx(L/I/M/V)(Y/F)Y(A/G) [SEQ ID NO: 7] (7-9 aa)(L/I)(I/V/L)(T/S)INxx(G/A)xx(I/V/M)(E/Q) xxYxxx(F/Y)(L/I/V/F)x(Y/F)Ax(K/R/N)xxxxx(T/A) [SEQ ID NO: 8] (7-8 aa)(V/F/L/I/M)(18-19 aa)(R/Q/H)xxxxGx(I/V) xxxxx(V/I/L/M)x(V/M)F(A/V)(A/S/T)PLx(I/V)(I/M/V/L) xxV(I/V)(K/R/Q)(T/S)(K/R)S(V/A)x(F/Y)MP(F/I/L)xLS (L/F/V)xL(T/V)(L/I)xAxxW(F/L)xYG(L/F)xxxDxx(V/I) xxPNxxGxx(L/F)(G/S)xxQMx(L/V/I)(Y/F)xx(Y/F).
[0116] The amino acid sequence of Consensus Sequence 2 can be, in other words, an amino acid sequence in which the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 6, 7 to 9 arbitrary amino acid residues, the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 7, 7 to 8 arbitrary amino acid residues, any amino acid residue of V/F/L/I/M, 18 to 19 amino acid residues, and the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 8 are connected in this order from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
[0117] Consensus Sequence 2 is an amino acid sequence that is shared between SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned document. More specifically, Consensus Sequence 2 is an amino acid sequence generated from multiple alignment obtained, as described above, by the ClustalW analysis of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Oryza sativa, the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Medicago denticulata, and the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Petunia hybrida classified in clade III in the aforementioned document. Therefore, Consensus Sequence 2 is a sequence that is characteristic of the SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned documents and that is a criterion for the clear distinction from those in clades I, II, IV, and V according to the aforementioned document.
[0118] FIGS. 3-1 to 3-3 illustrate a result of analysis of alignment of the amino acid sequences of the SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned document using ClustalW multiple sequence alignment program (available in DDBJ at National Institute Genetics; the version and various parameters used in the analysis are as described above). The SWEET protein classified in clade III in the aforementioned document are found to have Consensus Sequence 2 described above, as shown in FIGS. 3-1 to 3-3.
[0119] Furthermore, the aforementioned "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" can be defined as a protein having Consensus Sequence 3 consisting of an amino acid sequence in which certain amino acid residues are added at the N-terminal side of Consensus Sequence 2 described above and the variation of amino acids that can be present at certain positions are limited. The amino acid sequence of Consensus Sequence 3 is as follows.
TABLE-US-00011 [SEQ ID NO: 9] (A/V)xxxG(I/L/V)xGN(I/L/V)(I/L/V)S(F/L)x(V/T)xL (A/S)P(V/L/I)(P/A)TFxx(I/V)x(K/R)xK(S/T)xx(G/S) (F/Y)(Q/S/E)SxPYxx(A/S/T)LxS(A/C/S)xLx(L/I/M)(Y/F) Y(A/G)xx(K/T) [SEQ ID NO: 10] (3-5 aa)(L/M/P)(L/I)(I/L/V)(T/S)INxx(G/A)xx(I/V) (E/Q)xxY(I/L)x(L/M/V/I)(F/Y)(L/I/V/F)x(Y/F)Ax(K/R) xxxxx(T/A)xx(L/M/F/V/I)(L/F/V/I)xxx(N/D)(F/V/I/L) xx(F/L)xx(I/L/V)xxxxxx(L/I/V) [SEQ ID NO: 11] (5-6 aa)(R/Q)xxxxGx(I/V)xxxx(S/A)(V/L/M)(C/S/A)VF (A/V)(A/S)P Lx(I/V)(I/M/V)xxV(I/V)(K/R/Q)(T/S)(K/ R)S(V/A)E(F/Y)MP(F/I)xLS(L/F/V)xL(T/V)(L/I)(S/N)A (V/I)xW(F/L)xYGLxx(K/N)Dxx(V/I)xxPN(V/I)xGxx(F/L) (G/S)xxQMxL(Y/F)xx(Y/F).
[0120] The amino acid sequence of Consensus Sequence 3 can be, in other words, an amino acid sequence in which the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 9, 3 to 5 arbitrary amino acid residues, the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 10, 5 to 6 arbitrary amino acid residues and the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 11 are connected in this order from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
[0121] Consensus Sequence 3 is an amino acid sequence generated from multiple alignment obtained by ClustalW analysis, as described above, of the amino acid sequence of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana and the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation from derived Oryza sativa among the SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned document. Therefore, Consensus Sequence 3 is a sequence that is characteristic of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana and the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Oryza sativa classified in clade III in the aforementioned document and that is a criterion for the clear distinction from those in clades I, II, IV, and V according to the aforementioned document.
[0122] FIGS. 4-1 to 4-2 illustrate a result of analysis of alignment of the amino acid sequence of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana and the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Oryza sativa classified in clade III in the aforementioned document using ClustalW multiple sequence alignment program (available in DDBJ at National Institute Genetics; the version and various parameters used in the analysis are as described above). The transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana and the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Oryza sativa classified in clade III in the aforementioned document are found to have Consensus Sequence 3 described above, as shown in FIGS. 4-1 to 4-2.
[0123] Furthermore, the aforementioned "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" can be defined as a protein having Consensus Sequence 4 consisting of an amino acid sequence in which certain amino acid residues are added at the N-terminal side and the C-terminal side of Consensus Sequence 3 described above and the variation of amino acids that can be present at certain positions are limited. The amino acid sequence of Consensus Sequence 4 is as follows.
TABLE-US-00012 [SEQ ID NO: 12] (M/L/V)xx(T/K/N/S)xxxxAxxFG(L/I/V)LGN(I/L/V)(I/V) SFxVxL(S/A)P(V/I)PTFxxIxK(K/R)K(S/T)x(E/K)(G/S)(F/ Y)(Q/E)S(I/L)PYxx(A/S)LxS(A/C)xLx(L/I/M)YY(A/G)xxK [SEQ ID NO: 13] (4-5 aa)(L/M)(L/I)(I/V)(T/S)IN(A/S/T)(F/V)(G/A)x (F/V)(I/V)(E/Q)xxY(I/L)x(L/M/I)(F/Y)(F/V/I/L)x(Y/ F)Ax(K/R)xx(R/K)xx(T/A)(L/V/M)K(V/L/M/F)(L/I/V/F) xxx(N/D)(F/V/I)xx(F/L)xx(I/L)(L/I/V/F)(L/M/V)(L/V) xx(F/L)(L/I/V) [SEQ ID NO: 14] (5-6 aa)(R/Q)x(K/S/Q)x(L/I/V)Gx(I/V)Cxxx(S/A)(V/L) (S/C/A)VF(A/V)(A/S)PLx(I/V)(M/I/V)xxV(I/V)(K/R)T (K/R)S(V/A)E(Y/F)MPFxLS(L/F)xLT(I/L)(S/N)A(V/I)xW (L/F)xYGLx(L/I)(K/N)Dxx(V/I)A(L/F/I/M)PN(V/I)(L/ I/V)Gxx(L/F)GxxQM(I/V)L(Y/F)(V/L/I/M)(V/L/I/M)(Y/ F)(K/R/Q).
[0124] The amino acid sequence of Consensus Sequence 4 can be, in other words, an amino acid sequence in which the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 12, 4 to 5 arbitrary amino acid residues, the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 13, 5 to 6 arbitrary amino acid residues, and the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 14 are connected in this order from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
[0125] Consensus sequence 4 is an amino acid sequence generated from multiple alignment obtained by ClustalW analysis, as described above, of the amino acid sequences of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana among the SWEET proteins classified in clade III in the aforementioned document. Therefore, Consensus Sequence 4 is a sequence that is characteristic of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana classified in clade III in the aforementioned document and that is a criterion for the clear distinction from those in clades I, II, IV, and V according to the aforementioned document.
[0126] FIG. 5 illustrates a result of analysis of alignment of the amino acid sequence of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana classified in clade III in the aforementioned document using ClustalW multiple sequence alignment program (available in DDBJ at National Institute Genetics; the version and various parameters used in the analysis are as described above). The transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana classified in clade III in the aforementioned document are found to have Consensus Sequence 4 described above, as shown in FIG. 5.
[0127] As described in the foregoing, the "nucleic acids encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation" that can be used in the present invention are not particularly limited, as long as they encode a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 described above. In other words, the nucleic acids are not limited to those encoding the specific SWEET proteins listed Tables 2 to 5, but include those encoding SWEET proteins derived from organisms of species other than those listed in Tables 2 to 5. For example, nucleic acids that are derived from organisms whose sequence data is not stored in databases such as GenBank and that encode transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 can be also used.
[0128] Specific examples of the particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation can include proteins comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131, as illustrated in Tables 2 to 5. In particular, the particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation may be preferably a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 35 (Table 2), more preferably a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 26 (derived from Arabidopsis thaliana or Oryza sativa), or further preferably a protein comprising an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 21 (derived from Arabidopsis thaliana). The most preferred examples of the particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation are AtSWEET11 comprising the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 17, AtSWEET12 comprising the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 18, OsSWEET14 comprising the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 25, and OsSWEET15 comprising the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 26.
[0129] The "nucleic acids encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation" that can be used in the present invention are not limited to the nucleic acids encoding the particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation identified by a specific SEQ ID NO as described above, but any nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 described above can be used.
[0130] The nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation means that the protein encoded by the nucleic acid has the transporter activity involved in sugar transportation. The transporter activity involved in sugar transportation is an activity measured with a FRET(Forster resonance energy transfer or fluorescence resonance energy transfer) sugar sensor localized in cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum (ER) for sugar transport across the ER membrane, for example, those described in Methods in Non Patent Literature 1 and 2.
[0131] Whether a certain particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation has Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 or whether the nucleic acid encoding the protein encodes a protein having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 can be easily determined by comparing the amino acid sequence of the protein or the amino acid sequence encoded by the nucleic acid with an amino acid sequence set forth in Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4.
[0132] Examples of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation, comprising an amino acid sequence different from any of the amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131, and having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 may include those encoding proteins that comprise an amino acid sequence in which one or plural amino acid sequences are deleted from, substituted with, added to, or inserted into an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NO: 15 to 131, and that have Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 and transporter activity involved in sugar transportation. As used herein, the plural amino acids mean, for example, 1 to 20, preferably, 1 to 10, more preferably, 1 to 7, further preferably, 1 to 5, and most preferably, 1 to 3 amino acids. The deletion, substitution, or addition of the amino acids can be made by modifying the nucleotide sequence of nucleic acids encoding the aforementioned particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation by a known technique in the art. A mutation can be introduced into a nucleotide sequence by a known technique such as the Kunkel method or the gapped duplex method or a method similar to those. For example, a mutation is introduced using a kit for introducing mutation using a site-directed mutagenesis method (using, for example, Mutant-K or Mutant-G (both trade names, TAKARA Bio Inc.) or a kit of the LA PCR in vitro Mutagenesis series (trade name, TAKARA Bio Inc.)). The method for introducing mutation may be a method involving use of a chemical mutagen as represented by EMS (ethyl methanesulfonic acid), 5-bromouracil, 2-aminopurine, hydroxylamine, N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine, and other carcinogenic compounds or a method involving treatment with a radiation as represented by X-ray, alpha-, beta-, and gamma-rays, and ion beam, or ultraviolet treatment.
[0133] Examples of the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation, comprising an amino acid sequence different from any of the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131 and having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 may include those encoding proteins having amino acid sequences having a similarity or an identity to an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131 of, for example, 70% or more, preferably 80% or more, more preferably 90% or more, or most preferably 95% or more, having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation. The values of similarity and identity mean values calculated using a computer program equipped with a Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST).RTM. program with the default setting and a database storing genetic sequence information.
[0134] Furthermore, the nucleic acids encoding the transporter proteins involved in sugar transportation, comprising an amino acid sequence different from any of the amino acid sequences of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131, and having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 can be identified by extracting nucleic acid from the plant of interest and isolating a nucleic acid that hybridizes with a nucleic acid encoding an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131 under stringent conditions, when genome information of the plant is unknown. As used herein, the stringent conditions refer to conditions in which so-called specific hybrids are formed, but nonspecific hybrids are not formed. For example, the stringent conditions can include hybridization in 6.times.SSC (sodium chloride/sodium citrate) at 45.degree. C. and then washing with 0.2 to 1.times.SSC, 0.1% SDS at 50 to 65.degree. C.; or such conditions can include hybridization in 1.times.SSC at 65 to 70.degree. C. and then washing with 0.3.times.SSC at 65 to 70.degree. C. The hybridization can be carried out by a conventionally known method such as those described in J. Sambrook et al., Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 2nd Ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (1989).
[0135] As described in the foregoing, a "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" that is used in the present invention was defined as a protein having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4. However, the "particular transporter proteins involved in a sugar transportation" that can be used in the present invention are not limited to these proteins having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4.
[0136] More specifically, examples of the "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" may include those encoding proteins that comprise an amino acid sequence in which one or plural amino acid sequences are deleted from, substituted with, added to, or inserted into an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131 and that have transporter activity involved in sugar transportation. As used herein, the plural amino acids mean, for example, 1 to 20, preferably, 1 to 10, more preferably, 1 to 7, further preferably, 1 to 5, and most preferably, 1 to 3 amino acids. The deletion, substitution, or addition of the amino acids can be made by modifying the nucleotide sequence of nucleic acids encoding the particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation by a known technique in the art. The method of introducing a mutation into a nucleotide sequence can be selected from the methods described above as appropriate.
[0137] Examples of the "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" may include those encoding proteins having amino acid sequences having a similarity or an identity to an amino acid sequence set forth in any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131 of, for example, 70% or more, preferably 80% or more, more preferably 90% or more, or most preferably 95% or more, and having transporter activity involved in sugar transportation. The values of similarity and identity can be calculated by the method described above.
[0138] Furthermore, examples of the "particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" may include those encoding proteins that are encoded by nucleic acids that hybridize with a nucleic acid encoding an amino acid sequence of any of SEQ ID NOs: 15 to 131 under stringent conditions and that have transporter activity involved in sugar transportation. The stringent conditions here are the same as those described above.
[0139] The plant to which the present invention is applied can produce a high sugar concentration exudate by introducing a nucleic acid encoding a "particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation" as defined above into a cell, or enhancing the expression of the protein encoded by the nucleic acid. Examples of techniques for introducing the nucleic acid encoding this transporter involved in sugar transportation into a cell can include, for example, a technique for introducing into a cell an expression vector in which a DNA encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation is placed to allow the expression thereof. Also, examples of a technique for enhancing the expression of the nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation can include a technique for modifying a transcriptional promoter located in proximate to the DNA encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation in a plant of interest. In particular, a technique for introducing in a cell in the plant of interest an expression vector in which a DNA encoding the aforementioned transporter involved in sugar transportation is placed under the control of a promoter enabling constant expression to allow the expression thereof is preferred.
Artificial Gene Encoding Transporter Involved in Sugar Transportation
[0140] The aforementioned "nucleic acids encoding a particular transporter protein involved in a sugar transportation" are not limited to nucleic acids having a nucleotide sequence same as that of a naturally occurring nucleic acid, as long as they are nucleic acids having Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4 and encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation, and they may be nucleic acids having a nucleotide sequence designed artificially, i.e., artificial genes. As used herein, the artificial gene means a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) encoding an amino acid sequence designed artificially, and having a nucleotide sequence that does not occur naturally. The artificial gene may be a gene encoding a protein in which a part of a naturally occurring protein is modified (subjected to deletion, substitution, insertion, or the like of one or more amino acid residues), a gene encoding a chimeric protein in which naturally occurring amino acid sequences are connected, or a gene encoding a protein the whole sequence of which from the N-terminus to the C-terminus is designed uniquely.
[0141] The artificial gene may be a DNA having a nucleotide sequence encoding an amino acid sequence comprising Consensus Sequence 1, 2, 3, or 4. When a transporter gene involved in sugar transportation is designed as an artificial gene, the gene is preferably designed particularly to comprise the transmembrane domain. This domain is considered to localize the transporter at a more preferred position and contribute to the transporter activity.
[0142] More specific examples of the artificial gene encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation can include those designed to encode amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 132 to 137. These amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 132 to 137 comprise one of the aforementioned consensus sequences in the N-terminal side and the transmembrane domain in the C-terminal side. The protein having the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 132 is referred to as SWo1, the protein having the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 133 is referred to as SWo2, the protein having the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 134 is referred to as SWo3, the protein having the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 135 is referred to as SWo4, the protein having the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 136 is referred to as SWo5, and the protein having the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 137 is referred to as SWo6.
Expression Vector
[0143] The expression vector is constructed to comprise a nucleic acid having a promoter nucleotide sequence that allows constitutive expression and a nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation (including both of a nucleic acid having a naturally occurring nucleotide sequence and an artificial gene, which applies to the following as well). A variety of conventionally known vectors can be used as a base vector from which the expression vector is derived. For example, a plasmid, a bacteriophage, or a cosmid can be used and selected appropriately depending on the plant cell into which the vector is introduced and the method of introduction. Specific examples can include, for example, pBR322, pBR325, pUC19, pUC119, pBluescript, pBluescriptSK, and pBI vectors. In particular, use of a binary pBI vector is preferred when the method for introducing the vector into the plant cell is a method involving use of Agrobacterium. Specific examples of the binary pIB vector can include pBIG, pBIN19, pBI101, pBI121, pBI221, etc.
[0144] The promoter is not particularly limited, as long as it is a promoter capable of allowing the expression of the nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation in the plant, and a known promoter can be preferably used. Examples of such a promoter can include, for example, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter (CaMV35S), various actin gene promoters, various ubiquitin gene promoters, the nopaline synthetase gene promoter, the PR1a gene promoter in tobacco, ribulose 1 in tomato, the 5-diphosphate carboxylase/oxidase small subunit gene promoter, the napin gene promoter, the oleosin gene promoter, etc. Among these, use of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter, an actin gene promoter, or a ubiquitin gene promoter can be more preferred. Use of any of the aforementioned promoter allows strong expression of any nucleic acid when introduced in a plant cell.
[0145] Promoters that can be used include promoters having the function to express a nucleic acid regionspecifically in plant. Such a promoter that can be used may be any promoter conventionally known. By using such a promoter and regionspecifically introducing the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation, the sugar content can be increased in the exudate produced from the plant organ or tissue composed of the cells into which the nucleic acid has been introduced.
[0146] The expression vector may further comprise a nucleic acid having another segment sequence in addition to the promoter and the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation. The nucleic acid having another segment sequence is not particularly limited and examples can include a nucleic acid having a terminator nucleotide sequence, a nucleic acid having a transformant selection marker nucleotide sequence, a nucleic acid having an enhancer nucleotide sequence, a nucleic acid having a nucleotide sequence for increasing the translation efficiency, etc. Moreover, the aforementioned recombinant expression vector may have a T-DNA region. The T-DNA region can increase the efficiency of introduction of nucleic acid, especially when introducing a nucleic acid having the aforementioned nucleotide sequence in the recombination expression vector into a plant cell using Agrobacterium.
[0147] The nucleic acid having a terminator nucleotide sequence is not particularly limited as long as it has the function as a transcription termination site, and may be a known one. Specific examples of the nucleic acid that can be used include the terminator region of nopaline synthetase gene (Nos terminator), the terminator region of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S (CaMV35S terminator), etc. In particular, use of the Nos terminator may be more preferred. In the aforementioned recombinant vector, placing a terminator at an appropriate position may prevent the synthesis of needlessly long transcript after the vector is introduced into a plant cell.
[0148] Examples of the nucleic acid having a transformant selection marker nucleotide sequence that can be used include a nucleic acid containing a drug-resistance gene. Specific examples of such a drug-resistance gene can include nucleic acids containing drug-resistance genes for hygromycin, bleomycin, kanamycin, gentamicin, chloramphenicol, etc. This allows the facilitated selection of transformed plants by selecting plants growing in media containing the aforementioned antibiotics.
[0149] Examples of the nucleic acid having a nucleotide sequence for increasing the efficiency of translation can include a nucleic acid having the omega sequence derived from tobacco mosaic virus. By placing this nucleic acid having the omega sequence in the noncoding region (5' UTR) upstream of the protein coding region, the efficiency of expression of the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation can be increased. As seen above, nucleic acids having various DNA segment sequences can be included in the aforementioned recombinant expression vector depending on its purpose.
[0150] Methods for constructing the recombinant expression vector are not particularly limited and the recombinant expression vector can be constructed by introducing the aforementioned nucleic acid having a promoter nucleotide sequence, the nucleic acid encoding the particular transporter protein involved in sugar transportation, and optionally the aforementioned nucleic acid having another DNA segment sequence into the base vector selected as appropriate in a certain order. For example, the recombinant expression vector can be constructed by ligating the nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation, the nucleic acid having a promoter nucleotide sequence, and (optionally the nucleic acid having a terminator nucleotide sequence) and introducing this into the vector.
[0151] Methods for replicating (methods for producing) the aforementioned expression vector are not particularly limited and conventionally known methods can be used. Generally, Escherichia coli may be used as a host and the vector may be replicated in the host. Any preferred strain of Escherichia coli may be selected depending on the type of vector.
Transformation
[0152] The aforementioned expression vector is introduced into a plant cell of interest by a general transformation method. Methods for introducing the expression vector into (methods for transforming) a plant cell are not particularly limited and conventionally known methods suitable for the plant cell can be used. Specific examples of such methods that can be used include methods involving use of Agrobacterium and methods involving direct introduction into plant cells. Examples of the methods involving use of Agrobacterium that can be used include the methods described in Bechtold, E., Ellis, J. and Pelletier, G. (1993) In Planta, Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by infiltration of adult Arabidopsis plants. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sci. Vie, 316, 1194-1199. or Zyprian E, Kado Cl, Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation by novel mini-T vectors in conjunction with a high-copy vir region helper plasmid. Plant Molecular Biology, 1990, 15 (2), 245-256.
[0153] Examples of the methods for directly introducing the expression vector into a plant cell that can be used include microinjection, electroporation, the polyethyleneglycol method, the particle gun method, protoplast fusion, the calcium phosphate method, etc.
[0154] When using one of the aforementioned methods for directly introducing the nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation into a plant cell, a nucleic acid containing a transcription unit necessary for the expression of the nucleic acid encoding the transporter of interest, for example, a nucleic acid having a promoter nucleotide sequence and/or a nucleic acid having a transcription terminator nucleotide sequence; and the nucleic acid encoding the transporter of interest is sufficient and the vector function is not required. Furthermore, even a nucleic acid containing no transcription unit but only the protein-coding region of the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation is sufficient, if the nucleic acid can be integrated in a transcription unit in the host genome and express the gene of interest. Also, even when the nucleic acid is not integrated in the host genome, it is sufficient if the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation is transcribed and/or translated in the cell.
[0155] Examples of the plant cell into which the aforementioned expression vector or a nucleic acid containing no expression vector and encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation of interest is introduced can include cells in tissues in plant organs such as flower, leaf, and root, callus, cells in suspension culture, etc. The expression vector may be an appropriate expression vector constructed for the type of plant to be produced if necessary or a preconstructed general-purpose expression vector may be introduced into a plant cell.
[0156] The plant constituted of cells into which the expression vector is introduced is not particularly limited. This means that the concentration of sugar contained in an exudate such as guttation can be increased in any plant by introducing the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation. Preferred examples of such a plant are phanerogam plants. Among the phanerogam plants, angiosperm plants are more preferred. Examples of such angiosperm plants include, but are not limited to, dicot and monocot plants, for example, Brassicaceae, Gramineae, Solanaceae, Leguminosae, and Salicaceae plants (see below) [0157] Brassicaceae thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), Arabiopsis lyrata, rape (Brassica rapa, Brassica napus, Brassica campestris), cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata), Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa var. pekinensis), napa cabbage (Brassica rapa var. chinensis), turnip (Brassica rapa var. rapa), nozawana (Brassica rapa var. hakabura), potherb mustard (Brassica rapa var. lancinifolia), komatsuna (Brassica rapa var. peruviridis), bok Choy (Brassica rapa var. chinensis), komatsuna (Raphanus sativus), wasabi (Wasabia japonica), Capsella rubella, etc. [0158] Chenopodiaceae: sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). [0159] Aceraceae sugar maple (Acer saccharum): [0160] Euphorbiaceae: castorbean (Ricinus communis): [0161] Solanaceae: Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), eggplant (Solanum melongena), potato (Solaneum tuberosum), tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)), pepper (Capsicum annuum), petunia (Petunia hybrida), etc [0162] Fabaceae: Soybean (Glycine max), pea (Pisum sativum), broad beans (Vicia faba), Japanese wisteria (Wisteria floribunda), peanut (Arachis hypogaea), bird's-foot trefoil (Lotus japonicus), kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris), adzuki bean (Vigna angularis), acacia (Acacia), snail clover (Medicago truncatula), chick-pea (Cicer arietinum), etc. [0163] Compositae: chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium), sunflower (Helianthus annuus), etc. [0164] Arecaceae: oil palm (Elaeis guineensis, Elaeis oleifera), coconut palm (Cocos nucifera), date palm (Phoenix dactylifera), wax palm (Copernicia), eyc. [0165] Anacardiaceae: wax tree (Rhus succedanea), cashew tree (Anacardium occidentale), Chinese lacquer tree (Toxicodendron vernicifluum), mango (Mangifera indica), pistachio (Pistacia vera), etc. [0166] Cucurbitaceae: pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima, Cucurbita moschata, Cucurbita pepo), cucumber (Cucumis sativus), Japanese snake gourd (Trichosanthes cucumeroides), calabash (Lagenaria siceraria var. gourda), etc. [0167] Rosaceae: almond (Amygdalus communis), rose (Rosa), strawberry (Fragaria vesca), cherry tree (Prunus), apple (Malus pumila var. domestica), peach (Prunus persica), etc. [0168] Vitaceae: grape (Vitis vinifera) [0169] Caryophyllaceae: carnations (Dianthus caryophyllus), etc. [0170] Salicaceae: poplar (Populus trichocarpa, Populus nigra, Populus tremula), etc. [0171] Poaceae: corn (Zea mays), rice (Oryza sativa), barley (Hordeum vulgare), wheat (Triticum aestivum), red wild einkorn (Triticum urartu), Tausch's goatgrass (Aegilops tauschii), purple false brome (Brachypodium distachyon), bamboo (Phyllostachys), sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum), napier grass (Pennisetum pupureum), Erianthus (Erianthus ravenae), susuki grass (Miscanthus virgatum), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) switchgrass (Panicum), etc. [0172] Liliaceae: tulip (Tulipa), lily (Lilium), etc.
[0173] In particular, plants that produce relatively much exudate and have high productivity of sugar and starch, such as sugarcane, corn, rice, sorghum, wheat, sugar beet, and sugar maple, are preferred. This is because exudate collected from these plants can be used as raw materials for biofuel and bioplastics, as described in detail later.
[0174] While the nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in sugar transportation that can be used in the present invention can be isolated from a variety of plants and used, as mentioned above, the nucleic acid can be selected as appropriate depending on the class of the plant and used. Thus, when the plant cell of interest is derived from a monocot plant, the nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation to be introduced can be that isolated from a monocot plant. When the plant of interest is a plant in the family Poaceae, it is particularly preferred to introduce one of the following nucleic acids encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation derived from Oryza sativa: the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET13 (Os12g047620001) and the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET14 (Os11t050860001) and the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET15 (Os02t051310001). By introducing one of the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET13 (Os12g047620001) and the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET14 (Os11t050860001) and the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET15 (Os02t051310001), the amount of sugar contained in the exudate derived from Oryza sativa can be markedly increased.
[0175] Even when the plant cell of interest is derived from a monocot plant, a nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation derived from a dicot plant may be introduced. When the plant cell of interest is derived from a monocot plant, it is preferred to introduce the nucleic acid encoding AtSWEET11 (At3g48740) and the nucleic acid encoding AtSWEET12 (At5g23660), among the nucleic acids encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, a dicot plant. These nucleic acid encoding AtSWEET11 (At3g48740) and nucleic acid encoding AtSWEET12 (At5g23660) can markedly increase the amount of sugar contained in the exudate, even if the plant of interest is a monocot plant such as Oryza sativa.
Other Processes, Other Methods
[0176] After the aforementioned transformation process, a selection process for selecting an appropriate transformant from plants can be conducted by a conventionally known method. The method of the selection is not particularly limited. The appropriate transformant may be selected, for example, on the basis of drug resistance such as hygromycin resistance or by growing transformants, collecting exudate from the plants, measuring sugar contained in the collected exudate, and selecting the plant whose exudate has a concentration of sugar significantly increased in comparison with the wild type. The measurement of sugar contained in the collected exudate may be conducted by a qualitative method, but not a quantitative method. For example, the measurement may be conducted by a coloration method using a test paper that colors in response to sugar.
[0177] Progeny plants can be obtained according to a usual method from transformed plants obtained by the transformation process. By selecting progeny plants maintaining a trait associated with significantly increased expression of the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation in comparison with the wild type on the basis of the amount of sugar contained in the exudate, stable plant strains whose exudate has an increased amount of sugar due to the trait strains can be created. From such transformed plants or progeny thereof, breeding materials such as plant cells, seeds, fruits, rootstocks, calluses, tubers, cuttings, and masses can be obtained to mass-produce, from such materials, stable plant strains whose exudate has an increased amount of sugar due to the aforementioned trait.
[0178] As described in the foregoing, the concentration of sugar contained in exudate can be significantly increased in comparison with the wild type plant by introducing a nucleic acid encoding the transporter involved in the aforementioned particular sugar transportation into a cell or enhancing the expression of the nucleic acid according to the present invention. The sugar components contained in the exudate are meant to include monosaccharide such as glucose, galactose, mannose, and fructose, and disaccharides such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Accordingly, by introducing the nucleic acid encoding the particular transporter involved in a sugar transportation into a cell or enhancing the expression of the gene present endogenously, the concentration of one or more of sugar components such as glucose, galactose, mannose, fructose, sucrose, lactose and maltose contained in exudate can be increased. In particular, the concentrations of glucose, fructose, and sucrose in exudate can be greatly increased according to the present invention.
[0179] In particular, when collecting guttation produced from the hydathode as exudate, it is preferred to cultivate the plant in which the nucleic acid encoding the particular transporter involved in the sugar transportation is introduced into a cell or the expression of the nucleic acid is enhanced under conditions that prevent transpiration of the produced guttation. Furthermore, it is more preferred to culture the plant under conditions in which the amount of guttation production is increased. For example, the transpiration of guttation can be prevented and the amount of guttation production can be increased by cultivating the plant in a closed space under conditions at a humidity of 80% RH or more or more preferably 90% RH or more.
[0180] For example, whereas the concentration of sugar contained in guttation of the wild type Arabidopsis thaliana is about 2.0 .mu.M (the mean, monosaccharide equivalent), the sugar concentration in guttation is increased to about 98.5 to 6057.5 .mu.M in the transformed Arabidopsis thaliana in which the aforementioned particular transporter gene involved in a sugar transportation is introduced into cells. In particular, the transformed Arabidopsis thaliana in which the nucleic acid encoding AtSWEET12 (At5g23660) is introduced into cells can produce guttation containing sugar components at a higher concentration in comparison with other transformed Arabidopsis thaliana.
[0181] Moreover, the concentration of sugar in the guttation is increased to about 1074.3 to 185641.2 .mu.M in the transformant Oryza sativa in which the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding a particular transporter involved in a sugar transportation is introduced into cells, whereas the concentration of sugar in the guttation is included to about 1.3 .mu.M (mean, monosaccharide equivalent) in the wild type Oryza sativa. In particular, the transformed Oryza sativa in which the nucleic acid encoding AtSWEET11 (At3g48740) or the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET13 (Os12g0476200) or the nucleic acid encoding SWo5 is introduced into cells can produce guttation containing sugar components at higher concentrations in comparison with other transformed Oryza sativa plants can do. Furthermore, the transformed Oryza sativa in which the nucleic acid encoding OsSWEET15 (Os02g051310001) is introduced into cells can produce guttation containing sugar components at concentrations higher than the highest concentration of sugar in the guttation in the transformed Oryza sativa in which a nucleic acid encoding another particular transporter involved in a sugar transportation is introduced into cells, and the concentration of sugar in the guttation increases to up to 450340.4 .mu.M.
[0182] As described in the foregoing, exudate with a high sugar concentration can be collected according to the present invention. The collected exudate can be used for fermentative production of alcohol and/or organic acid. Furthermore, the collected exudate can be used as a raw material for biorefinery. For example, when guttation is used as an exudate for this, the aforementioned nucleic acid encoding the particular transporter involved in a sugar transportation is introduced into cells and the guttation collected from the plant in which the expression of the nucleic acid is enhanced can be used as it is in the reaction system for alcohol fermentation and organic acid fermentation and can be used as a raw material for biorefinery. Alternatively, the guttation collected from the plant can also be used in reaction systems for alcohol fermentation and organic acid fermentation after a concentration process or a process for adding another carbon or nitrogen source.
EXAMPLES
[0183] The present invention will be described in more detail with reference to Examples below. The technical scope of the present invention is however not limited to these Examples.
1. Construction of DNA Construct for Arabidopsis Thaliana Transformation
1.1. Preparation of DNA Encoding AtSWEET Protein by PCR
1.1.1. Amplification of DNA Encoding AtSWEET Protein
[0184] The DNAs encoding the AtSWEET1, AtSWEET2, AtSWEET3, AtSWEET4, AtSWEET5, AtSWEET6, AtSWEET7, AtSWEET9, AtSWEET11, AtSWEET12, AtSWEET13, AtSWEET15 and AtSWEET17 proteins for assessment were amplified by PCR using cDNA prepared from Arabidopsis thaliana as a template. To insert the DNAs for assessment into the pRI201AN vector (Takara Bio Inc., #3264), forward primers to which Sal I restriction enzyme recognition sequence is added to the 5' end and reverse primers to which Sac I or Pst I restriction enzyme recognition sequence was added to the 3' end were designed (Table 6).
TABLE-US-00013 TABLE 6 Name of SEQ Amplified ID DNA Name of Primer Sequence NO SWEET1 sal I-SWEET1-F26mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGAACATCGCTCACACTATCTTCGG-3' 138 sac I-SWEET1-R 5'-TATGAGCTCTTAAACTTGAAGGTCTTGCTTTCCATTAAC-3' 139 SWEET2 sal I-SWEET2-F27mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGATGTTTTTGCTTTCAATGCTTC-3' 140 sac I-SWEET2-R27mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCACACGTAAGAAACAATCAAAGGCTC-3' 141 SWEET3 sal I-SWEET3-F27mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGGTGATAAACTTCGATTATCCATC-3' 142 sac I-SWEET3-R28mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTTAGATCGATGAGGCATTGTTAGAATTC-3' 143 SWEET4 sal I-SWEET4-F31mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGTTAACGCTACAGTTGCGAGAAACATTG-3' 144 sac I-SWEET4-R30mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCAAGCTGAAACTCGTTTAGCTTGTCCAC-3' 145 SWEET5 sal I-SWEET5-F30mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGACGGACCCCCACACCGCCCGGACGATC-3' 146 sac I-SWEET5-R31mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCAAGCCTGGCCAAGTTCGATTCCAGCATTC-3' 147 SWEET6 sal I-SWEET6-F33mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGTGCATGAACAGTTGAATCTTATTCGGAAG-3' 148 sac I-SWEET6-R32mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCAAACGCCGCTAACTCTTTTGTTTAAATATG-3' 149 SWEET7 sal I-SWEET7-F28mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGTGTTTGCACATTTGAACCTTCTTC-3' 150 sac I-SWEET7-R31mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTTAAACATTGTTAGGTTCTTGGTTGGTATTC-3' 151 SWEET9 sal I-SWEET9-F31mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGTTCCTCAAGGTTCATGAAATTGCTTTTC-3' 152 sac I-SWEET9-R27mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCACTTCATTGGCCTCACCGATCCTTC-3' 153 SWEET11 sal I-SWEET11-F29mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGAGTCTCTTCAACACTGAAAACACATG-3' 154 sac I-SWEET11-R27mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCATGTAGCTGCTGCGGAAGAGGACTG-3' 155 SWEET12 sal I-SWEET12-F29mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGCTCTCTTCGACACTCATAACACATG-3' 156 sac I-SWEET12-R29mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCAAGTAGTTGCAGCACTGTTTCTAACTC-3' 157 SWEET13 Nde I-SWEET13-F30mer 5'-GGAATTCCATATGGCTCTAACTAACAATTTATGGGCATTTG-3' 158 sal I-SWEET13-R30mer 5'-TAATGTCGACTTAAACTTGACTTTGTTTCTGGACATCCTTG-3' 159 SWEET15 sal I-SWEET15-F30mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGGAGTCATGATCAATCACCATTTCCTC-3' 160 sac I-SWEET15-R27mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTCAAACGGTTTCAGGACGAGTAGCCTC-3' 161 SWEET17 sal I-SWEET17-F30mer 5'-TAATGTCGACATGGCAGAGGCAAGTTTCTATATCGGAGT-3' 162 sac I-SWEET17-R29mer 5'-TATGAGCTCTTAAGAGAGGAGAGGTTCAACACGTGATG-3' 163
[0185] And the PCR amplification was conducted using these primers and PrimeSTAR GXL DNA polymerase (TaKaRa, #R050A). The composition of the reaction solution was shown in Table 7 and the reaction conditions were shown in Table 8.
TABLE-US-00014 TABLE 7 Component (.mu.l) Template DNA (100 ng/.mu.l) 1 .mu.l 5 .times. Prime Star GXL buffer 4 .mu.l dNTP mixture (25 mM) 1.6 .mu.l Forward primer (10 ng/.mu.l) 0.4 .mu.l Reverse primer (10 ng/.mu.l) 0.4 .mu.l Prime Star GXL (1 u/.mu.l) 0.8 .mu.l Sterile water 12.6 .mu.l Total 20 .mu.l
TABLE-US-00015 TABLE 8 94.degree. C. 5 min .dwnarw. 98.degree. C. 10 sec 50.degree. C. 30 sec {close oversize parenthesis} .times.30 cycles 68.degree. C. 1 min .dwnarw. 20.degree. C.
[0186] Next, the following process was conducted to add adenine to the 5' and 3' ends in order to insert the DNA fragments obtained by the PCR amplification into the pCR2.1-TOPO.RTM. vector DNA (Invitrogen, #1(4500-01). The composition of the reaction solution was shown in Table 9. The reaction solution shown in Table 9 was reacted at 70.degree. C. for 15 minutes.
TABLE-US-00016 TABLE 9 Component PCR reaction solution 15 .mu.l 10 .times. ExTaq buffer 3 .mu.l dNTP mixture (25 mM) 2 .mu.l Ex Taq (0.5 u/.mu.l) 0.1 .mu.l Sterile water 9.9 .mu.l Total 30 .mu.l
1.1.2. Cutting Out and Purification of Amplified DNA Fragment
[0187] The DNA fragments amplified by PCR were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis and cut out and purified using MagExtractor-PCR & Gel Clean Up Kit (TOYOBO, #NPK-601). The cutting out and purification was conducted following the manual contained in the kit.
1.1.3. Transformation with Amplified DNA Fragment
[0188] The purified amplified DNA fragments were inserted into the pCR2.1-TOPO vector using TOPO TA Cloning.RTM. (Invitrogen, #1(4500-01). The composition of the reaction solution was shown in Table 10. The reaction solution shown in Table 10 was reacted at room temperature for 5 minutes.
TABLE-US-00017 TABLE 10 Component (.mu.l) Cut out purification product 2 .mu.l (amplified SWEET sequence) Salt solution 0.5 .mu.l pCR2.1-TOPO vector 0.5 .mu.l Total 3 .mu.l
[0189] Next, transformation was performed by adding 2 .mu.l of this reaction solution to Escherichia coli DH5.alpha. competent cells (TOYOBO, #DNA-903). After leaving the cells in ice bath for 30 minutes, the cells were subjected to heat-treatment at 42.degree. C. for 30 seconds. Subsequently, the cells were rapidly cooled in ice bath. 500 .mu.l of SOC medium (Invitrogen, #15544-034) was added and the cells were cultured in suspension at 37.degree. C., 180 rpm for 1 hour. To a LB agar plate containing kanamycin at a final concentration of 50 .mu.g/ml, 40 mg/ml X-gal and 40 .mu.l of 100 mM IPTG dissolved in 40 .mu.l of DMF (N,N-dimethylformamide) were applied and then 100 to 200 .mu.l of the culture were applied. The plate was incubated at 37.degree. C. overnight and colonies were obtained on the next morning.
1.1.4. Check of Transformation by Colony PCR and Selection for Positive Clone
[0190] As a result of the transformation, many colonies were obtained. To confirm the presence or absence of the inserted DNA in the colonies, colony PCR was conducted using M13-F: 5'-GTA AAA CGA CCA GTC TTA AG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 164) and M13-R: 5'-CAG GAA ACA GCT ATG AC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 165). The composition of the reaction solution for the colony PCR was shown in Table 11 and the PCR conditions were shown in Table 12.
TABLE-US-00018 TABLE 11 Component (.mu.l) Template DNA Colony Ampritaq Gold 360 Master Mix (ABI, #4398881) 10 .mu.l Forward primer (M13-F) (10 ng/.mu.l) 0.4 .mu.l Reverse primer (M13-R) (10 ng/.mu.l) 0.4 .mu.l Sterile water 9.2 .mu.l Total 20 .mu.l
TABLE-US-00019 TABLE 12 98.degree. C. 10 min .dwnarw. 95.degree. C. 15 sec 50.degree. C. 30 sec {close oversize parenthesis} .times.30 cycles 72.degree. C. 1 min .dwnarw. 72.degree. C. 7 min .dwnarw. 20.degree. C.
1.1.5. Purification of Plasmid DNA from Positive Clone
[0191] The plasmid DNAs were purified from the clones in which the inserted DNAs were confirmed. The purification of the plasmid DNAs were conducted using QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (QIAGEN, #27106) following the protocol contained in the kit.
1.1.6. Sequencing of Positive Clone
[0192] PCR amplification was conducted using the plasmid DNAs obtained in 1.1.5 as templates and M13-F and M13-R primers and the nucleotide sequences of the DNA fragments were determined by the dideoxy method (the Sanger method).
1.2. Preparation of DNA Encoding AtSWEET Protein by Chemical Synthesis
[0193] The DNA encoding the AtSWEET8, AtSWEET10, AtSWEET14, and AtSWEET16 proteins were chemically synthesized in total with their nucleotide sequences designed so as to add Pst I restriction enzyme recognition sequence to the 5' end and Sal I restriction enzyme recognition sequence to the 3' end. As a result, the DNAs encoding the AtSWEET8 and AtSWEET14 proteins inserted in the pEX-A vector (Operon Biotechnologies, Inc.) and the DNAs encoding the AtSWEET10 and AtSWEET16 proteins inserted in the pCR2.1-TOPO.RTM. vector were able to be obtained.
1.3. Cutting Out of DNA Encoding AtSWEET Protein by Restriction Enzyme Reaction and Purification
[0194] In order to cut out the DNA fragments encoding the AtSWEET proteins from the plasmid DNAs obtained in 1.1.5 and 1.2, twice of restriction enzyme treatments were conducted. The combination of restriction enzymes for each DNA is shown in Table 13.
TABLE-US-00020 TABLE 13 Name of DNA First Second AtSWEET1 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET2 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET3 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET4 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET5 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET6 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET7 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET8 Nde I Sal I AtSWEET9 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET10 Sal I Sac I AtSWEET11 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET12 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET13 Nde I Sal I AtSWEET14 Nde I Sal I AtSWEET15 Sac I Sal I AtSWEET16 Sal I Xba I AtSWEET17 Sac I Sal I
1.3.1. Sac I, Nde I, or Sal I Restriction Enzyme Reaction of Amplified DNA Fragment (First Round)
[0195] The reaction solutions shown in the tables below were prepared with Sac I (TaKaRa, #1078A), Nde I (TaKaRa, #1161A) or Sal I (TaKaRa, #1080A) and reacted at 37.degree. C. overnight to digest the plasmids obtained in 1.1.5 or 1.2. The composition of the reaction solution with Sal I was shown in Table 14, the composition of the reaction solution with Nde I was shown in Table 15, and the composition of the reaction solution with Sac I was shown in Table 16.
TABLE-US-00021 TABLE 14 Component (.mu.l) Plasmid 45 .mu.l 10 .times. L buffer 10 .mu.l Sac I 1 .mu.l DW 44 .mu.l Total 100 .mu.l
TABLE-US-00022 TABLE 15 Component (.mu.l) Plasmid 45 .mu.l 10 .times. H buffer 10 .mu.l Nde I 1 .mu.l DW 44 .mu.l Total 100 .mu.l
TABLE-US-00023 TABLE 16 Component (.mu.l) Plasmid 45 .mu.l 10 .times. H buffer 10 .mu.l Sal I 1 .mu.l DW 44 .mu.l Total 100 .mu.l
1.3.2. Purification of DNA Fragment Digested in Restriction Enzyme Reaction
[0196] Next, PCI (Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl alcohol=24:24:1) extraction and ethanol precipitation were performed to purify DNA. An equal volume of PCI was added to the reaction solution and the mixture was stirred and centrifuge at 15000 rpm for 5 minutes. The upper layer was collected and an equal volume of chloroform was added thereto. The mixture was similarly centrifuged and the upper layer was collected. To the collected upper layer, two times volume of ethanol was added and ethanol precipitation was conducted with Pellet Paint NF Co-Precipitant (Merck, #70748). The resultant DNA was dried and then dissolved in 44 .mu.l of sterile water.
1.3.3. Sal I, Xba I, and Sac I Restriction Enzyme Reaction of Amplified DNA Fragment (Second Round)
[0197] Next, the reaction solutions shown in the tables below were prepared with Sal I (TaKaRa, #1080A), Xba I (TaKaRa, #1093A), or Sac I (TaKaRa, #1078A) and reacted at 37.degree. C. overnight to digest the plasmids obtained in 1.3.2. The composition of the reaction solution with Sal I was shown in Table 17, the composition of the reaction solution with Xba I was shown in Table 18, and the composition of the reaction solution with Sac I was shown in Table 19.
TABLE-US-00024 TABLE 17 Component (.mu.l) Pellet 10 .times. H buffer 5 .mu.l Sal I 1 .mu.l DW 44 .mu.l Total 50 .mu.l
TABLE-US-00025 TABLE 18 Component (.mu.l) Pellet 10 .times. M buffer 5 .mu.l 100 .times. BSA 0.5 .mu.l Xba I 1 .mu.l DW 43.5 .mu.l Total 50 .mu.l
TABLE-US-00026 TABLE 19 Component (.mu.l) Pellet 10 .times. L buffer 5 .mu.l Sac I 1 .mu.l DW 44 .mu.l Total 50 .mu.l
1.3.4. Purification of DNA Fragment Digested in Restriction Enzyme Reaction
[0198] The reaction solutions obtained in 1.3.3 were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis in a similar way to the procedure of 1.1.2 and the DNAs were cut out and purified with the MagExtractor-PCR & Gel Clean up kit.
1.4. Cutting out of pRI201AN Vector in Restriction Enzyme Reaction and Purification
[0199] To ligate the pRI201AN vector with the DNA fragments encoding the AtSWEET proteins obtained in 1.3, the vector was treated with restriction enzymes in a way similar to the procedure of 1.3.
1.5. Ligation
1.5.1. Ligation Reaction
[0200] Ligation reaction was conducted to insert the DNA fragments encoding the AtSWEET proteins obtained in 1.3 into the pRI201AN vector obtained in 1.4. Ligation reaction was conducted with DNA Ligation Kit Ver.2.1 (Takara Bio, #6022) at 16.degree. C. overnight.
1.5.2. Transformation with Ligation Reaction Product
[0201] After the abovementioned ligation reaction, transformation with 2 .mu.l of the ligation reaction solution was conducted in a way similar to 1.1.3.
1.5.3. Check of Ligation Reaction by Colony PCR
[0202] Insertion of the DNAs encoding the AtSWEET proteins into the vector was confirmed by examining the length of visualized DNA fragments amplified by colony PCR in agarose gel electrophoresis.
1.5.4. Preparation of DNA Constructs Obtained by Ligation Reaction
[0203] From the colonies in which the inserted DNAs were confirmed, the plasmid DNAs were purified to obtain the clones in which the DNA fragments of interest were inserted. The plasmid DNAs were purified with QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (QIAGEN, #27106) following the protocol contained in the kit. FIG. 6 illustrates the physical map of the resultant DNA construct (AtSWEET/pRI201AN). In FIG. 6, LB stands for left border, RB stands for right border, TNOS stands for transcription terminator of the nopaline synthetase gene NOS derived from the Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, NPTII stands for neomycin phosphotransferase II gene from Escherichia coli, Pnos stands for transcription promoter of the nopaline synthetase gene NOS derived from the Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens, THSP stands for transcription terminator of the heat shock protein gene HSP derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, AtSWEET stands for DNA encoding a SWEET protein derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, P35S stands for Cauliflower mosaic virus 35S transcription promoter, AtADH 5'-UTR stands for translation enhancer of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH derived from Arabidopsis thaliana, ColE1 ori stands for the reproduction origin of Escherichia coli, Ri ori stands for the reproduction origin of Agrobacterium rhizogenes, respectively.
1.6.1. Preparation of DNA Encoding OsSWEET Protein by Chemical Synthesis and Construction of Construct
[0204] The DNAs encoding the OsSWEET5, OsSWEET11, OsSWEET12, OsSWEET13, OsSWEET14, and OsSWEET15 proteins, whose nucleotide sequences were newly designed in reference to the codon usage in Arabidopsis thaliana so that there will be no change in the amino acid sequence, were designed to have an Nde I restriction enzyme recognition sequence at the start codon side and a Sac I restriction enzyme recognition sequence at the stop codon side. The designed DNAs were totally chemically synthesized and inserted into the pRI201AN vector to obtain the respective DNA constructs. The DNAs were designed so that the ATG in the Nde I restriction enzyme recognition sequence (5'CATATG3') added to the 5' end coincides with the start codons of the DNAs encoding the SWEET proteins.
1.6.2. Preparation of Artificial Gene Encoding Transporter Involved in Sugar Transportation and Construct by Chemical Synthesis
[0205] Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNAs) encoding transporters involved in sugar transportation that have Consensus Sequence 1 and that have a nucleotide sequence that does not occur naturally, or 6 artificial genes of transporters involved in sugar transportation that have Consensus Sequence 1 were prepared as follows. First, SEQ ID NOs: 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, and 173 were designed respectively as nucleic acids encoding the transporters SWo1, SWo2, SWo3, SWo4, SWo5, and SWo6 having amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 132 to 137. DNAs were designed so that each of them has an Nde I restriction enzyme recognition sequence at the start codon side and a Sac I restriction enzyme recognition sequence at the stop codon side of SEQ ID NOs: 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, and 173. The designed DNAs were then totally chemically synthesized and inserted into the pRI201AN vector to obtain the 6 DNA constructs. The DNAs were designed so that the ATG in the Nde I restriction enzyme recognition sequence (5'CATATG3') added to the 5' end coincides with the start codons in SEQ ID NOs: 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, and 173.
1.7. Transformation ofArabidopsis Thaliana
[0206] The vectors for plant expression prepared in 1.5 and 1.6.1 and 1.6.2 were introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain C58C1 by electroporation (Plant Molecular Biology Manual, Second Edition, B. G. Stanton and A. S. Robbert, Kluwer Acdemic Publishers 1994). Then, Agrobacterium tumefaciens in which the vectors for plant expression were each introduced was introduced into the wild type Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Col-0 by dipping described by Clough, et al. (Steven J. Clough and Andrew F. Bent, 1998, The Plant Journal 16, 735-743) and T1 (the first generation transformant) seeds were collected. The collected T1 seeds were sown in sterile on MS agar medium (agar concentration 0.8%) containing kanamycin (50 mg/L), carbenicillin (100 mg/L) and Benlate wettable powder (10 mg/L: Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.) and cultured for about 2 weeks to select transformants. The selected transformants were transplanted onto a fresh preparation of the same MS agar medium, further cultivated for about 1 week, and then transplanted in a pot containing the soil which is a 1:1 mixture of vermiculite and Soil-mix (Sakata Seed Co.) to obtain T2 (the second generation transformant) seeds.
1.8. Preparation ofArabidopsis Thaliana Guttation
[0207] T1 or T2 plants of Arabidopsis thaliana transformed with the DNAs encoding the AtSWEET, OsSWEET, SWo1, SWo2, SWo3, SWo4, SWo5, and SWo6 proteins were cultivated with 18L/6D (24 hour cycles with 18 hours of light conditions followed by 6 hours of dark conditions) at 22.degree. C. After acclimation, 1/1000 Hyponex was given to plants cultivated for 1 to 2 weeks and the plants were wrapped with a plastic wrap (Saran Wrap (R), Asahi Chemical Industry) to increase humidity to 80% or more, or preferably 90% or more so that guttation is secreted (FIG. 7). Mainly, guttation attached to the back of leaves was collected and the sugar concentration in the guttation was analyzed. T1 seeds are defined as seeds harvested after infecting the wild type Arabidopsis thaliana with Agrobacterium and cultivating the resultant, T1 plants are defined as plants which has been confirmed to have introduction of DNA into cells, for example, by screening of T1 seeds with drug or by PCR, and T2 seeds are defined as seeds harvested after cultivating T1 plants.
2. Construction of DNA Construct for Oryza Sativa Transformation
2.1. Amplification of DNA Encoding AtSWEET Protein
[0208] Using the aforementioned DNA constructs (the DNA encoding the AtSWEET8 protein and the DNA encoding the AtSWEET11 protein and the DNA encoding the AtSWEET12 protein) for Arabidopsis thaliana transformation prepared in 1.5.4 as templates, the DNA encoding the AtSWEET8 protein and the DNA encoding the AtSWEET11 protein and the DNA encoding the AtSWEET12 protein were amplified by PCR. The sequence CACC was added to the 5' end of each amplification product for the introduction of the amplification product into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector.
2.2. Transformation with Amplified DNA Fragment
[0209] Parts of the resultant reaction solutions were subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis to confirm the presence of expected sizes of amplified products. The amplified products were then introduced into the pENTR/D-TOPO.RTM. vector using pENTER Directional TOPO Cloning Kit.RTM. (Invitrogen).
[0210] Next, Escherichia coli DH5.alpha. competent cells (Takara Bio) were transformed by adding the total amount of the reaction solutions. The cells were allowed to stand in ice bath for 30 minutes and then subjected to 45 seconds of heat treatment at 42.degree. C. Subsequently, the cells were rapidly cooled in ice bath and 300 .mu.l of SOC medium (Takara Bio) was added thereto. The mixture was cultured at 37.degree. C., with shaking at 180 rpm for 1 hour and this liquid culture was plated onto an LB agar plate containing kanamycin at a final concentration of 50 .mu.g/ml and cultured at 37.degree. C. overnight to obtain colonies on the next morning.
2.3. Check of Transformation by Colony PCR and Selection for Positive Clone
[0211] Insertion of the DNAs encoding the AtSWEET proteins into the vector was confirmed by examining the length of visualized DNA fragments amplified by colony PCR in agarose gel electrophoresis.
2.4. Purification of Plasmid DNA from Positive Clone
[0212] The plasmid DNAs were purified from the clones in which the inserted DNAs were able to be confirmed. The purification of the plasmid DNAs were conducted using QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (QIAGEN, #27106) following the protocol contained in the kit.
2.5. Sequencing of Positive Clone
[0213] Using the plasmid DNAs purified in 2.4 as templates and M13-F and M13-R primers, the DNA fragments were sequenced by a DNA sequencer (Beckman Coulter, CEQ8000).
2.6. LR Reaction and Transformation
[0214] The pENTR/D-TOPO.RTM. plasmid DNAs in which the DNA encoding the AtSWEET8 protein, the DNA encoding the AtSWEET11 protein, and the DNA encoding the AtSWEET12 protein were inserted obtained in 2.4 and a vector for Oryza sativa transformation (pZH2B_GWOx) were subjected to the Gateway LR reaction to construct the constructs for the overexpression in the plant of Oryza sativa, as shown in FIG. 8.
[0215] Next, Escherichia coli DH5.alpha. competent cells (Takara Bio) were transformed by adding the total amount of the reaction solutions. The cells were allowed to stand in ice bath for 30 minutes and then subjected to 45 seconds of heat treatment at 42.degree. C. Subsequently, the cells were rapidly cooled in ice bath and 300 .mu.l of SOC medium (Takara Bio) was added thereto. The mixture was cultured at 37.degree. C., with shaking at 180 rpm for 1 hour. This liquid culture was plated onto an LB agar plate containing spectionmycin at a final concentration of 50 .mu.g/ml and cultured at 37.degree. C. overnight to obtain colonies on the next morning.
2.7. Check of Transformation by Colony PCR and Selection for Positive Clone
[0216] Insertion of the DNAs encoding the AtSWEET proteins into the vector was confirmed by examining the length of visualized DNA fragments amplified by colony PCR in agarose gel electrophoresis.
2.8. Purification of Plasmid DNA from Positive Clone
[0217] The plasmid DNAs were purified from the clones in which the inserted DNAs were able to be confirmed. The plasmid DNAs were purified with QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (QIAGEN, #27106) following the protocol contained in the kit.
2.9. Sequencing of Positive Clone
[0218] Using the plasmid DNAs purified in 2.8 as templates and the following primers, the DNA fragments were sequenced by the DNA sequencer (Beckman Coulter, CEQ8000).
TABLE-US-00027 Ubi3'F: (SEQ ID NO: 166) 5'-TGC TGT ACT TGC TTG GTA TTG-3' UbiTseq3: (SEQ ID NO: 167) 5'-GGA CCA GAC CAG ACA ACC-3'
2.10.1. Preparation of DNA Encoding OsSWEET by Chemical Synthesis
[0219] DNAs encoding the OsSWEET13, OsSWEET14, or OsSWEET15 protein were designed to have the sequence CACC at the 5' end for the introduction into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector. The designed DNAs were totally chemically synthesized and inserted into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector.
2.10.2. Preparation of Artificial Gene Encoding Transporter Involved in Sugar Transportation by Chemical Synthesis
[0220] Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNAs) encoding transporters involved in sugar transportation that have Consensus Sequence 1 and that have a nucleotide sequence that does not occur naturally, or 2 artificial genes of transporters involved in sugar transportation that have Consensus Sequence 1 were prepared as follows. First, SEQ ID NOs: 174 and 175 were designed as nucleic acids encoding the transporters SWo1 and SWo5 having amino acid sequences set forth in SEQ ID NOs: 132 and 136. DNAs were designed to have the sequence CACC at the 5' end of SEQ ID NOs: 174 and 175 for the introduction into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector. The designed DNAs were totally chemically synthesized and inserted into the pENTR/D-TOPO vector.
2.11. Construction of Construct of DNA or Artificial Gene Encoding OsSWEET Protein
[0221] Vectors for Oryza sativa transformation were constructed using the DNAs synthesized in 2.10.1 and 2.10.2 in a way similar to 2.6 to 2.9 above.
2.12. Transformation of Oryza Sativa
[0222] The DNAs encoding the AtSWEET, OsSWEET, SWo1, and SWo5 proteins were introduced into Oryza sativa (c.v. Nipponbare) using the aforementioned vectors for plant expression constructed in 2.9 and 2.11 according to the method described in The Plant Journal (2006) 47, 969-976.
2.13. Preparation of Oryza Sativa Guttation
[0223] T1 transformants of Oryza sativa in which DNA encoding the AtSWEET, OsSWEET, SWo1, and SWo5 proteins were introduced were transplanted to a pot with a diameter of 6 cm containing 0.8 times volume of vermiculite and acclimated. Oryza sativa was cultivated with 18L (30.degree. C)/6D(25.degree. C.) (24 hours photocycle conditions with 18 hours light conditions at 30.degree. C. followed by 6 hours of dark conditions at 25.degree. C.). After acclimation, 1/1000 Hyponex was sufficiently given to plants cultivated for 1 to 2 weeks and the plants were wrapped with a plastic wrap (Saran Wrap (R), Asahi Chemical Industry) to increase humidity to 80% or more, or preferably 90% or more so that guttation is secreted from the hydathode in Oryza sativa (FIG. 9). Guttation attached to leaves was collected and analyzed for the sugar concentration.
3. Analysis for Sugar Concentration in Guttation
3.1. Dilution of Guttation Sample
[0224] The volumes of guttation from Arabidopsis thaliana obtained in 1.8 and guttation from Oryza sativa obtained in 2.13 were measured using a pipetter and pure water was added to a fixed volume of 0.35 ml. Next, the guttation was centrifuged at 10000.times.G for 10 minutes and then 0.3 mL of the supernatant was transferred to an automatic sampler vial and used for an HPLC analysis.
3.2. Analysis for Sugar Concentration by HPLC
[0225] The sugar concentration was analyzed using HPLC in the following conditions. In this analysis, a standard solution containing a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose at 50 .mu.M each as standard substances was used. [0226] Analytic column: CarboPac PA1 (Dionex) [0227] Eluent: 100 mM NaOH [0228] Flow rate: 1 ml/min [0229] Amount of injection: 25 .mu.l [0230] Detector: Pulsed amperometric detector (Dionex ED40)
4. Result of Analysis
[0231] The results of measurement of sugar concentrations in guttation from Arabidopsis thaliana obtained in 1.8 and guttation from Oryza sativa obtained in 2.13 are shown in Tables 20 and 21.
TABLE-US-00028 TABLE 20 Glc (.mu.M) Fru (.mu.M) Clade Transgene Host Ave Max Min Ave Max Min I AtSW01 A. thaliana 1.3 14.2 0.0 1.8 11.8 0.0 I AtSW02 A. thaliana 5.7 33.6 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 I AtSW03 A. thaliana 4.0 14.7 0.0 0.9 6.0 0.0 II AtSW04 A. thaliana 3.0 9.1 0.0 8.5 20.7 0.0 II AtSW05 A. thaliana 5.5 15.7 0.0 3.4 20.5 0.0 II AtSW06 A. thaliana 3.3 10.3 0.0 0.1 2.0 0.0 II AtSW07 A. thaliana 4.9 15.1 0.0 8.0 19.0 0.0 II AtSW08 A. thaliana 419.9 838.6 50.2 610.6 1,154.3 145.6 II AtSW08 O. sativa 571.4 1,205.6 152.4 419.0 845.5 153.1 III AtSW09 A. thaliana 399.5 2,708.3 36.4 552.5 2,838.7 69.5 III AtSW10 A. thaliana 331.6 586.3 77.0 650.9 1,085.9 215.8 III AtSW11 A. thaliana 711.1 2,137.9 80.1 674.6 1,384.7 117.6 III AtSW11 O. sativa 31,304.7 59,730.0 757.3 36,772.0 74,830.9 964.0 III AtSW12 A. thaliana 1,375.5 2,920.7 183.4 1,720.7 3,542.4 201.4 III AtSW12 O. sativa 14,006.2 45,976.5 1,081.6 11,477.3 43,830.5 1,690.7 III AtSW13 A. thaliana 230.5 941.5 51.1 304.3 1,336.8 85.5 III AtSW14 A. thaliana 60.4 211.6 24.9 163.2 451.8 74.8 III AtSW15 A. thaliana 796.6 2,064.2 143.1 1,140.0 2,727.5 226.1 IV AtSW16 A. thaliana 3.1 14.6 0.0 0.5 3.0 0.0 IV AtSW17 A. thaliana 2.0 3.5 0.0 1.2 3.7 0.0 Total Monosacharide Suc (.mu.M) Equivalent (.mu.M) Clade Transgene Ave Max Min Ave Max Min I AtSW01 0.0 0.0 0.0 3.1 22.1 0.0 I AtSW02 0.1 1.8 0.0 5.8 33.6 0.0 I AtSW03 0.2 3.4 0.0 5.2 19.6 0.0 II AtSW04 0.0 0.0 0.0 11.6 23.2 0.0 II AtSW05 0.0 0.0 0.0 8.8 30.8 0.0 II AtSW06 0.2 5.0 0.0 3.9 10.3 0.0 II AtSW07 1.6 4.9 0.0 16.1 36.9 0.0 II AtSW08 697.1 1,172.5 217.6 2,424.8 4,337.8 631.0 II AtSW08 41.9 47.8 33.6 1,074.3 2,146.7 394.3 III AtSW09 228.3 1,309.4 41.2 1,408.5 7,865.4 211.8 III AtSW10 280.9 516.6 45.2 1,544.3 2,705.4 383.1 III AtSW11 290.7 470.4 97.2 1,967.1 4,463.5 449.6 III AtSW11 8,196.6 19,339.4 110.8 84,469.9 173,239.6 1,942.9 III AtSW12 1,480.7 6,099.3 214.7 6,057.5 18,661.6 1,185.5 III AtSW12 2,598.2 22,209.9 56.4 30,679.9 130,872.6 3,247.4 III AtSW13 146.8 402.7 51.9 828.5 3,083.7 287.3 III AtSW14 48.8 118.7 22.2 321.2 900.7 151.6 III AtSW15 514.2 1,217.2 70.1 2,965.0 6,511.9 582.7 IV AtSW16 0.0 0.0 0.0 3.5 14.6 0.0 IV AtSW17 0.0 0.0 0.0 3.2 7.1 0.0
TABLE-US-00029 TABLE 21 Glc (.mu.M) Fru (.mu.M) Clade Transgene Host Ave Max Min Ave Max Min II OsSW05 A. thaliana 2.7 5.3 0.0 3.8 12.8 0.0 III OsSW11 A. thaliana 318.0 607.1 81.5 490.8 833.1 179.7 III OsSW12 A. thaliana 41.7 172.9 9.7 89.5 334.1 32.4 III OsSW13 A. thaliana 48.5 160.9 8.0 121.0 367.7 24.8 III OsSW13 O. sativa 62,407.2 125,776.4 3,917.0 77,858.6 156,842.0 4,650.0 III OsSW14 A. thaliana 37.5 128.5 10.7 115.6 460.4 45.5 III OsSW14 O. sativa 43,115.4 90,201.0 543.0 58,581.3 152,827.3 229.1 III OsSW15 A. thaliana 14.9 39.7 8.2 39.3 97.3 19.6 III OsSW15 O. sativa 33,018.8 246,007.1 197.8 31,135.4 197,244.2 461.9 III SWo1 A. thaliana 182.9 337.5 28.2 125.9 219.2 32.6 III SWo1 O. sativa 11,181.0 33,889.1 284.2 6,586.0 19,670.8 351.1 III SWo2 A. thaliana 81.6 128.4 30.6 103.3 146.3 26.7 III SWo3 A. thaliana 141.1 141.1 141.1 166.9 166.9 166.9 III SWo4 A. thaliana 41.9 96.3 12.7 35.5 88.2 3.8 III SWo5 A. thaliana 31.8 31.8 31.8 7.7 7.7 7.7 III SWo5 O. sativa 12,006.9 43,461.2 1,371.6 7,166.2 31,839.2 734.7 III SWo6 A. thaliana 179.1 455.3 33.5 121.1 155.1 64.6 -- none A. thaliana 1.6 8.1 0.0 0.3 7.3 0.0 -- none O. sativa 1.0 8.3 0.0 0.0 0.2 0.0 Total Monosacharide Suc (.mu.M) Equivalent (.mu.M) Clade Transgene Ave Max Min Ave Max Min II OsSW05 2.2 3.9 0.0 10.8 21.5 0.0 III OsSW11 221.0 723.7 14.0 1,250.7 2,887.6 360.7 III OsSW12 36.9 127.8 3.0 205.0 762.5 71.1 III OsSW13 41.3 93.7 19.6 252.1 716.0 71.9 III OsSW13 22,687.7 74,320.2 64.5 185,641.2 358,704.4 8,994.7 III OsSW14 51.2 118.0 19.4 255.6 824.9 95.0 III OsSW14 7,104.2 21,756.3 10.8 115,905.1 275,262.5 793.8 III OsSW15 25.5 82.0 7.2 105.3 300.9 59.8 III OsSW15 2,011.4 10,537.3 85.2 68,176.9 450,340.4 830.2 III SWo1 14.3 22.4 6.1 337.3 601.5 73.0 III SWo1 221.1 795.8 18.5 18,209.1 51,684.6 1,019.9 III SWo2 9.9 13.8 6.3 204.7 284.5 84.9 III SWo3 16.0 16.0 16.0 340.0 340.0 340.0 III SWo4 10.6 13.4 6.7 98.5 210.9 51.7 III SWo5 10.1 10.1 10.1 59.6 59.6 59.6 III SWo5 892.0 4,573.9 42.4 20,957.0 84,448.2 2,197.3 III SWo6 10.8 21.1 2.8 321.8 638.2 108.6 -- none 0.0 2.6 0.0 2.0 11.0 0.0 -- none 0.1 0.8 0.0 1.3 8.3 0.0
[0232] It was found that the concentration of sugar in guttation is greatly increased in all of Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa transformed with DNAs encoding AtSWEET9 to 15 and DNAs encoding OsSWEET13 to 15 classified in clade III among nucleic acids encoding SWEET proteins as seen from Tables 20 and 21. In particular, it was found that the sugar concentration in guttation can be more greatly increased when transformed with any of the DNA encoding AtSWEET11, the DNA encoding AtSWEET12, the DNA encoding AtSWEET15, the DNA encoding OsSWEET13, and the DNA encoding OsSWEET14. Moreover, it was found that the concentration of sugar in guttation is more increased in Oryza sativa transformed with DNAs encoding SWEET proteins classified in clade III than in Arabidopsis thaliana transformed with DNAs encoding SWEET proteins classified in clade III. In particular, it was found that the concentration of sugar in guttation is markedly increased in Oryza sativa transformed with any of the DNA encoding OsSWEET13, the DNA encoding OsSWEET14, and the DNA encoding OsSWEET15 than in Arabidopsis thaliana transformed with the same DNA.
[0233] Moreover, it was found that the concentration of sugar in guttation can be increased also in the plants in which an artificial gene of a transporter involved in sugar transportation that has Consensus Sequence 1 is introduced. The result revealed that the concentration of sugar in guttation can be increased in any plant, without limited by the host plant, by introducing a nucleic acid encoding a transporter involved in sugar transportation that has Consensus Sequence 1 and/or enhancing the expression of the protein.
[0234] Even in the wild type plants, sugar concentrations of around 50 .mu.M can be detected in guttation in some individuals. However, it was revealed that the effect of introducing the DNA encoding the SWEET proteins classified in Clade III is much higher than the highest concentration detected in the wild type plants as seen in the Examples.
Sequence CWU 1
1
175113PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
1misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is L, I, V, M or Fmisc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa is
G or Amisc_feature(4)..(5)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(6)..(6)Xaa is I, L, V, M or
Fmisc_feature(7)..(10)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(11)..(11)Xaa is L, I, V or
Fmisc_feature(12)..(12)Xaa is A or Smisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa is P
or S 1Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa1 5
10234PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
1misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is P, S, T or Amisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa is
F or Lmisc_feature(4)..(5)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(6)..(6)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(7)..(9)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(11)..(18)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(21)..(23)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa is L or
Imisc_feature(25)..(28)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(29)..(29)Xaa is L or Imisc_feature(30)..(30)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa
is I, L, M, V or Fmisc_feature(32)..(32)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(34)..(34)Xaa is A, S or G 2Xaa Thr
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Lys Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa1 5 10 15Xaa
Xaa Pro Tyr Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 20 25
30Tyr Xaa320PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
1misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(3)..(8)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(9)..(9)Xaa is E or
Qmisc_feature(10)..(11)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(13)..(15)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(16)..(16)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(17)..(18)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa
is Y or Fmisc_feature(20)..(20)Xaa is A, G or S 3Xaa Asn Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Tyr Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa1 5 10 15Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa 20424PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
1misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is R, Q or Hmisc_feature(2)..(5)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is V, I
or Lmisc_feature(9)..(13)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa is V, M, L, I or
Fmisc_feature(15)..(18)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is A, S or Tmisc_feature(21)..(21)Xaa
is L or Mmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa is I or
Vmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa is I, M, V or L 4Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Gly
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa1 5 10 15Xaa Xaa Xaa Pro Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa 20555PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
1misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is V or Imisc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa is V, I
or Mmisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(4)..(4)Xaa is T or Smisc_feature(5)..(5)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(6)..(6)Xaa is S or
Nmisc_feature(7)..(8)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(9)..(9)Xaa is F or Ymisc_feature(10)..(10)Xaa is M
or Lmisc_feature(11)..(11)Xaa is P or Smisc_feature(12)..(12)Xaa is
F, I, V or Lmisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(16)..(17)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa is L or
Imisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is T or Vmisc_feature(20)..(21)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa is A
or Gmisc_feature(23)..(24)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(26)..(26)Xaa is F or Lmisc_feature(27)..(27)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(30)..(33)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(35)..(36)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(37)..(37)Xaa
is V or Imisc_feature(38)..(39)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(42)..(43)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(45)..(46)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa is F or
Lmisc_feature(48)..(48)Xaa is G or Smisc_feature(49)..(50)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(52)..(52)Xaa is M
or Imisc_feature(53)..(53)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(54)..(54)Xaa is L, M, I, V or
Fmisc_feature(55)..(55)Xaa is Y, H or F 5Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Leu Ser Xaa1 5 10 15Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Trp Xaa Xaa Tyr Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa 20 25 30Xaa Asp Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Pro Asn Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Gln
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 50 55650PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus
sequence 2misc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa is L, I, V, F or
Mmisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(5)..(5)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(6)..(6)Xaa is I, V or Lmisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa is
I, V or Lmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is S or Tmisc_feature(9)..(12)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa
is A or Smisc_feature(16)..(16)Xaa is L, V, I or
Mmisc_feature(17)..(17)Xaa is P, S, T or Amisc_feature(20)..(21)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa
is I or Vmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa is K or
Rmisc_feature(25)..(25)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(27)..(27)Xaa is S or Tmisc_feature(28)..(30)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa
is F or Ymisc_feature(32)..(32)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(33)..(33)Xaa is S or
Amisc_feature(34)..(34)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(37)..(38)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(39)..(39)Xaa is A, S or Tmisc_feature(41)..(41)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(43)..(44)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(46)..(46)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa
is L, I, M or Vmisc_feature(48)..(48)Xaa is Y or
Fmisc_feature(50)..(50)Xaa is A or G 6Gly Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa Pro Xaa1 5 10 15Xaa Thr Phe Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Lys Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 20 25 30Xaa Xaa Pro Tyr Xaa
Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa Ser Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa Xaa Xaa 35 40 45Tyr Xaa
50731PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
2misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is L or Imisc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa is I, V
or Lmisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa is T or Smisc_feature(6)..(7)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is G or
Amisc_feature(9)..(10)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(11)..(11)Xaa is I, V or Mmisc_feature(12)..(12)Xaa
is E or Qmisc_feature(13)..(14)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(16)..(18)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is F or
Ymisc_feature(20)..(20)Xaa is L, I, V or Fmisc_feature(21)..(21)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa
is Y or Fmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(25)..(25)Xaa is K, R or
Nmisc_feature(26)..(30)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa is T or A 7Xaa Xaa Xaa Ile Asn Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Tyr Xaa1 5 10 15Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Ala Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 20 25 30884PRTArtificial
SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence 2misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is R,
Q or Hmisc_feature(2)..(5)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(9)..(13)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa is
V, I, L or Mmisc_feature(15)..(15)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(16)..(16)Xaa is V or
Mmisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa is A or Vmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is A,
S or Tmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa is I or
Vmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa is I, M, V or Lmisc_feature(25)..(26)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(28)..(28)Xaa
is I or Vmisc_feature(29)..(29)Xaa is K, R or
Qmisc_feature(30)..(30)Xaa is T or Smisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa is K
or Rmisc_feature(33)..(33)Xaa is V or Amisc_feature(34)..(34)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa
is F or Ymisc_feature(38)..(38)Xaa is F, I or
Lmisc_feature(39)..(39)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(42)..(42)Xaa is L, F or Vmisc_feature(43)..(43)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(45)..(45)Xaa
is T or Vmisc_feature(46)..(46)Xaa is L or
Imisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(49)..(50)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(52)..(52)Xaa is F or Lmisc_feature(53)..(53)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(56)..(56)Xaa
is L or Fmisc_feature(57)..(59)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(61)..(62)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(63)..(63)Xaa is V or
Imisc_feature(64)..(65)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(68)..(69)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(71)..(72)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(73)..(73)Xaa is L or Fmisc_feature(74)..(74)Xaa is
G or Smisc_feature(75)..(76)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(79)..(79)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(80)..(80)Xaa is L, V or
Imisc_feature(81)..(81)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(82)..(83)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(84)..(84)Xaa is Y
or F 8Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa1 5 10 15Phe Xaa Xaa Pro Leu Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Val Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Ser 20 25 30Xaa Xaa Xaa Met Pro Xaa Xaa Leu Ser Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa
Xaa Xaa Ala 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Trp Xaa Xaa Tyr Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Asp
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 50 55 60Xaa Pro Asn Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Gln Met Xaa Xaa65 70 75 80Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa957PRTArtificial
SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence 3misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is A
or Vmisc_feature(2)..(4)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(6)..(6)Xaa is I, L or Vmisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(10)..(10)Xaa is
I, L or Vmisc_feature(11)..(11)Xaa is I, L or
Vmisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa is F or Lmisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(15)..(15)Xaa is V
or Tmisc_feature(16)..(16)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa is A or Smisc_feature(20)..(20)Xaa is
V, L or Imisc_feature(21)..(21)Xaa is P or
Amisc_feature(24)..(25)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(26)..(26)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(27)..(27)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(28)..(28)Xaa
is K or Rmisc_feature(29)..(29)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa is S or
Tmisc_feature(32)..(33)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(34)..(34)Xaa is G or Smisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa is
F or Ymisc_feature(36)..(36)Xaa is Q, S or
Emisc_feature(38)..(38)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(41)..(42)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(43)..(43)Xaa is A, S or Tmisc_feature(45)..(45)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa
is A, C or Smisc_feature(48)..(48)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(50)..(50)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(51)..(51)Xaa is L, I or
Mmisc_feature(52)..(52)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(54)..(54)Xaa is A
or Gmisc_feature(55)..(56)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(57)..(57)Xaa is K or T 9Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa
Xaa Gly Asn Xaa Xaa Ser Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa1 5 10 15Leu Xaa Pro Xaa Xaa
Thr Phe Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Lys Xaa Xaa 20 25 30Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Ser Xaa Pro Tyr Xaa Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa Ser Xaa Xaa 35 40 45Leu Xaa Xaa
Xaa Tyr Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 50 551054PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic
consensus sequence 3misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is L, M or
Pmisc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa is L or Imisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa is I, L
or Vmisc_feature(4)..(4)Xaa is T or Smisc_feature(7)..(8)Xaa can be
any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(9)..(9)Xaa is G or
Amisc_feature(10)..(11)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(12)..(12)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa is
E or Qmisc_feature(14)..(15)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(17)..(17)Xaa is I or
Lmisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is L, M, V or
Imisc_feature(20)..(20)Xaa is F or Ymisc_feature(21)..(21)Xaa is L,
I, V or Fmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa is Y or
Fmisc_feature(25)..(25)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(26)..(26)Xaa is K or Rmisc_feature(27)..(31)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(32)..(32)Xaa
is T or Amisc_feature(33)..(34)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa is L, M, F, V or
Imisc_feature(36)..(36)Xaa is L, F, V or Imisc_feature(37)..(39)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(40)..(40)Xaa
is N or Dmisc_feature(41)..(41)Xaa is F, V, I or
Lmisc_feature(42)..(43)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(44)..(44)Xaa is F or Lmisc_feature(45)..(46)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa
is I, L or Vmisc_feature(48)..(53)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(54)..(54)Xaa is L, I or V 10Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Ile Asn Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Tyr1 5 10
15Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Ala Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
20 25 30Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 501184PRTArtificial
SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence 3misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is R
or Qmisc_feature(2)..(5)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(9)..(12)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa is S
or Amisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa is V, L or Mmisc_feature(15)..(15)Xaa
is C, S or Amisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa is A or
Vmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is A or Smisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa is I
or Vmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa is I, M or Vmisc_feature(25)..(26)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(28)..(28)Xaa
is I or Vmisc_feature(29)..(29)Xaa is K, R or
Qmisc_feature(30)..(30)Xaa is T or Smisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa is K
or Rmisc_feature(33)..(33)Xaa is V or Amisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa is
F or Ymisc_feature(38)..(38)Xaa is F or Imisc_feature(39)..(39)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(42)..(42)Xaa
is L, F or Vmisc_feature(43)..(43)Xaa can be any naturally
occurring amino acidmisc_feature(45)..(45)Xaa is T or
Vmisc_feature(46)..(46)Xaa is L or Imisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa is S
or Nmisc_feature(49)..(49)Xaa is V or Imisc_feature(50)..(50)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(52)..(52)Xaa
is F or Lmisc_feature(53)..(53)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(57)..(58)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(59)..(59)Xaa is K or
Nmisc_feature(61)..(62)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(63)..(63)Xaa is V or Imisc_feature(64)..(65)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(68)..(68)Xaa
is V or Imisc_feature(69)..(69)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(71)..(72)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(73)..(73)Xaa is F or
Lmisc_feature(74)..(74)Xaa is G or Smisc_feature(75)..(76)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(79)..(79)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(81)..(81)Xaa is Y
or
Fmisc_feature(82)..(83)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(84)..(84)Xaa is Y or F 11Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Gly
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Val1 5 10 15Phe Xaa Xaa Pro Leu
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Val Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Ser 20 25 30Xaa Glu Xaa Met
Pro Xaa Xaa Leu Ser Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa Xaa Xaa Ala 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Trp
Xaa Xaa Tyr Gly Leu Xaa Xaa Xaa Asp Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 50 55 60Xaa Pro
Asn Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Gln Met Xaa Leu65 70 75
80Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa1265PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus
sequence 4misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is M, L or
Vmisc_feature(2)..(3)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(4)..(4)Xaa is T, K, N or Smisc_feature(5)..(8)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(10)..(11)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa
is L, I or Vmisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa is I, L or
Vmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(26)..(26)Xaa is S
or Amisc_feature(28)..(28)Xaa is V or Imisc_feature(32)..(33)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(37)..(37)Xaa
is K or Rmisc_feature(39)..(39)Xaa is S or
Tmisc_feature(40)..(40)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(41)..(41)Xaa is E or Kmisc_feature(42)..(42)Xaa is
G or Smisc_feature(43)..(43)Xaa is F or Ymisc_feature(44)..(44)Xaa
is Q or Emisc_feature(46)..(46)Xaa is I or
Lmisc_feature(49)..(50)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(51)..(51)Xaa is A or Smisc_feature(53)..(53)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(55)..(55)Xaa
is A or Cmisc_feature(56)..(56)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(58)..(58)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(59)..(59)Xaa is L, I or
Mmisc_feature(62)..(62)Xaa is A or Gmisc_feature(63)..(64)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acid 12Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Ala Xaa Xaa Phe Gly Xaa Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Xaa Xaa Ser Phe Xaa
Val Xaa Leu Xaa Pro Xaa Pro Thr Phe Xaa 20 25 30Xaa Ile Xaa Lys Xaa
Lys Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Ser Xaa Pro Tyr 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Xaa Leu
Xaa Ser Xaa Xaa Leu Xaa Xaa Tyr Tyr Xaa Xaa Xaa 50 55
60Lys651354PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus sequence
4misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is L or Mmisc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa is L or
Imisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(4)..(4)Xaa is T or
Smisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa is A, S or Tmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is F
or Vmisc_feature(9)..(9)Xaa is G or Amisc_feature(10)..(10)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(11)..(11)Xaa is F
or Vmisc_feature(12)..(12)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa is
E or Qmisc_feature(14)..(15)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(17)..(17)Xaa is I or
Lmisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is L, M or Imisc_feature(20)..(20)Xaa
is F or Ymisc_feature(21)..(21)Xaa is F, V, I or
Lmisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(25)..(25)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(26)..(26)Xaa
is K or Rmisc_feature(27)..(28)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(29)..(29)Xaa is R or
Kmisc_feature(30)..(31)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(32)..(32)Xaa is T or Amisc_feature(33)..(33)Xaa is
L, V or Mmisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa is V, L, M or
Fmisc_feature(36)..(36)Xaa is L, I, V or Fmisc_feature(37)..(39)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(40)..(40)Xaa
is N or Dmisc_feature(41)..(41)Xaa is F, V or
Imisc_feature(42)..(43)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(44)..(44)Xaa is F or Lmisc_feature(45)..(46)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa
is I or Lmisc_feature(48)..(48)Xaa is L, I, V or
Fmisc_feature(49)..(49)Xaa is L, M or Vmisc_feature(50)..(50)Xaa is
L or Vmisc_feature(51)..(52)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(53)..(53)Xaa is F or
Lmisc_feature(54)..(54)Xaa is L, I or V 13Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Ile Asn
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Tyr1 5 10 15Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Ala Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 20 25 30Xaa Lys Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Xaa Xaa 501485PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic consensus
sequence 4misc_feature(1)..(1)Xaa is R or Qmisc_feature(2)..(2)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(3)..(3)Xaa is
K, S or Qmisc_feature(4)..(4)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(5)..(5)Xaa is L, I or
Vmisc_feature(7)..(7)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(8)..(8)Xaa is I or Vmisc_feature(10)..(12)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(13)..(13)Xaa is S
or Amisc_feature(14)..(14)Xaa is V or Lmisc_feature(15)..(15)Xaa is
S, C or Amisc_feature(18)..(18)Xaa is A or
Vmisc_feature(19)..(19)Xaa is A or Smisc_feature(22)..(22)Xaa can
be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(23)..(23)Xaa is I
or Vmisc_feature(24)..(24)Xaa is M, I or Vmisc_feature(25)..(26)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(28)..(28)Xaa
is I or Vmisc_feature(29)..(29)Xaa is K or
Rmisc_feature(31)..(31)Xaa is K or Rmisc_feature(33)..(33)Xaa is V
or Amisc_feature(35)..(35)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(39)..(39)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(42)..(42)Xaa
is L or Fmisc_feature(43)..(43)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(46)..(46)Xaa is I or
Lmisc_feature(47)..(47)Xaa is S or Nmisc_feature(49)..(49)Xaa is V
or Imisc_feature(50)..(50)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(52)..(52)Xaa is L or Fmisc_feature(53)..(53)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(57)..(57)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(58)..(58)Xaa
is L or Imisc_feature(59)..(59)Xaa is K or
Nmisc_feature(61)..(62)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(63)..(63)Xaa is V or Imisc_feature(65)..(65)Xaa is
L, F, I or Mmisc_feature(68)..(68)Xaa is V or
Imisc_feature(69)..(69)Xaa is L, I or Vmisc_feature(71)..(72)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino acidmisc_feature(73)..(73)Xaa
is L or Fmisc_feature(75)..(76)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acidmisc_feature(79)..(79)Xaa is I or
Vmisc_feature(81)..(81)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(82)..(82)Xaa is V,
L, I or Mmisc_feature(83)..(83)Xaa is V, I or
Mmisc_feature(84)..(84)Xaa is Y or Fmisc_feature(85)..(85)Xaa is K,
R or Q 14Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Cys Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
Xaa Val1 5 10 15Phe Xaa Xaa Pro Leu Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Val Xaa Xaa
Thr Xaa Ser 20 25 30Xaa Glu Xaa Met Pro Phe Xaa Leu Ser Xaa Xaa Leu
Thr Xaa Xaa Ala 35 40 45Xaa Xaa Trp Xaa Xaa Tyr Gly Leu Xaa Xaa Xaa
Asp Xaa Xaa Xaa Ala 50 55 60Xaa Pro Asn Xaa Xaa Gly Xaa Xaa Xaa Gly
Xaa Xaa Gln Met Xaa Leu65 70 75 80Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa Xaa
8515258PRTArabidopsis thaliana 15Met Phe Leu Lys Val His Glu Ile
Ala Phe Leu Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Gly Val
Phe Leu Ser Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gly Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Ser Ser Lys Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ile Cys Ala Leu Ala
Ser Ala Thr Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Gly Ile Met 50 55 60Lys Thr His Ala
Tyr Leu Ile Ile Ser Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Cys Phe65 70 75 80Ile Glu
Ile Ser Tyr Leu Phe Leu Tyr Ile Leu Tyr Ala Pro Arg Glu 85 90 95Ala
Lys Ile Ser Thr Leu Lys Leu Ile Val Ile Cys Asn Ile Gly Gly 100 105
110Leu Gly Leu Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Asn Leu Leu Val Pro Lys Gln His
115 120 125Arg Val Ser Thr Val Gly Trp Val Cys Ala Ala Tyr Ser Leu
Ala Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ser Pro Leu Ser Val Met Arg Lys Val Ile
Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Leu Leu Ser
Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Asn Ala 165 170 175Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Phe Ile Ala 180 185 190Met Pro Asn Ile Leu
Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Val Ala Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Met Met
Tyr Gln Gly Ser Thr Lys Thr Asp Leu Pro Thr Glu Asn 210 215 220Gln
Leu Ala Asn Lys Thr Asp Val Asn Glu Val Pro Ile Val Ala Val225 230
235 240Glu Leu Pro Asp Val Gly Ser Asp Asn Val Glu Gly Ser Val Arg
Pro 245 250 255Met Lys16289PRTArabidopsis thaliana 16Met Ala Ile
Ser Gln Ala Val Leu Ala Thr Val Phe Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile
Ile Ser Phe Phe Val Cys Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr Phe Val 20 25 30Arg
Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40
45Val Ile Ser Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Met Tyr Tyr Ala Met Ile
50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Met Met Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Ala Phe
Val65 70 75 80Val Gln Ile Val Tyr Ile Ser Leu Phe Phe Phe Tyr Ala
Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Glu Lys Thr Leu Thr Val Lys Phe Val Leu Phe Val
Asp Val Leu Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly Ala Ile Phe Val Leu Thr Tyr Phe
Ile Ile His Ala Asn Lys 115 120 125Arg Val Gln Val Leu Gly Tyr Ile
Cys Met Val Phe Ala Leu Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Gly
Ile Ile Arg Lys Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Ala Glu Phe
Met Pro Phe Gly Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Val
Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Met Asn Ile Ala 180 185
190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Val Leu Gln Met Ile Leu
195 200 205Phe Leu Ile Tyr Lys Lys Pro Gly Thr Lys Val Leu Glu Pro
Pro Gly 210 215 220Ile Lys Leu Gln Asp Ile Ser Glu His Val Val Asp
Val Val Arg Leu225 230 235 240Ser Thr Met Val Cys Asn Ser Gln Met
Arg Thr Leu Val Pro Gln Asp 245 250 255Ser Ala Asp Met Glu Ala Thr
Ile Asp Ile Asp Glu Lys Ile Lys Gly 260 265 270Asp Ile Glu Lys Asn
Lys Asp Glu Lys Glu Val Phe Leu Ile Ser Lys 275 280
285Asn17289PRTArabidopsis thaliana 17Met Ser Leu Phe Asn Thr Glu
Asn Thr Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser
Phe Ala Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Trp
Lys Lys Lys Thr Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Thr Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Thr Gln Lys
Lys Asp Val Phe Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys
Phe Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ser Met Phe Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro 85 90
95Lys Pro Ala Arg Met Leu Thr Val Lys Met Leu Leu Leu Met Asn Phe
100 105 110Gly Gly Phe Cys Ala Ile Leu Leu Leu Cys Gln Phe Leu Val
Lys Gly 115 120 125Ala Thr Arg Ala Lys Ile Ile Gly Gly Ile Cys Val
Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile
Arg Thr Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro
Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr Ile 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Ile Trp
Leu Leu Tyr Gly Leu Ala Leu Lys Asp Ile Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Phe
Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ala Leu Gly Ala Leu Gln Met 195 200 205Ile
Leu Tyr Val Val Tyr Lys Tyr Cys Lys Thr Ser Pro His Leu Gly 210 215
220Glu Lys Glu Val Glu Ala Ala Lys Leu Pro Glu Val Ser Leu Asp
Met225 230 235 240Leu Lys Leu Gly Thr Val Ser Ser Pro Glu Pro Ile
Ser Val Val Arg 245 250 255Gln Ala Asn Lys Cys Thr Cys Gly Asn Asp
Arg Arg Ala Glu Ile Glu 260 265 270Asp Gly Gln Thr Pro Lys His Gly
Lys Gln Ser Ser Ser Ala Ala Ala 275 280 285Thr18285PRTArabidopsis
thaliana 18Met Ala Leu Phe Asp Thr His Asn Thr Trp Ala Phe Val Phe
Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser Phe Ala Val Phe Leu Ser Pro
Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys Thr Thr Glu Gly
Phe Gln Ser Ile 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu
Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Thr Gln Lys Lys Asp Val Phe Leu Leu Val
Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Phe Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile
Ser Ile Phe Val Ala Phe Ala Ser 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala Arg Met Leu Thr
Val Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Met Asn Phe 100 105 110Gly Gly Phe Cys Leu
Ile Leu Leu Leu Cys Gln Phe Leu Ala Lys Gly 115 120 125Thr Thr Arg
Ala Lys Ile Ile Gly Gly Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys
Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg Thr Val Ile Lys Thr145 150
155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr
Ile 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Leu Leu Tyr Gly Leu Ala Leu Lys
Asp Ile Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Phe Pro Asn Val Ile Gly Phe Val Leu
Gly Ala Leu Gln Met 195 200 205Ile Leu Tyr Val Val Tyr Lys Tyr Cys
Lys Thr Pro Ser Asp Leu Val 210 215 220Glu Lys Glu Leu Glu Ala Ala
Lys Leu Pro Glu Val Ser Ile Asp Met225 230 235 240Val Lys Leu Gly
Thr Leu Thr Ser Pro Glu Pro Val Ala Ile Thr Val 245 250 255Val Arg
Ser Val Asn Thr Cys Asn Cys Asn Asp Arg Asn Ala Glu Ile 260 265
270Glu Asn Gly Gln Gly Val Arg Asn Ser Ala Ala Thr Thr 275 280
28519294PRTArabidopsis thaliana 19Met Ala Leu Thr Asn Asn Leu Trp
Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Val Val
Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Val 20 25 30Arg Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys
Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Ser Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Met Gln 50 55 60Lys Asp Gly Thr
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile
Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Leu Phe Val Ser Tyr Ala Asn Lys 85 90 95Lys
Thr Arg Ile Ser Thr Leu Lys Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Asn Phe Leu 100 105
110Gly Phe Ala Ala Ile Val Leu Val Cys Glu Leu Leu Thr Lys Gly Ser
115 120 125Thr Arg Glu Lys Val Leu Gly Gly Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser
Val Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Val Val
Val Arg Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu
Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Ile Ser 165 170 175Ala Val Thr Trp Leu Phe Tyr
Gly Leu Ala Ile Lys Asp Phe Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Val
Leu Gly Ala Phe Leu Gly Ala Val Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Leu Tyr Ile
Ile Phe Lys Tyr Tyr Lys Thr Pro Val Ala Gln Lys Thr 210 215 220Asp
Lys Ser Lys Asp Val Ser Asp His Ser Ile Asp Ile Ala Lys Leu225
230 235 240Thr Thr Val Ile Pro Gly Ala Val Leu Asp Ser Ala Val His
Gln Pro 245 250 255Pro Ala Leu His Asn Val Pro Glu Thr Lys Ile Gln
Leu Thr Glu Val 260 265 270Lys Ser Gln Asn Met Thr Asp Pro Lys Asp
Gln Ile Asn Lys Asp Val 275 280 285Gln Lys Gln Ser Gln Val
29020281PRTArabidopsis thaliana 20Met Val Leu Thr His Asn Val Leu
Ala Val Thr Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val
Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Val 20 25 30Arg Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys
Ser Ile Glu Gly Phe Glu Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Ser Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Gln 50 55 60Lys Asp Gly Ala
Gly Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala Val Gly Cys65 70 75 80Phe Ile
Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ile Leu Phe Ile Thr Tyr Ala Asn Lys 85 90 95Lys
Ala Arg Ile Ser Thr Leu Lys Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Asn Phe Leu 100 105
110Gly Phe Ala Ala Ile Ile Leu Val Cys Glu Leu Leu Thr Lys Gly Ser
115 120 125Asn Arg Glu Lys Val Leu Gly Gly Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser
Val Cys 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Val Val
Ile Arg Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu
Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Ile Ser 165 170 175Ala Ile Thr Trp Leu Phe Tyr
Gly Leu Ala Ile Lys Asp Phe Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile
Leu Gly Ala Phe Leu Gly Ala Val Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Leu Tyr Val
Ile Phe Lys Tyr Tyr Lys Thr Pro Leu Val Val Asp Glu 210 215 220Thr
Glu Lys Pro Lys Thr Val Ser Asp His Ser Ile Asn Met Val Lys225 230
235 240Leu Ser Ser Thr Pro Ala Ser Gly Asp Leu Thr Val Gln Pro Gln
Thr 245 250 255Asn Pro Asp Val Ser His Pro Ile Lys Thr His Gly Gly
Asp Leu Glu 260 265 270Asp Gln Met Asp Lys Lys Met Pro Asn 275
28021292PRTArabidopsis thaliana 21Met Gly Val Met Ile Asn His His
Phe Leu Ala Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe
Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys
Arg Lys Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Leu 35 40 45Pro Tyr Gln Val Ser
Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys Lys
Asp Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val
Val Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Ala Met Phe Phe Ala Tyr Ala Thr 85 90 95Arg
Glu Lys Arg Ile Ser Ala Met Lys Leu Phe Ile Ala Met Asn Val 100 105
110Ala Phe Phe Ser Leu Ile Leu Met Val Thr His Phe Val Val Lys Thr
115 120 125Pro Pro Leu Gln Val Ser Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Ile Ser 130 135 140Val Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Met Ile Val Ala
Arg Val Ile Lys145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe
Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Ile Ser Ala Val Met Trp Phe
Ala Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu Asn Asp Ile 180 185 190Cys Ile Ala Ile Pro
Asn Val Val Gly Phe Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln 195 200 205Met Val Leu
Tyr Leu Val Tyr Arg Asn Ser Asn Glu Lys Pro Glu Lys 210 215 220Ile
Asn Ser Ser Glu Gln Gln Leu Lys Ser Ile Val Val Met Ser Pro225 230
235 240Leu Gly Val Ser Glu Val His Pro Val Val Thr Glu Ser Val Asp
Pro 245 250 255Leu Ser Glu Ala Val His His Glu Asp Leu Ser Lys Val
Thr Lys Val 260 265 270Glu Glu Pro Ser Ile Glu Asn Gly Lys Cys Tyr
Val Glu Ala Thr Arg 275 280 285Pro Glu Thr Val 29022307PRTOryza
sativa 22Met Ala Gly Gly Phe Leu Ser Met Ala Asn Pro Ala Val Thr
Leu Ser1 5 10 15Gly Val Ala Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu
Ala Pro Val 20 25 30Ala Thr Phe Leu Gln Val Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr
Gly Gly Tyr Ser 35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser
Val Leu Trp Ile Phe 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu Val Lys Thr Asn Ser Arg Pro
Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala65 70 75 80Phe Gly Cys Gly Val Glu Ala Ala
Tyr Ile Val Leu Tyr Leu Val Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro Arg Arg Ala Arg Leu
Arg Thr Leu Ala Phe Phe Leu Leu Leu 100 105 110Asp Val Ala Ala Phe
Ala Leu Ile Val Val Thr Thr Leu Tyr Leu Val 115 120 125Pro Lys Pro
His Gln Val Lys Phe Leu Gly Ser Val Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser
Met Ala Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Phe Lys Val Ile145 150
155 160Lys Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Ile Gly Leu Ser Val Cys
Leu 165 170 175Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp Phe Cys Tyr Gly Leu Phe
Thr Lys Asp 180 185 190Pro Tyr Val Met Tyr Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe
Phe Phe Ser Cys Val 195 200 205Gln Met Gly Leu Tyr Phe Trp Tyr Arg
Lys Pro Arg Asn Thr Ala Val 210 215 220Leu Pro Thr Thr Ser Asp Ser
Met Ser Pro Ile Ser Ala Ala Ala Ala225 230 235 240Ala Thr Gln Arg
Val Ile Glu Leu Pro Ala Gly Thr His Ala Phe Thr 245 250 255Ile Leu
Ser Val Ser Pro Ile Pro Ile Leu Gly Val His Lys Val Glu 260 265
270Val Val Ala Ala Glu Gln Ala Ala Asp Gly Val Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala
275 280 285Ala Asp Lys Glu Leu Leu Gln Asn Lys Pro Glu Val Ile Glu
Ile Thr 290 295 300Ala Ala Val30523300PRTOryza sativa 23Met Val Gln
Ala Leu Val Phe Ala Val Gly Ile Val Gly Asn Ile Leu1 5 10 15Ser Phe
Leu Val Ile Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val Tyr 20 25 30Lys
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr Ala Val Ala 35 40
45Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu Thr Ser Asp
50 55 60Leu Leu Leu Leu Ser Ile Asn Ser Ile Gly Cys Leu Val Glu Ser
Leu65 70 75 80Tyr Leu Thr Val Tyr Leu Leu Tyr Ala Pro Arg Gln Ala
Met Ala Phe 85 90 95Thr Leu Lys Leu Val Cys Ala Met Asn Leu Ala Leu
Phe Ala Ala Val 100 105 110Val Ala Ala Leu Gln Leu Leu Val Lys Ala
Thr Asp Arg Arg Val Thr 115 120 125Leu Ala Gly Gly Ile Gly Ala Ser
Phe Ala Leu Ala Val Phe Val Ala 130 135 140Pro Leu Thr Ile Ile Arg
Gln Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe145 150 155 160Met Pro Phe
Trp Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Val Trp 165 170 175Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Met Lys Asp Phe Phe Val Ala Thr Pro Asn 180 185
190Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Val Leu Tyr Val Val
195 200 205Tyr Lys Asn Pro Lys Lys Asn Ser Ala Val Ser Glu Ala Ala
Ala Ala 210 215 220Gln Gln Val Glu Val Lys Asp Gln Gln Gln Leu Gln
Met Gln Leu Gln225 230 235 240Ala Ser Pro Ala Val Ala Pro Leu Asp
Val Asp Ala Asp Ala Asp Ala 245 250 255Asp Leu Glu Ala Ala Ala Pro
Ala Thr Pro Gln Arg Pro Ala Asp Asp 260 265 270Asp Ala Ile Asp His
Arg Ser Val Val Val Asp Ile Pro Pro Pro Pro 275 280 285Gln Pro Pro
Pro Ala Leu Pro Ala Val Glu Val Ala 290 295 30024296PRTOryza sativa
24Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Leu Gln His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1
5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser Phe Thr Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro
Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln
Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile
Phe Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys Ser Asn Glu Ala Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Met
Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala Lys Val Phe Thr Thr Lys
Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Val Ile Leu
Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Ser His Gly 115 120 125Glu Gln Arg Val Val
Ser Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Ala Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe
Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Lys Arg Val Ile Gln Ser145 150 155
160Arg Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr Leu
165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp
Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly
Val Val Gln Met 195 200 205Gly Leu Tyr Val Phe Tyr Met Asn Ala Thr
Pro Val Ala Gly Glu Gly 210 215 220Lys Glu Gly Lys Gly Lys Leu Ala
Ala Ala Glu Glu Leu Pro Val Val225 230 235 240Val Asn Val Gly Lys
Leu Ala Ala Ala Thr Pro Asp Arg Ser Thr Gly 245 250 255Ala Val His
Val His Pro Val Pro Arg Ser Cys Ala Ala Glu Ala Ala 260 265 270Ala
Ala Glu Pro Glu Val Leu Val Asp Ile Pro Pro Pro Pro Pro Pro 275 280
285Arg Ala Val Glu Val Ala Ala Val 290 29525303PRTOryza sativa
25Met Ala Gly Met Ser Leu Gln His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1
5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro
Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Gln Gly Phe Gln
Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile
Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Leu Lys Ser Asp Glu Cys Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ser Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ala Val
Tyr Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala Lys Met Phe Thr Ala Lys
Leu Leu Leu Leu Val Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu
Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Ser Ala Gly 115 120 125Asp Arg Arg Ile Val
Val Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe
Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg Leu Val Val Arg Thr145 150 155
160Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Ser Leu Thr Ile
165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp
Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ser Phe Gly
Val Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Gly Leu Tyr Ala Met Tyr Arg Asn Ser Thr
Pro Lys Ala Val Leu Thr 210 215 220Lys Glu Val Glu Ala Ala Thr Ala
Thr Gly Asp Asp Asp His Ser Ala225 230 235 240Ala Gly Val Lys Glu
His Val Val Asn Ile Ala Lys Leu Ser Ala Ala 245 250 255Val Asp Val
Val Lys Thr Arg Glu Val His Pro Val Asp Val Glu Ser 260 265 270Pro
Pro Ala Glu Ala Pro Pro Glu Glu Asp Asp Lys Ala Ala Ala Ala 275 280
285Thr Ala Ala Ala Val Ala Gly Ala Gly Glu Lys Lys Val Ala Ala 290
295 30026319PRTOryza sativa 26Met Ala Phe Met Ser Met Glu Arg Ser
Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser Leu
Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val Tyr Arg
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Thr Pro Tyr Val Val Thr
Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Met Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Phe Val Lys Ser
Gly Ala Glu Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Gly Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Val
Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Leu Ala Met Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys
Ser Ala Arg Met Leu Thr Ala Lys Met Leu Leu Gly Leu Asn 100 105
110Ile Gly Leu Phe Gly Val Ile Ala Leu Val Thr Leu Leu Leu Ser Arg
115 120 125Gly Glu Leu Arg Val His Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Val Ser 130 135 140Leu Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg
Leu Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Val 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Phe
Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Lys Lys Asp Val 180 185 190Phe Val Ala Leu Pro
Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Val Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ala Leu
Tyr Met Ala Tyr Arg Ser Lys Lys Pro Leu Val Ala Ser 210 215 220Ser
Ser Ser Ala Val Val Ala Ala Gly Leu Glu Ile Lys Leu Pro Glu225 230
235 240His Val Lys Glu Val Gln Ala Val Ala Lys Gly Ala Val Ala Ala
Ala 245 250 255Pro Glu Gly Arg Ile Ser Cys Gly Ala Glu Val His Pro
Ile Asp Asp 260 265 270Val Met Pro Ser Glu Val Val Glu Val Lys Val
Asp Asp Glu Glu Thr 275 280 285Asn Arg Thr Asp Glu Met Ala Gly Asp
Gly Asp His Ala Met Val Arg 290 295 300Thr Glu Gln Ile Ile Lys Pro
Asp Met Ala Ile Val Val Glu Val305 310 31527252PRTMedicago
truncatula 27Met Phe Pro Phe Ser Asn Leu Lys Met Val Leu Leu Phe
Gly Phe Leu1 5 10 15Gly Ile Val Thr Phe Met Ser Phe Leu Ala Pro Leu
Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Ser Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Phe
His Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Thr Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Leu Phe
Val Tyr Tyr Gly Phe Leu 50 55 60Lys Thr Asn Ala Ile Phe Leu Ile Thr
Ile Asn Ser Ile Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Met Glu Val Ala Tyr Leu Ile
Met Tyr Ile Thr Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Leu Lys Ile Ser Thr Leu
Val Leu Ile Leu Ile Val Asp Met Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly Leu Thr
Met Ile Ile Thr Thr Phe Ile Val Lys Gly Ser Phe 115 120 125His Val
Gln Val Val Gly Met Ile Cys Thr Ile Phe Asn Ile Gly Met 130 135
140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Lys Lys Val Ile Lys Thr Arg
Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Pro Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu
Thr Ile Cys Ala 165 170 175Thr Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Phe Phe Asp
Lys Asp Lys Tyr Ile Met 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Gly Leu Gly Phe Leu
Leu Gly Val Ser Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Lys Asn
Ala Lys Asn Asn Val Glu Ala Ser Ser Thr 210 215 220Asn Gln Leu Gln
Glu His Gly Cys Asp Gly Gly Asn Asn Gln Ile Phe225 230 235 240Pro
Thr Val Val Glu Met Lys Glu Ile Asn Ile Val 245 25028270PRTMedicago
truncatula 28Met Ala Leu Phe Tyr Ser Glu Tyr Trp Ala Phe Val Phe
Gly Val Ile1 5 10 15Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Cys Met Thr Phe Leu Ala Pro
Leu Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly
Phe Gln Ser Val Pro
35 40 45Tyr Val Thr Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala
His 50 55 60Val Lys Asn Lys Ala Thr Leu Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ile
Tyr Gly65 70 75 80Phe Gly Ile Glu Ala Ile Tyr Ile Ile Ile Phe Leu
Leu Tyr Ala Ser 85 90 95Asn Lys Ala Arg Leu Ser Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu
Phe Leu Thr Val Cys 100 105 110Gly Tyr Gly Thr Met Val Ile Leu Thr
Thr Tyr Leu Thr Lys Gly Ser 115 120 125Lys Arg Leu Ser Ile Ile Gly
Trp Ile Cys Met Val Phe Asn Ile Cys 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ser Pro
Leu Phe Ile Leu Lys Gln Val Ile Lys Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val
Ala Phe Met Pro Leu Asn Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Asn 165 170
175Ala Ile Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Asp Asp Phe Tyr Ile
180 185 190Ala Ile Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Val Gln
Met Val 195 200 205Ile Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Lys Asp Ala Ile Pro Leu Glu
Ser Thr Lys Leu 210 215 220Gln Lys Pro Asn Asp His Val Leu Asn Ile
Cys Glu Asp Val Pro Asn225 230 235 240Gly Ala Leu Gln Pro Asp Pro
Asn Gln Val Val Lys Ser Gly Ala Pro 245 250 255Ala Val Ala Val Ile
Gly Asp Glu Asp Pro Asn Asn Gly Lys 260 265 27029255PRTMedicago
truncatula 29Met Ala Met Thr Arg Glu Ser Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly
Ile Ile Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Ala Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu
Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Val Ile Phe Lys Lys Lys Ser Ala Glu Gly Phe
Gln Ala Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp
Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Val 50 55 60Lys Arg Glu Ser Ala Leu Leu Leu Ile
Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Ile65 70 75 80Val Val Glu Ser Ala Tyr Ile
Ile Met Phe Leu Ile Tyr Ala Pro Lys 85 90 95Lys Gln Arg Leu Ser Thr
Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val Phe 100 105 110Gly Phe Gly Ala
Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Tyr Leu Ser Lys Gly Ala 115 120 125Lys Arg
Leu Ala Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Asn Ile Ser 130 135
140Val Phe Ala Thr Pro Leu Phe Val Ile Ser Lys Val Ile Arg Ser
Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Phe Leu Ser Phe Phe
Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu
Leu Arg Asp Tyr Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe
Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val 195 200 205Val Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Arg
Asn Ala Thr Pro Val Val Glu Ala Pro Met 210 215 220Lys Gly Gln Glu
Leu Ser Gly Gly His Ile Ile Asp Val Val Lys Ile225 230 235 240Gly
Thr Asp Pro Asn Arg Ala Gly Gly Gly Ala Gly Ser Lys Val 245 250
25530255PRTMedicago truncatula 30Met Ala Met Thr Arg Glu Ser Trp
Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Ala Val
Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Val Ile Phe Lys Lys Lys
Ser Ala Glu Gly Phe Gln Ala Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Val 50 55 60Lys Arg Glu Ser
Ala Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Ile65 70 75 80Val Val
Glu Ser Ala Tyr Ile Ile Met Phe Leu Ile Tyr Ala Pro Lys 85 90 95Lys
Gln Arg Leu Ser Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val Phe 100 105
110Gly Phe Gly Ala Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Tyr Leu Ser Lys Gly Ala
115 120 125Lys Arg Leu Ala Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Asn
Ile Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Phe Val Ile Ser Lys Val
Ile Arg Ser Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Phe Leu
Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Leu Leu Leu Arg Asp Tyr Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr
Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val 195 200 205Val Tyr Leu
Ile Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr Pro Val Val Glu Ala Pro Met 210 215 220Lys
Gly Gln Glu Leu Ser Gly Gly His Ile Ile Asp Val Val Lys Ile225 230
235 240Gly Thr Asp Ser Asn Arg Ala Gly Gly Gly Ala Gly Ser Lys Val
245 250 25531268PRTMedicago truncatulamisc_feature(192)..(192)Xaa
can be any naturally occurring amino
acidmisc_feature(199)..(199)Xaa can be any naturally occurring
amino acid 31Met Ala Ile Ser His Asn Thr Leu Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly
Met Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Ile
Ser Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe
Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp
Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr
Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Val Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ile
Leu Tyr Ile Ile Tyr Ala Pro Arg Asp 85 90 95Ala Arg Asn Leu Thr Phe
Lys Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Asn Val Gly Ser 100 105 110Phe Ala Leu Ile
Leu Ile Val Thr Asn Tyr Ala Val His Gly Pro Leu 115 120 125Arg Val
Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Ser Leu Ser Val Ser Val 130 135
140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val Ala Gln Val Val Arg Thr Lys
Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Asn Leu Ser Phe Thr Leu
Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Thr Met Trp Phe Gly Tyr Gly Phe Phe Leu
Lys Asp Ile Cys Ile Xaa 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Xaa Val
Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln Met Leu Leu 195 200 205Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn
Gly Gly Glu Lys Ala Met Lys Lys Glu Lys 210 215 220Lys Ala Pro Ile
Glu Pro Pro Lys Ser Ile Val Ile Glu Thr Gln Leu225 230 235 240Glu
Lys Ile Glu Gln Glu Lys Lys Asn Lys Asp Asp Asp Asn Glu Glu 245 250
255Lys Asp Lys Ser Glu Glu Pro Ile Gly Cys Gly Val 260
26532268PRTMedicago truncatula 32Met Ala Ile Ser His Asn Thr Leu
Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Met Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Val
Phe Leu Ala Pro Met Thr Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu Val Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Leu 50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Glu
Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Val Glu
Leu Ile Tyr Ile Ile Leu Tyr Ile Ile Tyr Ala Thr Lys Asp 85 90 95Ala
Arg Lys Leu Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Ala Met Asn Ile Gly Ser 100 105
110Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Thr Lys Tyr Ala Val His Gly Pro Ile
115 120 125Arg Val Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ser Ile Ser Val
Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Thr Ile Val Ala Gln Val Val
Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Asn Leu Ser
Phe Thr Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Ile Met Trp Phe Gly Tyr Gly
Leu Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile Cys Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu
Gly Phe Ala Leu Gly Leu Val Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Cys Ile
Tyr Arg Asn Gly Asp Lys Lys Lys Ala Asn Ser Lys Ala 210 215 220Ala
Leu Lys Ser Val Val Ile Glu Ser Ser Leu Gly Gly Thr Gly Glu225 230
235 240Val Phe Gln Val Glu Lys Asn Asp Gly Glu Glu Glu Glu Glu Lys
Lys 245 250 255Lys Thr Ile Glu Glu Thr Glu Tyr Asp Ser Lys Val 260
26533269PRTMedicago truncatula 33Met Asp Pro His Asp His Asp Arg
Leu Ala Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Ser Met
Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Arg Ile Trp Lys Lys
Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro 35 40 45Tyr Leu Val Ala Leu
Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Gly Phe 50 55 60Val Lys Lys His
Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Ala Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile
Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Thr Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Ala Thr Lys 85 90 95Asp
Ala Arg Ile Leu Thr Ile Lys Leu Phe Met Ala Met Asn Val Ala 100 105
110Cys Ser Val Leu Ile Val Leu Thr Thr Gln Leu Ala Met His Gly Lys
115 120 125Leu Arg Val His Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Thr Ser Phe Ala
Ile Cys 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Thr Ile Met Ala Lys Val
Ile Arg Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Ile Asn Leu
Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser 165 170 175Ala Ile Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Leu Leu Leu His Asp Ile Cys Ile 180 185 190Ala Ile Pro Asn Val
Leu Gly Phe Ile Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln Met Leu 195 200 205Leu Tyr Ala
Ile Tyr Asn Lys Ser Val Lys Glu Glu Tyr Ala Leu Glu 210 215 220Pro
Met Thr Asn Ile Val Ile Val Asn Pro Leu Gly Ile Pro Cys Glu225 230
235 240Val Phe Ser Leu Pro Val Ile Asp Asn Val Asn Lys Ile Glu Lys
Glu 245 250 255Gly Ala Glu Glu Met Glu Lys Ser Val Glu Asn Leu Thr
260 26534288PRTMedicago truncatula 34Met Ala Met Ile Ser Met Asn
His His Phe Leu Val Ile Ala Phe Gly1 5 10 15Leu Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile
Ser Cys Met Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Ile Gln Ile
Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Cys Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Leu Pro Tyr Leu
Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Gly Ile Gln
Thr Asn Ala Ile Phe Ile Val Ser Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys
Val Ile Glu Ile Ile Tyr Cys Ile Met Tyr Ile Ala Tyr Ala Thr 85 90
95Lys Asp Ala Arg Lys Leu Thr Ile Lys Leu Cys Ala Ala Leu Asn Val
100 105 110Val Ser Phe Val Leu Ile Phe Leu Ile Ile Gln Phe Ser Ile
Pro Glu 115 120 125Asn His Arg Val Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Thr
Ser Ile Ser Ile 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val
Val Arg Val Val Lys Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Asn Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp
Phe Leu Tyr Gly Phe Val Lys Arg Asp Ile Cys 180 185 190Ile Tyr Leu
Pro Asn Val Val Gly Phe Ile Leu Gly Ile Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Val
Leu Tyr Gly Tyr Tyr Ser Lys Tyr Ser Val Glu Lys Glu Lys Glu 210 215
220Gln Ala Val Ile Asn Ile Val Val Val Asn Pro Leu Gly Ser Ser
Glu225 230 235 240Val Phe Pro Ile Pro Leu Asp Glu Asn Lys Glu Ser
Ile Glu Asp Val 245 250 255Ile Asn Gln Gln Phe Gln Val Lys Lys Val
Gly Glu Glu Asp Ala Lys 260 265 270Glu Lys His Asp Asn Asn Val Glu
Ala Ile Glu Phe Gln Cys Val Val 275 280 28535265PRTPetunia hybrida
35Met Ala Gln Leu Arg Ala Asp Asp Leu Ser Phe Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu1
5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Met Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr
Phe 20 25 30Tyr Lys Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ala
Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Met Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Gly Leu Leu Leu Tyr
Tyr Ala Tyr 50 55 60Leu Arg Lys Asn Ala Tyr Leu Ile Val Ser Ile Asn
Gly Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Ala Ile Glu Leu Thr Tyr Ile Ser Leu Phe
Leu Phe Tyr Ala Pro Arg 85 90 95Lys Ser Lys Ile Phe Thr Gly Trp Leu
Met Leu Leu Glu Leu Gly Ala 100 105 110Leu Gly Met Val Met Pro Ile
Thr Tyr Leu Leu Ala Glu Gly Ser His 115 120 125Arg Val Met Ile Val
Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala Ala Ile Asn Val Ala Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala
Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Gln Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155
160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Leu Cys Ala
165 170 175Thr Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Phe Phe Lys Lys Asp Phe Tyr
Ile Ala 180 185 190Phe Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Val
Gln Met Leu Leu 195 200 205Tyr Phe Val Tyr Lys Asp Ser Lys Arg Ile
Asp Asp Glu Lys Ser Asp 210 215 220Pro Val Arg Glu Ala Thr Lys Ser
Lys Glu Gly Val Glu Ile Ile Ile225 230 235 240Asn Ile Glu Asp Asp
Asn Ser Asp Asn Ala Leu Gln Ser Met Glu Lys 245 250 255Asp Phe Ser
Arg Leu Arg Thr Ser Lys 260 26536301PRTCapsicum annuum 36Met Thr
Gly Ile Ser Gly His Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn
Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Ile Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25
30Thr Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Thr Ala Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr
35 40 45Val Ile Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe
Leu 50 55 60Lys Thr Asn Val Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly
Ile Phe65 70 75 80Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Val Gly Leu Tyr Leu Phe Tyr
Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Ala Arg Val His Thr Val Lys Met Leu Leu Leu
Thr Val Val Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly Ala Ile Val Leu Val Thr Gln
Phe Leu Phe Lys Gly Val Val 115 120 125Arg Gly Gln Ile Val Gly Trp
Ile Cys Leu Ile Phe Ala Leu Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu
Gly Ile Val Arg Gln Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu
Tyr Met Pro Leu Leu Leu Ser Val Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170
175Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile Asn Ile Ala
180 185 190Ala Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Val Leu Gln Ile
Val Leu 195 200 205Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Ser Lys Lys Glu Lys Val Ile Leu
Lys Glu Gln Lys 210 215 220Leu Pro Glu Ile Gln Lys Pro Ala Val Ile
Val Ala Asp Asp Asn Thr225 230 235 240Asn Ala Asn Lys Lys Leu Pro
Glu Leu Thr His Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp 245 250 255Ile Val Lys Leu Ala
Gly Leu Leu Thr Cys Thr Glu Lys Ser His Val 260 265 270Ala Thr Cys
Pro His Asp Val Asn Cys Gly Val Glu Ala Thr Asn Val 275 280 285Glu
Asn Asn Ile Pro Lys Leu Gln Thr Val Glu Ala Thr 290 295
30037260PRTLotus japonicus 37Met Ala Leu Ser His Asn Thr Leu Ala
Phe Thr Phe Gly Met Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Val Phe
Leu Ala Pro Ile Ala Thr Phe Tyr
20 25 30Arg Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro
Tyr 35 40 45Leu Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala
Met Val 50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe
Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Ile Glu Ile Ile Tyr Ile Ile Leu Tyr Met Ile
Tyr Ala Pro Arg Asp 85 90 95Ala Arg Asn Leu Thr Leu Lys Leu Phe Thr
Ala Met Asn Val Gly Ser 100 105 110Phe Ala Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Thr
His Phe Ala Val His Gly Pro Leu 115 120 125Arg Val Gln Val Leu Gly
Trp Ile Cys Val Ser Ile Ala Val Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro
Leu Ser Ile Val Ala Gln Val Val Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val
Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Asn Leu Ser Phe Thr Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170
175Thr Met Trp Phe Gly Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile Cys Ile Ala
180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Gly Leu Gly Leu Ile Gln Met
Val Leu 195 200 205Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn Gly Asn Glu Lys Gly Lys
Lys Pro Ala Ala 210 215 220Ala Leu Lys Ser Val Val Ile Glu Ile Pro
Thr Ser Asn Val Ile Gly225 230 235 240Glu Glu Val Gly Glu Glu Lys
Glu Lys Thr Glu Glu Pro Pro Val Asn 245 250 255Ala Cys Ala Ala
26038247PRTLotus japonicus 38Met Ala Met Thr Arg Glu Ser Trp Ala
Phe Val Phe Gly Leu Met Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Val Phe
Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Thr
Ala Glu Gly Phe Gln Ala Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser
Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Val 50 55 60Lys Arg Glu Ser Ala
Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Ile65 70 75 80Val Val Glu
Ser Ile Tyr Ile Ala Phe Phe Leu Phe Tyr Ala Pro Lys 85 90 95Lys Ser
Arg Leu Ser Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val Phe 100 105
110Gly Phe Gly Ala Met Leu Leu Ala Thr Leu Tyr Leu Ser Lys Gly Ala
115 120 125Lys Arg Leu Gln Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Asn
Ile Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Phe Ile Ile Ser Lys Val
Ile Arg Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Phe Leu
Ser Phe Ser Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Met Leu Leu Arg Asp Tyr Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr
Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val 195 200 205Val Tyr Leu
Ile Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr Pro Val Val Ile Glu Glu Lys 210 215 220Val
Lys Gly Gln Glu Met Ser Gly Asp His Ile Ile Asp Val Ala Lys225 230
235 240Gly Gly Ala Val Ser Lys Val 24539333PRTZea mays 39Met Ala
Phe Leu Asn Met Glu Gln Gln Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile
Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Leu Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro 20 25
30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser
35 40 45Thr Pro Tyr Val Val Thr Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Ile Phe
Tyr 50 55 60Ala Leu Leu Lys Ser Gly Ala Glu Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn
Gly Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Val Ile Glu Ala Ala Tyr Leu Ala Ala Tyr
Leu Val Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys Ala Ala Arg Ala Leu Thr Ala Lys Met
Leu Leu Gly Leu Asn 100 105 110Val Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Ala Ala Leu
Ala Thr Met Val Val Ser Ser 115 120 125Ala Gly Leu Arg Val Arg Val
Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ser Val Ala 130 135 140Leu Ser Val Phe Ala
Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Gln Val Val Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys
Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Val 165 170
175Leu Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Ala Leu Lys Arg Asp Val
180 185 190Phe Val Ala Phe Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Val
Ala Gln 195 200 205Ile Ala Leu Tyr Met Ala Tyr Arg Asn Lys Glu Pro
Ala Ala Val Thr 210 215 220Val Glu Glu Ala Lys Leu Pro Glu His Ala
Lys Glu Val Val Val Ala225 230 235 240Ala Ala Ala Ala Glu Ala Arg
Ala Ser Cys Gly Ala Glu Val His Pro 245 250 255Ile Asp Ile Asp Ile
Glu Ala Thr Pro Thr Pro Val Glu Glu Val His 260 265 270Glu Pro Gln
Val Val Val Val Val Asp Val Asp Val Glu Pro Val Thr 275 280 285Cys
Ala Gly Ala Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala Gly Ala Gly Ala Asp Ala Ser 290 295
300Gly Val Ala Asp Gly Gly Val Pro Gly Pro Met Ala Pro Pro Glu
Gln305 310 315 320Leu Ala Ile Lys Pro Asp Met Ala Ile Ser Val Glu
Ala 325 33040305PRTZea mays 40Met Ile Thr Val Gly His Pro Val Ala
Phe Ala Val Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Leu Ser Phe Leu Val Ile
Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val Tyr Ala Lys Lys Ser
Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Leu Ser
Ala Thr Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Ser Thr Asp Leu Leu
Leu Leu Ser Ile Asn Thr Val Ala Cys Val Ala65 70 75 80Glu Ser Val
Tyr Leu Ala Val Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro Gly Pro Ala 85 90 95Lys Ala
Phe Thr Leu Lys Leu Leu Cys Ala Ile Asn Met Gly Leu Phe 100 105
110Gly Ala Met Val Ala Phe Leu Gln Phe Tyr Val Val Asp Thr Gln Arg
115 120 125Arg Val Ser Ile Ala Gly Gly Val Gly Ala Ala Phe Ala Leu
Ala Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ala Ile Ile Arg Arg Val Met
Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Trp Leu Ser
Phe Phe Leu Thr Val Ser Ala 165 170 175Val Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Phe Phe Val Ala 180 185 190Met Pro Asn Val Leu
Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Val Leu 195 200 205Phe Phe Val
Tyr Arg Asn Arg Asn Pro Lys Lys Asn Gly Ala Val Ser 210 215 220Glu
Met Gln Gln Ala Ala Val Gln Ala Asp Ala Glu Lys Glu Arg Arg225 230
235 240Ser His Ala Asn Ala Asp Gly Glu Ala Asp Val Arg Thr Val Ile
Val 245 250 255Asp Ile Met Pro Pro Pro Pro Ala Met Met Arg His Ala
Asp Arg Glu 260 265 270Ala Arg Gly Gly Ala Gly Thr Gly Arg Arg Ala
Ala Ala Arg Glu Gln 275 280 285Gly Gly Ala Arg Arg Arg Glu Asp Arg
Glu Ala Leu Gly Gly Gly Gly 290 295 300Ile30541289PRTHordeum
vulgare 41Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Met Glu His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe
Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Thr Ser Leu Leu Ala Pro
Ile Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Phe Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly
Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu
Trp Ile Phe Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Val Lys Thr Gly Glu Gly Leu Leu Ile
Thr Ile Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Ile
Ile Met Tyr Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Arg Lys Ala Lys Ile Phe Thr
Ala Lys Ile Val Leu Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Ala Gly Phe Gly Leu
Ile Phe Leu Leu Thr Leu Phe Ala Phe His Gly 115 120 125Glu Thr Arg
Val Val Ser Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys
Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Gly Arg Val Ile Lys Thr145 150
155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr
Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys
Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe
Gly Met Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Met Phe Tyr Met Asn Ala
Thr Pro Val Val Ala Ser Asp 210 215 220Ala Lys Glu Gly Lys Glu Ala
Trp Lys Val Pro Ala Glu Asp His Val225 230 235 240Val Val Ile Asn
Val Gly Lys Ala Asp Lys Ser Ser Cys Ala Glu Val 245 250 255Arg Pro
Val Ala Asp Val Pro Arg Arg Cys Ala Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala 260 265
270Pro Gly Gln Gln Val Met Ala Val Asp Phe Ala Arg Ser Val Glu Val
275 280 285Val42292PRTHordeum vulgare 42Met Gly Gly Leu Ser Ala Gln
His Pro Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser
Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr
Lys Asn Lys Ser Thr Gln Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Leu Lys
Ser Asp Glu Tyr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys
Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Leu Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro 85 90
95Lys Gln Ala Arg Leu Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val
100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Thr
Ala Gly 115 120 125Glu Arg Arg Val Val Met Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val
Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile
Arg Leu Val Val Arg Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Ala 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp
Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu
Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Gly
Leu Tyr Ala Leu Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr Pro Ile Pro Ala Pro Lys 210 215
220Glu Met Asp Ala Pro Glu Ser Glu Asp Gly Ala Val Lys Ala Pro
Glu225 230 235 240His Val Val Asn Ile Ala Lys Leu Gly Thr Ala Ala
Ala Ala Ile Glu 245 250 255Leu Asn Thr Asn His Pro Val Glu Pro Pro
Pro Pro Met Lys Glu Gly 260 265 270Thr Ala Lys Ala Cys Ala Thr Gly
Glu Lys Leu Asp Lys Ala Thr His 275 280 285Val Glu Gln Val
29043314PRTHordeum vulgare 43Met Ala Ala Val Gly Ser Pro Leu Ile
Phe Ala Val Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Leu Ser Phe Leu Val Ile
Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser
Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ala Met Ala Leu Leu Ser
Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Thr Lys Asp Leu Leu
Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Thr Val Gly Cys Val Val65 70 75 80Glu Thr Ala
Tyr Leu Ala Ile Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro Lys Gln Ala 85 90 95Lys Ala
Phe Thr Ala Lys Leu Val Cys Ile Met Asn Val Ala Leu Tyr 100 105
110Gly Ala Met Val Cys Val Leu Gln Leu Leu Val Arg Asp Gly Glu Ser
115 120 125Arg Val Thr Ile Ala Gly Gly Ile Gly Ser Ala Phe Ala Leu
Ala Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ala Ile Ile Arg Gln Val Ile
Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Leu Pro Phe Trp Leu Ser
Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Ser Ala 165 170 175Val Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Met Lys Asp Phe Phe Val Ala 180 185 190Thr Pro Asn Val Leu
Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Ala Leu 195 200 205His Leu Val
Tyr Lys Asn Pro Lys Lys Lys Gly Asp Val Ser Glu Val 210 215 220Gln
Leu Pro Asp Asp Asp Glu Lys Asn Gln Leu Pro Leu His His Gln225 230
235 240Gln Gln Gln Gln Ala Gly Thr Thr Gly His Val Val Ala Pro Pro
Ile 245 250 255Ile Asp Asp Gly Glu Gln Val Val Asn Gly Ser Glu Asp
Asp Val Gly 260 265 270Gly Asn Lys Gln Gln Ser Val Ser Val Met Asp
Ile Val Leu Pro Pro 275 280 285Pro Glu Glu His Pro Thr Leu Pro Pro
Leu Asp His Pro Ala Pro Leu 290 295 300Pro Pro Met Arg Met Ala Val
Glu Val Val305 31044287PRTHordeum vulgare 44Met Ala Gly Gly Leu Phe
Ser Met Ala His Pro Trp Ala Ser Ala Phe1 5 10 15Gly Ile Leu Gly Asn
Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Thr 20 25 30Pro Thr Phe Leu
Arg Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Ser 35 40 45Ser Val Pro
Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Thr Leu Trp Ile Leu 50 55 60Tyr Ala
Leu Val Lys Thr Asn Ser Ser Pro Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala65 70 75
80Phe Gly Cys Val Val Glu Ala Phe Tyr Ile Val Leu Tyr Leu Val Tyr
85 90 95Ala Pro Arg Pro Ala Arg Met Arg Ala Leu Ala Phe Phe Leu Leu
Leu 100 105 110Asn Val Ala Ala Phe Ser Leu Ile Val Ala Val Thr Val
Phe Leu Val 115 120 125Pro Gln Pro Ser Arg Val Lys Val Leu Gly Ser
Val Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu
Ser Val Ile Phe Val Val Ile145 150 155 160Lys Thr Lys Ser Ala Glu
Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu 165 170 175Thr Leu Ser Ala
Val Ala Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr Lys Asp 180 185 190Ile Tyr
Val Thr Leu Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe Phe Gly Val Ala 195 200
205Gln Met Thr Leu Tyr Phe Cys Tyr Arg Lys Pro Asp Thr Ser Ala Leu
210 215 220Val Leu Pro Thr Gly Ile His Asp Val Ser Thr Glu Ala Ala
Ala Gln225 230 235 240Gln Glu Val Glu Leu Pro Glu Gly Thr His Pro
Ala Val Ala Met Leu 245 250 255Thr Val Ser Thr Leu Pro Met Leu Ala
Glu Leu Gln Lys Met Glu Gln 260 265 270Glu Ile Ser Ser Pro Thr Pro
Arg Lys Gly Tyr Ile Lys Ala Phe 275 280 28545288PRTVitis vinifera
45Met Ala Met Phe Thr Val Gly His His Pro Trp Val Phe Ala Ser Gly1
5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Leu Met Ser Phe Leu Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Ile
Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Thr Arg Val Ile Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe
Gln Ser 35 40 45Val Pro Tyr Val Ile Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp
Met Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Gly Leu Val Asn Thr Asn Ala Ser Phe Leu Leu Ser
Val Asn Gly Phe65 70 75 80Gly Cys Phe Ile Glu Ile Ile Tyr Ile Ser
Ile Tyr Leu Ile Phe Ala 85 90 95Pro Arg Arg Ala Arg Ile Leu Thr Leu
Arg Leu Leu Leu Leu Ile Asn 100 105 110Leu Gly Ala Phe Cys Leu Ile
Leu Ile Val Thr Asn Phe Met Val Lys 115 120 125Arg Pro His Arg Val
Lys Ala Val Gly Trp Val Cys Leu Ile Phe Ala 130 135 140Val Ser Val
Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Ala Ser Ile Leu Tyr145 150 155
160Arg Leu Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Leu Pro Leu
165 170 175Ser Ile Cys Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Gly Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Ile 180 185 190Leu Gln Met Asp Leu Tyr Ile Ala Met Pro Asn Thr
Leu Gly Phe Val 195 200 205Phe Gly Leu Ile Gln Met Ile Leu Tyr Ala
Met Tyr Arg Asn Ser Thr 210 215 220Pro Val Thr Lys Glu Pro Lys Leu
Pro Glu Gln Val Ile Asp Ile Val225 230 235 240Lys Leu Asn Thr Asn
Ser Thr Pro Glu Val His Pro Val Ser Thr Leu 245 250 255Gln Pro Asn
Cys Val Glu Asn Glu Gly Gly Asn Gly Gln Asn Ala Arg 260 265 270Lys
Glu Thr Glu His Ala Glu Glu Ser Met Gly Gly Ser Asn Arg Val 275 280
28546341PRTVitis vinifera 46Met Ala Met Leu Thr Val Pro His Met Ala
Phe Ala Phe Gly Ile Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Leu Val Tyr
Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser
Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Ser Val Ala Leu Phe Ser
Ala Met Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Phe 50 55 60Leu Lys Thr Asp Asn Gln
Ile Met Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly65 70 75 80Thr Cys Ile Glu
Ala Thr Tyr Leu Leu Val Tyr Met Ile Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Arg Thr Ala
Lys Ile Tyr Thr Ala Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Phe Asn Thr 100 105 110Gly
Val Tyr Gly Ala Ile Val Leu Ser Thr Phe Phe Leu Ser Lys Gly 115 120
125His Arg Arg Ala Lys Ile Val Gly Trp Val Cys Ala Ala Phe Ser Leu
130 135 140Cys Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Leu Val Ile
Arg Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Pro Leu Ser
Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile 165 170 175Cys Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Ile Arg Asp Phe Tyr 180 185 190Ile Ala Phe Pro Asn Ile Leu
Gly Phe Ala Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met 195 200 205Ile Leu Tyr Thr Ile
Tyr Lys Asn Ala Lys Lys Gly Val Leu Ala Glu 210 215 220Phe Lys Leu
Gln Glu Leu Pro Asn Gly Leu Val Phe Pro Thr Leu Lys225 230 235
240Lys Ala Glu Asn Thr Asp Thr Asn Pro Asn Asp Gln Pro Glu Asp Thr
245 250 255Ala Met Thr Glu Gly Gly Ala Arg Asp Lys Ala Val Glu Pro
Ser Gly 260 265 270Glu Leu Lys His Asn Ser Ser Ser Leu Val Val Arg
Phe Cys Leu Arg 275 280 285Ala Leu Arg Leu Ser Phe His His Val Ser
Phe Ser Arg Ile Ile Ala 290 295 300Tyr Thr Asn Gln Arg Asn Thr Val
Asn Thr Met Arg Val Tyr Leu Leu305 310 315 320Tyr Ile Ala Met Tyr
Glu Asn Lys Ser Ile Leu Val Phe Ile Thr Leu 325 330 335Phe Ser Gln
Ile Leu 34047293PRTOryza sativa Indica 47Met Asp His Leu Trp Ala
Ser Val Phe Gly Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Val1 5 10 15Ser Phe Leu Val Phe
Leu Ala Pro Met Pro Thr Phe Leu Arg Val Tyr 20 25 30Arg Lys Lys Ser
Thr Glu Gly Phe Ser Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val Ala 35 40 45Leu Phe Ser
Cys Thr Leu Trp Ile Leu Tyr Ala Met Val Lys Thr Asn 50 55 60Ser Ser
Pro Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly Cys Val Val Glu Ala65 70 75
80Ala Tyr Ile Ala Val Tyr Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro Arg Pro Ala Arg Leu
85 90 95Arg Ala Leu Ala Ser Phe Leu Leu Leu Asn Val Ala Ala Phe Ser
Leu 100 105 110Val Val Val Val Thr Val Ala Ala Val Val Gln Pro His
Arg Val Arg 115 120 125Val Leu Gly Ser Ile Cys Leu Ala Phe Ser Met
Ala Val Phe Val Ala 130 135 140Pro Met Ser Val Ile Met Val Val Ile
Lys Thr Lys Ser Ala Glu Phe145 150 155 160Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser
Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp 165 170 175Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Phe Thr Asn Asp Leu Tyr Val Thr Leu Pro Asn 180 185 190Val Gly
Gly Phe Phe Phe Gly Cys Val Gln Met Ala Leu Tyr Phe Lys 195 200
205Tyr Arg Lys Pro Asn Thr Ala Ala Gly Gly Val Met Ile Leu Pro Thr
210 215 220Thr Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala Val Asp Gly Ala Val Ala Glu Pro
Ala Ala225 230 235 240Ala Ala Gln Gln Leu Ala Glu Glu Leu Glu Met
Glu Leu Ala Ala Ala 245 250 255Gly Ala His Ala Val Ala Val Leu Pro
Ala Ser Ala Leu Pro Val Leu 260 265 270Ala Glu Leu His Lys Met Glu
Gln Glu Ile Gly Thr Pro Arg Lys Gly 275 280 285Ala Thr Lys Thr Val
29048284PRTPrunus persica 48Met Ala Ala Pro Asp Ala Phe Leu Leu Ala
Ser Val Phe Gly Ile Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Val Ala Phe Met Val Tyr
Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Arg Ile Phe Lys Lys Lys Ser
Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Ser Val Ala Leu Phe Ser
Ala Met Leu Met Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Phe 50 55 60Leu Lys Thr Asn Ala Phe
Met Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly Cys65 70 75 80Ile Ile Glu Thr
Ser Tyr Leu Val Met Tyr Met Ile Tyr Ala Pro Ala 85 90 95Lys Thr Arg
Ile Tyr Thr Ala Lys Leu Leu Val Leu Phe Asn Val Gly 100 105 110Val
Tyr Gly Val Ile Val Leu Ser Thr Tyr Leu Ile Pro Asn His Phe 115 120
125Leu Arg Ile Lys Val Val Gly Trp Ile Ser Val Val Phe Ser Val Cys
130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Leu Val Ile Arg
Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Ser Phe Pro Leu Ser Phe
Cys Leu Thr Leu Cys 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu
Leu Val Arg Asp Leu Phe Ile 180 185 190Ala Ala Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly
Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Met Tyr Leu Met Phe
Lys Asn Ser Lys Lys Ser Met Leu Pro Glu Phe 210 215 220Ser Leu Asn
Gln Ile Pro Asn Val Val Ala Val Asn Asp Ile Val Ala225 230 235
240Ser Asp Ser Gln Leu Lys Thr Glu Asp Thr Lys Lys Ser Ser Glu Ala
245 250 255Glu Glu Asn Gln Ser Thr Glu Ser Met Thr Asn Asp Arg Arg
Ala Gly 260 265 270Asp Ala Ala Ala Ala Glu Pro Asn Glu Ser Ile Val
275 28049293PRTPrunus persica 49Met Ala Ile Gln His Pro Leu Thr Leu
Ser Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu
Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr Thr 20 25 30Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys Thr Ala
Glu Gly Phe Gln Ala Leu Pro Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile Ala Leu Leu Ser Ser
Met Leu Tyr Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu Lys 50 55 60Glu Glu Phe Lys Glu
Asp Ala Thr Phe Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe65 70 75 80Gly Cys Val
Val Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Ser Leu Phe Leu Phe Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys
Lys Ala Arg Ile Ser Thr Leu Thr Leu Val Phe Leu Leu Asn 100 105
110Leu Phe Gly Phe Gly Leu Met Met Leu Leu Thr His Phe Leu Ala Thr
115 120 125Gly Glu Met Arg Leu Lys Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val
Phe Ser 130 135 140Leu Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Gly Val Leu Arg
Arg Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Pro Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Leu Gly Ala Val Thr Trp Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Tyr 180 185 190Asn Ile Ala Phe Pro
Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Val Leu
Tyr Ile Val Tyr Lys Asn Thr Lys Lys Val Leu Glu Glu 210 215 220Gln
Pro Lys Val Gln Glu Leu Ser Glu His Ile Ile Asp Val Val Lys225 230
235 240Ile Ser Ser Leu Val Cys Pro Glu Leu Asn Pro Val Val Leu Gln
Pro 245 250 255Thr Leu Asp Ile Thr Asn Asp Met Ile Glu Ala Val Gln
Asn Ile Ile 260 265 270Val Met Ala Glu Lys Thr Glu Glu Ala Lys Glu
Ala Met Asp Ile Asp 275 280 285Ala Ser Thr Lys Val
29050277PRTPrunus persica 50Met Gly Ala Leu Ala Asp Ser His His Pro
Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Leu
Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Gly Ile Tyr Lys Lys
Lys Ser Thr Gln Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Val Pro Tyr Leu Val Ala Leu
Phe Ser Gly Met Leu Trp Phe Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Leu Leu Lys Lys Asn
Ala Met Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe65 70 75 80Gly Thr Val Ile
Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Met Phe Ile Phe Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys Asp
Ala Arg Lys Phe Thr Leu Lys Leu Phe Gly Phe Met Asn 100 105 110Val
Gly Leu Phe Cys Ser Ile Leu Val Leu Ser His Phe Ala Val Arg 115 120
125Ser Glu Tyr Arg Val Pro Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Asn Val Ala Ile Ser
130 135 140Val Ile Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val Ala Gln Val
Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu
Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Met Trp Phe Ser Tyr
Gly Leu Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile 180 185 190Cys Ile Ala Ile Pro Asn Val
Leu Gly Phe Ile Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln 195 200 205Met Leu Leu Tyr Ala
Ile Tyr Arg Asn Arg Lys Pro Ile Glu Asp Asp 210 215 220Glu Lys Lys
Ile Pro Ala Ala Asp Gln His Val Lys Asn Val Val Gly225 230 235
240Leu Thr Thr Leu Ala Thr Ser Glu Val His Pro Val Asp Pro Pro Pro
245 250 255Arg Asp His Asp Lys Ser Val Glu Val Asp Ala Gly Ser His
Thr Ala 260 265 270Ala Ala Ser Cys Ala 27551287PRTTriticum urartu
51Met Ala Glu Gly Leu Phe Ser Met Ala His Pro Trp Ala Ser Ala Phe1
5 10 15Gly Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro
Thr 20 25 30Pro Thr Phe Leu Arg Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly
Phe Ser 35 40 45Ala Val Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu
Trp Ile Phe 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu Val Lys Thr Asn Ser Ser Pro Leu Leu
Thr Ile Asn Ala65 70 75 80Phe Gly Cys Val Val Glu Ser Phe Tyr Ile
Leu Leu Tyr Val Val Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro Arg Asn Ala Arg His Arg Ala
Leu Ala Phe Phe Leu Leu Leu 100 105 110Asp Val Ala Ala Phe Ser Leu
Ile Val Val Val Thr Val Phe Leu Val 115 120 125Pro Gln Pro Ser Arg
Val Lys Val Leu Gly Ser Val Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala
Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile Phe Val Val Ile145 150 155
160Lys Thr Lys Ser Ala Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu
165 170 175Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr
Lys Asp 180 185 190Ile Tyr Val Thr Leu Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe
Phe Gly Val Ala 195 200 205Gln Met Thr Leu Tyr Phe Cys Tyr Arg Lys
Pro Asp Thr Ser Ala Leu 210 215 220Val Leu Pro Thr Gly Ile His Asp
Val Ser Thr Glu Ala Ala Ala Gln225 230 235 240Gln Glu Val Glu Leu
Pro Glu Gly Thr His Pro Ala Ala Ala Met Leu 245 250 255Thr Val Ser
Thr Leu Pro Met Leu Ala Glu Leu Gln Lys Met Glu Gln 260 265 270Glu
Ile Ser Ser Pro Thr Pro Arg Lys Gly Tyr Ile Lys Ala Phe 275 280
28552345PRTTriticum urartu 52Met Ala Phe Leu Asn Met Glu Gln His
Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Leu
Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val Tyr Arg
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Thr Pro Tyr Leu Val Thr
Leu Phe Ser Cys Leu Leu Trp Met Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Phe Leu Lys Ser
Gly Ser Glu Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Val
Ile Glu Ser Leu Tyr Ile Ala Met Tyr Leu Val Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys
Ser Ala Arg Leu Leu Thr Ala Lys Leu Phe Ile Gly Leu Asp 100 105
110Val Gly Leu Phe Gly Leu Ile Ala Leu Val Thr Met Leu Ala Ser His
115 120 125Gly Pro Leu Arg Val Gln Val Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Val Ala 130 135 140Leu Gly Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg
Leu Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Val 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Phe
Ala Tyr Gly Ala Leu Lys Lys Asp Ile 180 185 190Phe Val Ala Met Pro
Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Val Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ala Leu
Tyr Met Ala Tyr Arg Asn Lys Lys Pro Ala Thr Val Ala 210 215 220Val
Ile Asp Thr Thr Pro Arg Gln Arg Gln Arg Cys Thr Met Pro Val225 230
235 240Gly Arg Gln Thr Arg Arg His Lys Pro Phe Ala Thr Glu Lys Asn
Arg 245 250 255Gly Ser Thr Asn Asp Ala Leu Lys Arg Gly Met Thr Pro
Ser Ala Thr 260 265 270Asp Val Lys Ser Lys Arg Trp Thr Arg Ile Phe
Thr Pro Asp Pro Trp 275 280 285His Leu Glu Gly Thr Leu Asn Asn Ala
Pro Lys Arg Glu Ala Thr Leu 290 295 300Val Gly Ala Gly Val Thr Gly
Ala Gly Ala Gln Ser Phe Arg Ser Asp305 310 315 320Pro His Lys Cys
His Gln Arg Thr His Gly Cys Gln Pro Thr Pro Arg 325 330 335Arg Glu
Val Ile Val Gly Asn Met Pro 340 34553290PRTTriticum urartu 53Met
Gly Gly Leu Ser Met Glu His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10
15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Ser Ser Leu Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr
20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Phe Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser
Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Phe
Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Val Lys Thr Gly Glu Gly Leu Leu Ile Ser Ile Asn
Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Ile Val Met Tyr
Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Arg Lys Ala Lys Ile Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile
Val Val Leu Leu Asn Ile 100 105 110Thr Gly Phe Gly Leu Ile Phe Leu
Leu Thr Leu Phe Ala Phe His Gly 115 120 125Glu Thr Arg Val Val Ser
Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Val
Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Gly Arg Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Lys
Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr Leu 165 170
175Ser Ala Ile Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr
180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly Val
Ile
Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Val Phe Tyr Met Asn Lys Thr Pro Val
Ala Ser Glu Val 210 215 220Lys Glu Gly Lys Glu Ala Trp Lys Ala Pro
Ala Glu Asp His Val Val225 230 235 240Val Ile Asn Val Gly Lys Thr
Asp Lys Gly Ser Cys Ala Glu Val Arg 245 250 255Pro Val Thr Glu Met
Ala Ser Ala Val Asp Val Pro Arg Arg Cys Ala 260 265 270Ala Glu Ala
Ala Ala Ala Pro Gly Val Asp Phe Ala Arg Ser Val Asp 275 280 285Val
Val 29054310PRTAegilops tauschii 54Met Ala Phe Leu Asn Met Glu Gln
His Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser
Leu Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val Tyr
Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Val Gln Pro 35 40 45Thr Pro Tyr Leu Val
Thr Leu Phe Ser Cys Leu Leu Trp Met Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Phe Leu Lys
Ser Gly Ser Glu Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys
Val Ile Glu Ser Leu Tyr Ile Ala Met Tyr Leu Val Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro
Lys Ser Ala Arg Leu Leu Thr Ala Lys Leu Phe Ile Gly Leu Asp 100 105
110Val Gly Leu Phe Gly Leu Ile Ala Leu Val Thr Met Leu Ala Ser Tyr
115 120 125Gly Pro Leu Arg Val Gln Val Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Val Ala 130 135 140Leu Gly Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg
Leu Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Val 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Phe
Ala Tyr Gly Ala Leu Lys Lys Asp Ile 180 185 190Phe Val Ala Met Pro
Asn Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Val Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ala Leu
Tyr Met Ala Tyr Arg Asn Lys Lys Pro Ala Thr Val Val 210 215 220Leu
Val His Glu Glu Met Lys Leu Pro Glu His Val Lys Glu Val Ala225 230
235 240Gly Gly Ala Lys Pro Gln Gly Gly Ala Pro Thr Glu Gly Arg Ile
Ser 245 250 255Cys Gly Ala Glu Val His Pro Ile Asp Val Leu Pro Ala
Val Ala Val 260 265 270Asp Glu Gln Ala Ala Gly Ala Ala Asp Glu Asp
Val Ile Arg Asp Asp 275 280 285Gln Asn Met Leu Arg Pro Glu Gln Pro
Val Val Ile Lys Pro Asp Val 290 295 300Ala Ile Val Val Gln Ala305
31055285PRTAegilops tauschii 55Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Leu Glu His Pro
Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Thr
Ser Leu Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Phe Lys Ser
Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu
Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Phe Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Val Lys Thr Gly
Glu Gly Leu Leu Ile Ser Ile Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile
Glu Thr Val Tyr Ile Val Met Tyr Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Arg Lys
Ala Lys Ile Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Val Val Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105
110Ala Gly Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Phe Ala Phe His Gly
115 120 125Glu Thr Arg Val Ile Ser Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe
Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Gly Arg
Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser
Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu
Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn
Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly Met Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr
Met Phe Tyr Met Asn Ala Thr Pro Val Val Ser Asp Leu 210 215 220Lys
Glu Gly Lys Glu Gly Leu Lys Met Ser Ala Glu Glu His Val Val225 230
235 240Val Ile Asn Val Gly Lys Ser Glu Lys Ser Ser Gly Ala Val Val
Arg 245 250 255Pro Val Thr Glu Met Val Lys Ala Val Pro Ala Ala Pro
Gly Gln Gln 260 265 270Val Met Ala Leu Asp Ser Ala Arg Ser Val Asp
Val Val 275 280 28556287PRTAegilops tauschii 56Met Gly Gly Leu Ser
Leu Gln His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val
Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg
Ile Tyr Arg Ser Lys Ser Thr Gln Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr
Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu
Leu Lys Ser Asp Glu Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Ala Gly65 70 75
80Cys Ile Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Met Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro
85 90 95Lys Gln Ala Lys Ile Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn
Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu
Ala Gly Gly 115 120 125Glu Lys Arg Val Val Met Leu Gly Trp Val Cys
Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile
Ile Arg Leu Val Val Arg Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met
Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Val 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val
Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala
Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Ile Gln Met 195 200
205Gly Leu Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Cys Asn Ala Thr Pro Thr Leu Ala Pro Lys
210 215 220Glu Val Asp Arg Pro Leu Pro Glu His Val Ile Asn Val Ala
Lys Leu225 230 235 240Gly Pro Thr Ala Thr Ile Glu Leu Asn Met Pro
Ala Ala Val Gln Pro 245 250 255Pro Thr Lys Glu Asn Ile Val Ala Cys
Ala Ser Gly Glu Thr Lys Glu 260 265 270Ile Ser Val Glu Lys Val Asp
Met Ala Thr Asn Val Glu His Val 275 280 28557293PRTAegilops
tauschii 57Met Gly Gly Leu Ser Leu Glu His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe
Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro
Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Arg Ser Lys Ser Thr Gln Gly
Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu
Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Leu Lys Ser Asp Glu Leu Leu Leu Ile
Thr Ile Asn Ser Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile
Ile Met Tyr Leu Thr Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Gln Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr
Ala Lys Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Leu
Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Ala Gly Gly 115 120 125Glu Lys Arg
Val Val Met Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser
Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile Arg Leu Val Val Arg Thr145 150
155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr
Val 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys
Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ala Phe
Gly Val Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Gly Leu Tyr Ala Leu Tyr Cys Asn Ala
Met Pro Arg Gln Ala Pro Lys 210 215 220Glu Val Asp Asp Pro Met Ser
Asp His Gly Ala Ala Val Lys Ala Pro225 230 235 240Glu His Val Val
Asn Ile Ser Lys Leu Ser Pro Ala Ala Gly Ile Glu 245 250 255Leu Asn
Thr Thr Val Asn Ala Glu Pro Pro Leu Lys Ser Leu Gly Val 260 265
270Ala Cys Ala Asn Glu Glu Thr Ile Gly Val Ser Val Asp Lys Ala Thr
275 280 285His Ile Glu Gln Val 29058290PRTAegilops tauschii 58Met
Gly Gly Leu Ser Met Glu His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10
15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Ser Ser Leu Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr
20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Phe Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser
Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Phe
Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Val Lys Thr Gly Glu Gly Leu Leu Ile Ser Ile Asn
Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Ile Val Met Tyr
Leu Val Tyr Ala Asp 85 90 95Arg Lys Ala Lys Ile Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile
Val Val Leu Leu Asn Ile 100 105 110Ala Gly Phe Gly Leu Ile Phe Leu
Leu Thr Leu Phe Ala Phe His Gly 115 120 125Glu Thr Arg Val Val Thr
Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Val
Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Gly Arg Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Lys
Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr Leu 165 170
175Ser Ala Ile Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr
180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly Val Ile
Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Val Phe Tyr Met Asn Lys Thr Pro Val
Ala Ser Gln Val 210 215 220Lys Glu Gly Lys Glu Ala Trp Lys Ala Pro
Ala Glu Asp His Val Val225 230 235 240Val Ile Asn Val Gly Lys Ala
Asp Lys Ser Ser Cys Ala Glu Val Arg 245 250 255Pro Val Thr Glu Met
Ala Gly Ala Val Asp Val Pro Arg Arg Cys Ala 260 265 270Ala Glu Ala
Ala Ala Ala Pro Gly Val Asp Phe Ala Arg Ser Val Asn 275 280 285Val
Val 29059237PRTAegilops tauschii 59Met Gly Ala Val Gly Ser Pro Leu
Val Phe Ala Val Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Leu Ser Phe Leu Val
Ile Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val Tyr Lys Arg Lys
Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ala Met Ala Leu Leu
Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Thr Lys Asp Leu
Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Thr Val Gly Cys Val Val65 70 75 80Glu Ser
Ala Tyr Leu Ala Ile Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro Lys Gln Ala 85 90 95Arg
Thr Phe Thr Ala Lys Leu Val Cys Ile Met Asn Val Ala Leu Tyr 100 105
110Gly Ala Met Val Cys Val Leu Gln Leu Leu Val Lys Asp Gly Glu Ser
115 120 125Arg Val Thr Ile Ala Gly Gly Ile Gly Ser Ala Phe Ala Leu
Ala Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ala Ile Ile Arg Gln Val Ile
Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Leu Pro Phe Trp Leu Ser
Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Ser Ala 165 170 175Val Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Met Lys Asp Phe Phe Val Ala 180 185 190Thr Pro Asn Val Leu
Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Ser Leu 195 200 205His Leu Val
Tyr Lys Asn Pro Lys Lys Lys Gly Ala Val Ser Glu Val 210 215 220Gln
Tyr Ser Ile Gly Leu Leu Val Trp Ala Arg Leu Ile225 230
23560275PRTAegilops tauschii 60Met Ala Gly Gly Leu Phe Asp Met Ser
His Pro Ala Ser Ala Leu Ala1 5 10 15Gly Ile Ala Gly Asn Ile Val Ser
Phe Phe Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Met 20 25 30Ala Thr Phe Leu Gln Ile Tyr
Arg Lys Lys Thr Thr Gly Gly Phe Ser 35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Ser Leu Leu Ile Phe 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu Leu Lys
Thr Asp Ser Pro Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ser65 70 75 80Phe Gly Cys
Cys Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Ile Val Ala Tyr Leu Val Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro
Pro Arg Ala Arg Leu Arg Thr Leu Ala Tyr Phe Phe Val Leu 100 105
110Asp Val Ala Ala Phe Gly Leu Val Leu Val Val Thr Met Tyr Ala Phe
115 120 125Ala Pro Ala His Arg Val Lys Phe Leu Gly Ser Val Cys Leu
Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile
Val Lys Val Ile145 150 155 160Lys Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Leu Pro
Val Gly Leu Ser Phe Cys Leu 165 170 175Val Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp
Phe Cys Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr Lys Asp 180 185 190Pro Phe Val Met Tyr
Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe Phe Ser Cys Val 195 200 205Gln Ile Gly
Leu Tyr Cys Trp Tyr Arg Lys Pro Ser Asn Ala Val Leu 210 215 220Pro
Thr Thr Thr Ala Asp Ala Gly Asn Gly Asn Gly Gly Pro Thr Pro225 230
235 240Ala Ala Gly Ala Glu Gln Gln Thr Val Ile Asp Val Lys Asp Ala
Ala 245 250 255Arg Ala Ala Glu Val Asp Gln Pro Glu Val Ile Glu Ile
Val Pro Ala 260 265 270Pro Ala Val 27561290PRTCapsella rubella
61Met Ala Ile Ser Gln Ala Val Leu Ala Thr Val Phe Gly Ile Leu Gly1
5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Phe Val Cys Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr Phe
Ile 20 25 30Arg Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Val
Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Ile Ser Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr
Ala Met Ile 50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Val Met Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser
Phe Ala Phe Val65 70 75 80Ile Gln Ile Val Tyr Ile Ser Leu Phe Phe
Phe Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Asp Lys Ile Leu Thr Val Lys Phe Val
Leu Phe Val Asp Val Phe Ala 100 105 110Phe Gly Leu Ile Phe Phe Ser
Thr Tyr Phe Pro Ile His Gly Asn Lys 115 120 125Arg Val Gln Val Leu
Gly Tyr Ile Cys Met Val Phe Ala Leu Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala
Pro Leu Gly Ile Ile Arg Lys Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155
160Ala Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Gly Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala
165 170 175Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Lys Asn
Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Val Leu
Gln Met Val Leu 195 200 205Phe Val Ile Tyr Lys Lys Pro Gly Thr Lys
Val Leu Glu Pro Ser Val 210 215 220Ile Lys Leu Gln Asp Ile Ser Glu
His Val Val Asp Val Val Arg Leu225 230 235 240Ser Ser Met Val Cys
Asn Ser Gln Met Arg Thr Leu Val Pro Gln Asp 245 250 255Ser Ala Asp
Met Glu Asp Thr Ile Asp Ile Glu Glu Lys Met Lys Gly 260 265 270Asp
Ile Glu Lys Asn Lys Asp Asn Asn Lys Glu Ala Phe Leu Ile Ser 275 280
285Lys Asn 29062292PRTCapsella rubella 62Met Ala Leu Thr His Asn
Val Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Met Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe
Val Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Ile 20 25 30Arg Ile Cys Lys
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu Ser Ala
Ile Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Met Gln 50 55 60Lys Asp
Gly Ser Gly Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala Val Gly Cys65 70 75
80Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Leu Phe Val Thr Tyr Ala Asn Lys
85
90 95Lys Thr Arg Ile Ser Thr Leu Lys Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Asn Phe
Leu 100 105 110Gly Phe Ala Ala Ile Val Leu Val Cys Glu Leu Leu Thr
Lys Gly Ser 115 120 125Thr Arg Ala Lys Val Leu Gly Gly Ile Cys Val
Gly Phe Ser Val Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met
Arg Leu Val Val Arg Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser 165 170 175Ala Val Thr Trp
Leu Phe Tyr Gly Leu Ala Ile Lys Asp Phe Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu
Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Ala Phe Leu Gly Ala Val Gln Met Ile 195 200
205Leu Tyr Ile Val Phe Lys Tyr Tyr Met Thr Pro Val Ala Glu Lys Thr
210 215 220Asp Lys Ser Lys Ala Val Ser Ser Asp His Ser Ile Asp Ile
Ala Lys225 230 235 240Leu Thr Thr Val Ile Pro Gly Ser Thr Val His
Glu Pro Pro Ala Val 245 250 255His Asn Val Pro Glu Thr Gln Ile Gln
Val Thr Glu Val Lys Ser Gln 260 265 270Asn Met Thr Glu Pro Asn Asp
Gln Thr Thr Ser Lys Asp Val Gln Asn 275 280 285Gln Asn Gln Val
29063278PRTCapsella rubella 63Met Val Leu Ala His Asn Val Leu Ala
Val Thr Phe Gly Val Met Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val Phe
Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Val 20 25 30Arg Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys Ser
Thr Glu Gly Phe Glu Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Ser Ala Leu Phe Ser
Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Met Gln 50 55 60Lys Asp Gly Ala Gly
Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala Val Gly Cys65 70 75 80Phe Ile Glu
Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ile Leu Phe Leu Thr Tyr Ala Asn Lys 85 90 95Lys Ala
Arg Ile Ser Thr Leu Lys Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Asn Phe Leu 100 105
110Gly Phe Ala Ala Ile Ile Leu Val Cys Glu Leu Leu Thr Lys Gly Ser
115 120 125Asn Arg Glu Lys Val Leu Gly Gly Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser
Val Cys 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Val Val
Ile Arg Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu
Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser 165 170 175Ala Ile Thr Trp Leu Phe Tyr
Gly Leu Ala Ile Lys Asp Phe Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile
Met Gly Ala Phe Leu Gly Ala Val Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Leu Tyr Val
Ile Phe Lys Tyr Tyr Lys Ser Pro Val Val Val Asp Glu 210 215 220Thr
Glu Lys Pro Lys Thr Val Ser Ala Asp His Ser Ile Asn Met Ala225 230
235 240Lys Leu Ser Ser Thr Pro Ala Ser Gly Glu Leu Thr Val His Ser
Ser 245 250 255Gln Thr Asn Pro Val Gln Thr Gly Ala Gly Asp Leu Glu
Asp Gln Met 260 265 270Asp Lys Lys Ile Ser Asn 27564287PRTCapsella
rubella 64Met Ala Leu Phe Asp Thr His Asn Thr Trp Ala Phe Val Phe
Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser Phe Ala Val Phe Leu Ser Pro
Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys Thr Thr Glu Gly
Phe Gln Ser Ile 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu
Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Thr Gln Lys Lys Asp Val Phe Leu Leu Val
Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Phe Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile
Ser Ile Phe Leu Ala Phe Ala Thr 85 90 95Lys Asn Ala Arg Met Leu Thr
Val Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Met Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Gly Phe Cys Ala
Ile Leu Leu Leu Cys Gln Phe Leu Ala Lys Gly 115 120 125Ala Thr Arg
Ala Lys Ile Ile Gly Gly Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys
Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg Thr Val Ile Lys Thr145 150
155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr
Ile 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Leu Leu Tyr Gly Leu Ala Leu Lys
Asp Ile Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Phe Pro Asn Val Ile Gly Phe Ala Leu
Gly Ala Leu Gln Met 195 200 205Ile Leu Tyr Val Val Tyr Lys Tyr Cys
Lys Thr Ser Ser Asp Leu Val 210 215 220Glu Lys Glu Leu Glu Asn Ala
Lys Leu Pro Glu Val Ser Ile Asp Met225 230 235 240Leu Lys Leu Gly
Gly Ala Ala Glu Pro Ala Cys Gly Ile Thr Val Val 245 250 255Arg Ser
Val Asn Met Cys Asn Cys Asn Asp Arg Arg Val Glu Ile Glu 260 265
270Asn Gly His Gly Leu Val Arg Asn Ser Ala Thr Ala Ala Ala Thr 275
280 28565286PRTCapsella rubella 65Met Gly Val Val Met Asn His His
Leu Leu Thr Ile Ile Phe Gly Ile1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Ala Val Ser Phe
Leu Val Leu Val Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Leu 35 40 45Pro Tyr Gln Val Ser
Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys Lys
Asn Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val
Val Gln Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ala Met Phe Leu Ala Tyr Ala Thr 85 90 95Arg
Asp Lys Arg Ile Ser Ala Met Lys Leu Phe Ile Ala Ile Asn Val 100 105
110Val Phe Phe Ser Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe Val Val Lys Thr
115 120 125Pro Thr Leu Gln Val Ser Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Ile Ser 130 135 140Val Ala Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Met Ile Val Ala
Arg Val Val Lys145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe
Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Ile Ser Ala Val Met Trp Phe
Gly Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu Asn Asp Ile 180 185 190Cys Ile Ala Ile Pro
Asn Val Val Gly Phe Val Leu Gly Met Leu Gln 195 200 205Met Val Leu
Tyr Cys Val Tyr Arg Asn Ala Ser Glu Lys Pro Glu Ile 210 215 220Glu
Lys Lys Ile Asn Leu Ser Glu Gln Gln Leu Lys Ser Ile Val Val225 230
235 240Met Ser Pro Leu Gly Val Ser Glu Val His Pro Val Val Thr Ala
Ser 245 250 255Val Gly Pro Pro Ser Asp Ala Val His His Glu Glu Pro
Ser Asn Gly 260 265 270Asn Arg Lys Cys His Val Glu Thr Ser Arg Pro
Glu Asn Val 275 280 28566291PRTCapsella rubella 66Met Thr Leu Phe
Asn Thr Glu Asn Thr Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn
Val Ile Ser Phe Ala Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr
Arg Ile Trp Lys Lys Lys Thr Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile 35 40 45Pro
Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Thr Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55
60Thr Gln Lys Lys Asp Val Phe Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly65
70 75 80Cys Phe Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ser Met Phe Leu Ala Tyr Ala
Pro 85 90 95Lys Pro Ala Arg Met Leu Thr Val Lys Ile Leu Leu Leu Met
Asn Phe 100 105 110Gly Gly Phe Cys Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu Cys Gln Leu
Leu Leu Lys Gly 115 120 125Ala Thr Arg Ala Lys Ile Ile Gly Gly Ile
Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser
Ile Ile Arg Thr Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Tyr
Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Thr Ile 165 170 175Ser Ala Ile
Ile Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Ala Leu Lys Asp Ile Tyr 180 185 190Val
Ala Phe Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ala Leu Gly Ala Leu Gln Met 195 200
205Ile Leu Tyr Val Val Tyr Lys Tyr Cys Lys Thr Ser Pro His Pro His
210 215 220Leu Gly Glu Lys Glu Val Glu Ala Ala Lys Leu Pro Glu Val
Val Thr225 230 235 240Leu Asp Met Leu Lys Leu Gly Ala Val Ala Ser
Pro Asp Pro Gly His 245 250 255Val Val Arg Gln Cys Asn Lys Cys Thr
Cys Gly Asn Asp Arg Arg Val 260 265 270Ala Glu Ile Glu Asp Gly Arg
Gln Thr Pro Arg Asn Ser Ser Ser Ala 275 280 285Ala Ala Thr
29067260PRTCapsella rubella 67Met Val Phe Ile Lys Val His Gln Leu
Ala Phe Phe Phe Gly Leu Met1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Gly Val
Phe Leu Ser Pro Val Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Gly Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Ser Ser Lys Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Ile Cys Ala Leu Ala
Ser Ala Thr Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Gly Ile 50 55 60Met Lys Thr His Ala
Tyr Leu Ile Ile Ser Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Phe Ile Glu
Ile Thr Tyr Leu Phe Leu Tyr Ile Phe Tyr Ala Pro Arg 85 90 95Glu Ala
Arg Ile Phe Thr Leu Lys Leu Ile Val Ile Cys Asn Ile Gly 100 105
110Gly Leu Gly Leu Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Asn Leu Leu Val Pro Lys Pro
115 120 125His Arg Val Ser Thr Val Gly Trp Val Cys Ala Ala Tyr Ser
Leu Ala 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ser Pro Leu Ser Val Met Arg Lys Val
Ile Lys Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Leu Leu
Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Phe Ile 180 185 190Ala Met Pro Asn Ile
Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Val Ala Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Leu Tyr Met
Met Tyr Gln Gly Ser Thr Lys Thr Asp Leu Pro Thr Glu 210 215 220His
Gln Leu Gly Asn Lys Thr Asp Val Asn Glu Ile Ala Val Val Ala225 230
235 240Val Glu Leu Pro Asp Ala Arg Leu Asp Asn Val Glu Gly Ser Ala
Arg 245 250 255Pro Ala Met Lys 26068344PRTZea mays 68Met Ala Gly
Leu Ser Leu Gln His Pro Met Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly
Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe
Cys Arg Ile Tyr Arg Asn Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40
45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala
50 55 60Leu Leu Lys Ser Asn Glu Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Ala
Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Ala Thr Tyr Leu Leu
Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Asn Lys Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Leu Leu
Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr
Leu Leu Leu Ser Ala Gly 115 120 125Pro His Arg Val Val Val Leu Gly
Trp Val Cys Val Ala Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro
Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg Gln Val Val Arg Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val
Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Ser Leu Thr Ala 165 170 175Ser
Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185
190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly Val Val Gln Met
195 200 205Gly Met Tyr Ala Leu Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr Pro Arg Val Pro
Ala Ala 210 215 220Lys Glu Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala Asp Asp Gly Asn Thr
Phe Asn Phe Lys225 230 235 240Ala Pro Gly Glu His Val Val Thr Ile
Ala Lys Leu Thr Ala Ala Ala 245 250 255Pro Ala Thr Ala Ala Glu Leu
Ile Ile Lys Ala Arg Asp Asp Ala Gln 260 265 270His Pro Pro Glu Glu
Glu Ala Ala Ala Ala Lys Ala Ala Pro Ala Lys 275 280 285Ser Lys Leu
Leu Ile Pro Leu Pro Glu His Ala Tyr Ala Cys Met Cys 290 295 300Ile
Ile Arg Ser Gly Ser His His Lys Leu Gly Arg Ala Cys Leu Leu305 310
315 320Gly Thr Ser Thr Arg Pro Pro Ala Cys Leu Pro Ala Arg Met Ile
Gln 325 330 335Ser Ser Cys Tyr Ile Arg Lys Gly 34069295PRTZea mays
69Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Leu Gln His Pro Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly Leu1
5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Phe Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro
Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln
Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile
Phe Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys Ser Asn Glu Thr Phe Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Val Val Met
Tyr Phe Val Tyr Ala Thr 85 90 95Lys Lys Gly Arg Met Phe Thr Ala Lys
Ile Met Leu Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Ala Phe Gly Ala Ile Leu
Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Phe Lys Gly 115 120 125Asp Lys Arg Val Val
Met Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe
Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Arg Val Ile Gln Thr145 150 155
160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu
165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp
Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly
Val Val Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Val Val Tyr Met Asn Lys Thr
Pro Leu Pro Val Ala Asp 210 215 220Gly Lys Ala Ala Gly Lys Leu Pro
Ser Ala Ala Asp Glu His Val Val225 230 235 240Val Asn Val Thr Lys
Leu Ser Pro Gly Arg Leu Pro Pro Val Thr Gln 245 250 255Met Ala Ala
Val Pro Thr Lys Ser Cys Ala Thr Glu Ala Ala Ala Pro 260 265 270Ala
Thr Leu Pro Ser Arg Asp Val Val Asp Val Leu Val Asn Arg His 275 280
285Ser Pro Ala Val His Val Thr 290 29570301PRTZea mays 70Met Ala
Gly Leu Ser Leu Glu His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu
Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Phe Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr 20 25
30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val
35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Phe Tyr
Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys Ser Asn Glu Thr Phe Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala
Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Met Tyr Phe
Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Met
Ala Leu Leu Asn Gly 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Val Ile Leu Leu Leu
Thr Leu Leu Leu Phe Lys Gly 115 120 125Ser Lys Arg Val Val Leu Leu
Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Val Ala
Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Arg Val Ile Gln Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser
Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu 165 170
175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr
180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Val Val
Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Val Phe Tyr Met Asn Lys Thr Pro Val
Ala Ala Ala Val 210
215 220Gly Lys Asp Ala Gly Lys Leu Pro Ser Ala Ala Asp Glu His Val
Leu225 230 235 240Val Asn Ile Ala Lys Leu Asn Pro Ala Leu Pro Glu
Arg Thr Ser Gly 245 250 255Met His Pro Val Thr Gln Met Ala Ala Val
Pro Ala Arg Ser Cys Ala 260 265 270Ala Glu Ala Ile Ala Pro Ala Met
Leu Pro Asn Arg Asp Val Val Asp 275 280 285Val Phe Val Ser Arg His
Ser Pro Ala Val His Val Val 290 295 30071310PRTZea mays 71Met Ala
Gly Gly Leu Phe Ser Met Ala His Pro Ala Val Thr Leu Ser1 5 10 15Gly
Ile Ala Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val 20 25
30Ala Thr Phe Leu Gln Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Gly Gly Phe Ser
35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Val Leu Trp Ile
Phe 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu Val Lys Thr Asn Ser Arg Pro Leu Leu Thr Ile
Asn Ala65 70 75 80Phe Gly Cys Gly Val Glu Ala Ala Tyr Ile Val Leu
Tyr Leu Ala Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro Arg Arg Ala Arg Leu Arg Thr Leu Ala
Tyr Phe Phe Leu Leu 100 105 110Asp Val Ala Ala Phe Ala Leu Val Val
Ala Val Thr Leu Phe Ala Val 115 120 125Arg Glu Pro His Arg Val Lys
Phe Leu Gly Ser Val Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala Val Phe
Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Val Lys Val Val145 150 155 160Lys Thr
Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Leu Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Cys Leu 165 170
175Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp Phe Cys Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr Lys Asp
180 185 190Pro Phe Val Met Tyr Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe Phe Ser
Cys Val 195 200 205Gln Met Gly Leu Tyr Phe Trp Tyr Arg Lys Pro Arg
Pro Ala Ala Lys 210 215 220Asn Asn Ala Val Leu Pro Thr Thr Thr Asp
Gly Gly Asn Ala Val Gln225 230 235 240Val Gln Gly Gln Val Ile Glu
Leu Ala Pro Asn Thr Val Ala Ile Leu 245 250 255Ser Val Ser Pro Ile
Pro Ile Val Gly Val His Lys Ile Glu Val Val 260 265 270Glu Gln Gln
His Lys Glu Ala Ala Val Ala Ala Glu Thr Arg Arg Met 275 280 285Ala
Ala Ala Asn Pro Asp Gly Ala Met Pro Glu Val Ile Glu Ile Val 290 295
300Pro Ala Ala Ala Ala Val305 31072307PRTZea mays 72Met Ala Phe Leu
Asn Met Glu Gln Gln Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly
Asn Ile Val Ser Leu Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe
Tyr Arg Val Tyr Arg Asn Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Thr
Pro Tyr Val Val Thr Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Ile Leu Tyr 50 55
60Ala Leu Leu Lys Pro Gly Ala Glu Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Gly Val65
70 75 80Gly Cys Val Val Glu Thr Val Tyr Leu Ala Met Tyr Leu Val Tyr
Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys Ala Ala Arg Val Leu Ala Ala Lys Met Leu Leu Gly
Leu Asn 100 105 110Val Ala Val Phe Gly Leu Val Ala Leu Val Thr Met
Leu Leu Ser Asp 115 120 125Ala Gly Leu Arg Val His Val Leu Gly Trp
Ile Cys Val Ser Val Ser 130 135 140Leu Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu
Ser Ile Met Arg Gln Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu
Phe Met Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Val 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala
Val Val Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Ala Leu Lys Lys Asp Val 180 185 190Phe
Val Ala Phe Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln 195 200
205Met Ala Leu Tyr Met Ala Tyr Ser Arg Asn Arg Lys Pro Ala Ala Ala
210 215 220Leu Val Ile Leu Pro Glu Gln Ser Lys Glu Glu Ala Ala Glu
Gly Lys225 230 235 240Ala Ser Cys Gly Gly Ala Glu Val His Pro Ile
Asp Ile Ala Glu Val 245 250 255His Asp Leu Gln Ala Val Val Val Asp
Val Asp Val Glu Pro Val Thr 260 265 270Tyr Ala Ala Ala Ser Gly Met
Val Asp Gly Ser Val Gly Arg Pro Arg 275 280 285Ala Pro Glu Gln Leu
Val Ile Lys Pro Asp Met Val Thr Val Ile Ala 290 295 300Ala Glu
Ala30573260PRTGlycine max 73Met Ala Ile Asn His Glu Thr Trp Ala Phe
Val Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Val Phe Leu
Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr
Glu Glu Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser
Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Val 50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Ser Leu
Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu Thr
Ile Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Leu Ile Tyr Ala Pro Ser 85 90 95Lys Thr Arg
Leu Trp Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Met Leu Asn Val Phe 100 105 110Gly
Phe Gly Ala Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Tyr Leu Thr Thr Gly Ser 115 120
125Lys Arg Leu Thr Val Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Asn Ile Ser
130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Cys Ile Ile Lys Arg Val Ile Lys
Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe
Phe Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu
Leu Leu Lys Asp Tyr Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly
Phe Leu Phe Ser Ile Ile Gln Met Val 195 200 205Leu Tyr Leu Ile Tyr
Arg Asn Ala Lys Thr Pro Asp Leu Pro Met Lys 210 215 220Leu Gln Glu
Leu Asn Ser His Thr Ile Asp Val Gly Lys Leu Ser Arg225 230 235
240Met Glu Pro Ser Glu Pro Asn His Val Thr Lys Asn Gly Thr Leu Thr
245 250 255Glu Arg Glu Ile 26074268PRTGlycine max 74Met Ala Ile Ser
His Ser Thr Leu Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Met Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile
Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Ile Thr Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Ile
Phe Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu
Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55
60Lys Lys Asp Ala Met Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys Val65
70 75 80Ile Glu Val Ile Tyr Ile Ile Leu Tyr Ile Thr Tyr Ala Thr Arg
Asp 85 90 95Ala Arg Asn Leu Thr Leu Lys Leu Phe Phe Ala Met Asn Val
Gly Ala 100 105 110Phe Ala Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe Ala Val
His Gly Ser Leu 115 120 125Arg Val Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val
Ser Leu Ser Ile Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val
Ala Gln Val Val Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Asn Leu Ser Phe Thr Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Ile Met Trp
Phe Gly Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile Cys Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu
Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ala Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln Met Leu Leu 195 200
205Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn Gly Asn Lys Lys Val Asp Lys Ile Met Glu
210 215 220Lys Lys Ala Pro Leu Glu Pro Leu Lys Thr Val Val Ile Glu
Thr Gly225 230 235 240Leu Glu Glu Lys Gln Gln Gly Lys Lys Ser Lys
Glu Asn Ser Glu Glu 245 250 255Lys Glu Lys Ser Asp Glu Pro Asn Asp
Cys Ala Val 260 26575257PRTGlycine max 75Met Thr Met His Arg Glu
Ser Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Val Met Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe
Gly Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala
Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Val 50 55 60Lys Arg
Glu Ala Ala Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Ile65 70 75
80Val Val Glu Ser Ile Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Leu Leu Tyr Ala Pro Arg
85 90 95Lys Pro Arg Leu Thr Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val
Phe 100 105 110Gly Phe Gly Ala Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Tyr Leu Ser
Lys Gly Ala 115 120 125Lys Arg Leu Ala Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu
Val Phe Asn Ile Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Phe Ile Ile
Arg Arg Val Ile Lys Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro
Phe Thr Leu Ser Met Phe Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp
Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Arg Asp Tyr Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu
Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Gly 195 200
205Met Tyr Leu Met Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr Pro Val Ala Leu Glu Glu Pro
210 215 220Val Lys Ala Gln Glu Leu Asn Gly His Ile Ile Asp Val Gly
Lys Met225 230 235 240Gly Thr Met Glu Pro Asn His Ala Ala Thr Ala
Gly Ala Val Gly Lys 245 250 255Val76258PRTGlycine max 76Met Ala Ile
Asn His Glu Thr Trp Ala Phe Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val
Ile Ser Phe Met Val Phe Leu Ala Ser Leu Pro Thr Leu Tyr 20 25 30Gln
Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Asp Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40
45Ile Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Val
50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Ser Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly
Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Leu Ile Tyr
Ala Pro Ser 85 90 95Lys Thr Arg Leu Trp Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Met
Leu Asn Val Phe 100 105 110Gly Phe Gly Ala Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu
Tyr Leu Thr Thr Gly Ser 115 120 125Lys Arg Leu Ser Val Ile Gly Trp
Ile Cys Leu Val Leu Asn Ile Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu
Cys Ile Met Lys Arg Val Ile Lys Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu
Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala
Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Tyr Tyr Ile 180 185
190Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val
195 200 205Leu Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Arg Asn Ala Lys Pro Gln Gly Leu Glu
Glu Pro 210 215 220Thr Lys Val Gln Glu Leu Asn Gly His Ile Ile Asp
Val Val Lys Pro225 230 235 240Asn His Val Thr Lys Asn Gly Pro Val
Pro Val Ile Glu Thr Ala Ser 245 250 255Asn Val77289PRTVitis
vinifera 77Met Ala Met Ala Met Ala Asn His His Thr Leu Gly Leu Ile
Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Tyr Phe Ala
Pro Ala Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser Ala Glu
Gly Phe His Ser 35 40 45Leu Pro Tyr Ile Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met
Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Leu Leu Lys Lys Asp Ala Phe Leu Leu
Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe65 70 75 80Gly Cys Ala Ile Glu Ser Phe Tyr
Ile Leu Leu Tyr Phe Phe Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Met Gln Ala Lys Lys Gln
Thr Leu Lys Val Val Ile Ser Leu Asn 100 105 110Val Gly Val Phe Ser
Ile Leu Val Val Leu Ile Gln Phe Leu Leu Lys 115 120 125Gly Ser Asn
Arg Ile Asn Val Phe Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala Ser Phe Ser 130 135 140Val
Ala Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val Ala Lys Val Ile Arg145 150
155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu
Thr 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Ile Met Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Leu Leu Lys
Asn Asp Pro 180 185 190Cys Val Ala Ile Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Val Ile
Leu Gly Leu Val Gln 195 200 205Met Val Leu Tyr Gly Phe Tyr Arg Asn
Ala Gly Lys Glu Lys Met Glu 210 215 220Lys Lys Leu Pro Glu His Ile
Ile Asp Met Val Met Leu Ser Thr Leu225 230 235 240Gly Thr Ser Asp
Ile His Pro Ile Gly Ala Gln Gln Asn Gly Ile Lys 245 250 255Lys Ser
Gly Ser Glu Asp Val Lys Asp Asp Glu Glu Thr Gly Asn Arg 260 265
270Glu Lys Ser Thr Glu Asn Ser Gly Glu Leu Gln Pro Asn Gly Ser Thr
275 280 285Val78278PRTVitis vinifera 78Met Ala Val Val Thr Val Lys
Gln Leu Ala Phe Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Leu Val Ser Phe
Met Val Tyr Leu Ser Pro Val Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Phe Lys Ile Tyr Lys
Arg Lys Thr Ser Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ala Leu Pro 35 40 45Tyr Ser Val Gly
Leu Leu Cys Ala Ser Leu Phe Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu 50 55 60Leu Gln Ser
Gly Lys Phe Leu Ile Leu Ser Ile Asn Thr Ile Gly Ser65 70 75 80Thr
Ile Gln Ala Thr Tyr Leu Val Leu Phe Ile Ile Tyr Ser Pro Arg 85 90
95Ala Gly Lys Val Ala Thr Leu Lys Met Ile Leu Ile Leu Asn Val Ala
100 105 110Ser Leu Gly Leu Val Leu Leu Leu Thr Thr Leu Phe Ser Lys
Gly Lys 115 120 125Thr Arg Ile Gln Val Val Gly Trp Ile Ser Ala Gly
Val Asn Ile Gly 130 135 140Thr Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Lys
Arg Val Ile Glu Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe
Asn Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Cys 165 170 175Ala Thr Met Trp Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Ile Phe Val Arg Asp Phe Phe Ile 180 185 190Ala Ile Pro
Asn Val Val Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met Phe 195 200 205Leu
Tyr Ile Ile Tyr Lys Tyr Met Met Lys Ser Asp Glu Thr Thr Leu 210 215
220Glu Gln Leu Glu Glu Thr Thr Glu Arg Pro Leu Tyr Val Pro Thr
Ala225 230 235 240Asn His Glu Pro Ser Gly Gln Glu Leu Lys Ala Val
Thr Ile Thr Ser 245 250 255Pro Arg Gln Val Asp Tyr Phe Thr Glu His
His Pro Met Phe Met Glu 260 265 270Arg Asp Glu Tyr Leu Ser
27579270PRTVitis vinifera 79Met Ala Leu Phe Pro Ile His His Pro Leu
Val Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser Phe Met Val
Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Gln Ile Tyr Lys Arg Lys
Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Phe Leu Asn Thr Asp Ala
Ser Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu
Thr Ser Tyr Ile Val Met Phe Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala
Arg Ile Thr Thr Val Lys Leu Val Phe Leu Met Asn Ile 100 105 110Cys
Gly Phe Gly Ser Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Ala Glu Gly 115 120
125Ala Asn Arg Val Arg Ile Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Leu Val Phe Ser Leu
130 135 140Ser Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Leu
Cys Ile Met Arg Gln Val Ile Arg Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu
Tyr Met Pro Phe Leu Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala
Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Met Leu Lys Asp Phe Tyr 180 185
190Ile Ala Gly Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Val Gln Met
195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Arg Asn Arg Lys Lys Val Leu Glu
Asn Glu 210 215 220Lys Leu Pro Glu Leu Ser Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp Val
Val Lys Leu Ser225 230 235 240Thr Met Val Cys Ser Glu Val Asn Leu
Thr Asn Gln Gln His Ser Asn 245 250 255Glu Gly His Gly Thr Thr Gly
Leu Glu Val Ile Val Ala Leu 260 265 27080217PRTPopulus trichocarpa
80Met Thr Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro1
5 10 15Thr Phe Ile Arg Ile Leu Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Asp Phe Gln
Ser 20 25 30Leu Pro Tyr Leu Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu
Tyr Tyr 35 40 45Ala Met Leu Lys Asn Asp Glu Ile Leu Leu Val Thr Ile
Asn Ser Phe 50 55 60Gly Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ala Ile Tyr
Ile Ala Tyr Ala65 70 75 80Thr Arg Glu Ser Lys Val Ser Thr Ile Lys
Leu Leu Leu Ser Met Asn 85 90 95Met Gly Leu Phe Ser Leu Ile Ile Leu
Leu Thr His Phe Leu Ala Ser 100 105 110Gly Ser Thr Arg Val Lys Ala
Leu Gly Trp Leu Cys Val Ala Phe Ser 115 120 125Val Cys Val Phe Ala
Ala Pro Leu Asn Ile Val Lys Gln Ile Ile Arg 130 135 140Thr Lys Ser
Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr145 150 155
160Leu Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Leu Phe Ile Lys Asp Met
165 170 175Cys Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Val Leu Gly Leu
Leu Gln 180 185 190Met Leu Leu Tyr Gly Ile Tyr Arg Asn Ala Glu Lys
Lys Lys Ile Pro 195 200 205Ala Glu Asn Leu Lys Ser Ile Val Ile 210
21581269PRTPopulus trichocarpa 81Met Ala Leu His Phe Thr Trp Val
Phe Gly Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Ile Ile Ser Cys Leu Val Cys
Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr Gln 20 25 30Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys Thr
Ser Gln Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile Ala Leu Phe Ser
Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Phe Tyr Ala Ser Phe Ser 50 55 60Glu Asn Ala Met
Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Ala Phe Phe Met65 70 75 80Glu Ile
Gly Tyr Ile Ala Val Tyr Leu Phe Tyr Ala Thr Lys Lys Asp 85 90 95Lys
Ile Leu Thr Phe Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Phe Asn Ile Phe Gly Phe 100 105
110Gly Leu Ile Cys Ala Leu Ser Leu Leu Leu Thr Glu Gly Thr Lys Arg
115 120 125Val His Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Met Val Phe Ala Leu Cys
Val Phe 130 135 140Val Ala Pro Leu Gly Val Val Arg Lys Val Ile Arg
Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155 160Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe
Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val 165 170 175Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Tyr
Leu Lys Lys Asp Lys Phe Val Ala Ile 180 185 190Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly
Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile Leu Gln Met Val Leu Tyr 195 200 205Leu Ile Tyr
Arg Asn Pro Lys Lys Asn Glu Val Ala Glu Pro Arg Thr 210 215 220Gln
Glu Leu Ser Glu Gln Tyr Cys Ser Asp Ile Asn Ile Ala Met Pro225 230
235 240Lys Leu Asn Glu Gly Gly Asn Glu Val Phe Glu Ala His Ser Ala
Lys 245 250 255Asp Gln Thr Lys Glu Ala Met Asp Val Thr Asn Lys Val
260 26582283PRTPopulus trichocarpa 82Met Ala Leu His Leu Thr Trp
Met Leu Ala Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Leu Ile Ser Cys Leu Val
Cys Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr Gln 20 25 30Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Thr Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Phe Tyr Ala Ile Phe Ser 50 55 60Glu Asp Ala
Ile Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Ala Phe Phe Met65 70 75 80Glu
Phe Gly Tyr Ile Thr Val Tyr Leu Leu Tyr Ala Thr Lys Lys Asp 85 90
95Lys Ile Leu Thr Phe Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Phe Asn Ser Phe Gly Phe
100 105 110Gly Leu Ile Cys Val Leu Thr Leu Phe Leu Thr Gln Gly Gln
Lys Arg 115 120 125Val Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Met Ile Phe Ser
Leu Cys Val Phe 130 135 140Val Ala Pro Leu Phe Ile Val Arg Glu Val
Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155 160Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu
Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val 165 170 175Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Tyr Leu Lys Lys Asp Gln Phe Val Ala Val 180 185 190Pro Asn Ile
Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val Leu Tyr 195 200 205Val
Ile Tyr Arg Asn Pro Met Lys Ile Leu Val Val Glu Pro Lys Leu 210 215
220Gln Glu Leu Ser His Glu His Ile Val Asp Ile Arg Lys Leu Gly
Thr225 230 235 240Ala Ile Cys Ser Glu Ile Asn Ile Val Ile Pro Gln
Leu Asn Asp Ser 245 250 255Gly Lys Val Val Phe Glu Asp Gln Ile Ala
Lys Glu Leu Thr Lys Gln 260 265 270Thr Gln Glu Ile Thr Asn Ala Thr
Asn Lys Ile 275 28083283PRTPopulus trichocarpa 83Met Ala Leu His
Leu Thr Trp Val Phe Gly Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Phe Ile Ser
Cys Leu Val Cys Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr Arg 20 25 30Ile Cys
Lys Lys Lys Thr Ser Gln Gly Phe His Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile
Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Phe Tyr Ala Leu Phe Lys 50 55
60Glu Asp Ala Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Thr Phe Phe Met65
70 75 80Glu Ile Gly Tyr Ile Phe Met Tyr Leu Leu Tyr Ala Thr Lys Lys
Asp 85 90 95Lys Ile Leu Thr Phe Lys Leu Leu Leu Phe Phe Asn Val Phe
Gly Phe 100 105 110Gly Leu Ile Cys Val Leu Thr Arg Phe Leu Thr Gln
Arg Gln Lys Arg 115 120 125Val Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Met Thr
Phe Ser Leu Cys Val Phe 130 135 140Val Ala Pro Leu Phe Ile Val Arg
Lys Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155 160Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val 165 170 175Met Trp Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Phe Leu Lys Lys Asp Gln Phe Val Ala Val 180 185 190Pro
Asn Ile Leu Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Ile Leu Gln Met Val Leu Tyr 195 200
205Met Ile Tyr Gly Asn Ser Lys Lys Val Val Val Leu Glu Pro Lys Leu
210 215 220Lys Leu Asp Ile Ser Glu His Val Val Asp Leu Glu Lys Leu
Gly Ala225 230 235 240Ala Ile Cys Ser Glu Ile Ala Ile Gly Ile Pro
Lys Leu Asn Asp Gly 245 250 255Gly Asp Gly Ile Ile Glu Asp Gln Asn
Ala Lys Glu Gln Thr Lys Lys 260 265 270Ile Met Lys Ala Met Asp Val
Thr Asn Lys Leu 275 28084259PRTPopulus trichocarpa 84Met Gly Phe
Leu Ser Asn Asp Gln Leu Thr Phe Leu Phe Gly Leu Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn
Ile Val Ala Ala Gly Met Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr
Thr Ile Phe Lys Arg Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40
45Tyr Ser Val Ala Leu Met Ser Ala Ser Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Gly Leu
50 55 60Leu Lys Thr Asn Ala Tyr Leu Leu Ile Ser Ile Asn Ser Ile Gly
Cys65 70 75 80Ala Phe Glu Val Thr Tyr Leu Ile Ile Tyr Leu Ile Tyr
Ala Pro Lys 85 90 95Gln Glu Lys Met His Thr Met Lys Leu Leu Leu Ile
Phe Asn Met Gly 100 105 110Ser Phe Gly Val Val Leu Leu Leu Thr Met
Leu Leu Met Lys Gly Lys 115 120 125Pro Arg Leu Ser Val Val Gly Trp
Ile Cys Ala Val Phe Ser Val Ala 130 135 140Val Cys Ala Ala Pro Leu
Ser Ile Met Arg Arg Val Val Arg Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu
Tyr Leu Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Ala Ser Ile Thr Leu Asn 165 170 175Ala
Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Gln His Asp Tyr Tyr Ile 180 185
190Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met Ile
195 200 205Leu Tyr Met Val Tyr Lys Asn Leu Lys Lys Asn Val Glu Glu
Lys Ser 210 215 220Glu Gln Leu Ala Gly Asn Met Glu Val Val Gln Met
Thr Lys Glu Thr225 230 235 240Glu Ser Cys Thr Val Asp Asp Pro His
Met Glu Thr Lys Ile Cys Ile 245 250 255Cys Asp Leu85302PRTSorghum
bicolor 85Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Leu Gln His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe
Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Leu Thr Phe Leu Ala Pro
Ile Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly
Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu
Trp Ile Phe Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys Ser Asn Glu Thr Phe Leu Ile
Thr Ile Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile
Val Met Tyr Phe Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr
Ala Lys Ile Met Leu Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Val
Ile Leu Leu Val Thr Leu Leu Leu Phe Lys Gly 115 120 125Asp Lys Arg
Val Val Met Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser
Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Arg Val Ile Gln Thr145 150
155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr
Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys
Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe
Gly Val Val Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr Val Leu Tyr Met Asn Lys
Thr Pro Val Ala Val Ala Glu 210 215 220Gly Lys Asp Ala Gly Val Lys
Leu Pro Ser Ala Ala Asp Glu His Val225 230 235 240Leu Val Asn Ile
Thr Lys Leu Ser Pro Ala Leu Pro Asp Arg Ser Ser 245 250 255Gly Val
His Arg Ala Thr Gln Met Ala Ala Val Pro Ala Ser Ser Cys 260 265
270Ala Ala Glu Ala Ala Ala Pro Ala Met Leu Pro Asn Arg Asp Val Val
275 280 285Asp Val Phe Val Ser Arg Gln Ser Pro Ala Val His Val Val
290 295 30086302PRTSorghum bicolor 86Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Leu Gln
His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Ile Ser
Phe Leu Thr Phe Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr
Lys Thr Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Phe Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Ile Lys
Ser Asn Glu Thr Phe Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys
Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Met Tyr Phe Val Tyr Ala Pro 85 90
95Lys Lys Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Met Leu Leu Leu Asn Val
100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Val Ile Leu Leu Val Thr Leu Leu Leu Phe
Lys Gly 115 120 125Asp Lys Arg Val Val Met Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val
Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met
Arg Arg Val Ile Gln Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Met Glu Tyr Met Pro
Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp
Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu
Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Phe Gly Met Val Gln Met 195 200 205Val
Leu Tyr Val Leu Tyr Met Asn Lys Thr Pro Val Ala Val Ala Glu 210 215
220Gly Lys Asp Ala Gly Gly Lys Leu Pro Ser Ala Gly Asp Lys His
Val225 230 235 240Leu Val Asn Ile Ala Lys Leu Ser Pro Ala Leu Pro
Glu Arg Ser Ser 245 250 255Gly Val His Arg Ala Thr Gln Met Ser Ala
Val Pro Ala Lys Ser Cys 260 265 270Ala Ala Glu Ala Thr Ala Pro Lys
Val Met Leu Pro Asn Arg Asp Val 275 280 285Val Asp Val Phe Leu Ser
Gln Ala Leu His Arg Lys Gln Ala 290 295 30087309PRTSorghum bicolor
87Met Ala Gly Gly Leu Phe Ser Met Ala His Pro Ala Ile Thr Leu Ser1
5 10 15Gly Ile Ala Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro
Val 20 25 30Ala Thr Phe Leu Gln Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Gly Gly
Phe Ser 35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Val Leu
Trp Ile Phe 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu Val Lys Thr Asn Ser Arg Pro Leu Leu
Thr Ile Asn Ala65 70 75 80Phe Gly Cys Gly Val Glu Ala Ala Tyr Ile
Val Phe Tyr Leu Ala Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro Arg Lys Ala Arg Leu Arg Thr
Leu Ala Tyr Phe Phe Leu Leu 100 105 110Asp Val Ala Ala Phe Ala Leu
Val Val Val Val Thr Leu Phe Val Val 115 120 125Arg Glu Pro His Arg
Val Lys Phe Leu Gly Ser Val Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala
Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Val Lys Val Val145 150 155
160Lys Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Leu Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Cys Leu
165 170 175Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp Phe Cys Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr
Lys Asp 180 185 190Pro Phe Val Met Tyr Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe
Phe Ser Cys Val 195 200 205Gln Met Gly Leu Tyr Phe Trp Tyr Arg Lys
Pro Arg Pro Ala Lys Asn 210 215 220Asn Ala Val Leu Pro Thr Thr Thr
Asp Gly Ala Ser Ala Val Gln Met225 230 235 240Gln Gly Gln Val Ile
Glu Leu Ala Pro Asn Thr Val Ala Ile Leu Ser 245 250 255Val Ser Pro
Ile Pro Ile Val Gly Val His Lys Ile Glu Val Val Glu 260 265 270Gln
Gln His Lys Glu Ala Ala Val Ala Ala Glu Thr Arg Arg Met Ala 275 280
285Ala Ala Asn Pro Asp Gly Ala Met Pro Glu Val Ile Glu Ile Val Pro
290 295 300Ala Val Ala Thr Val30588291PRTSorghum bicolor 88Met Ala
Gly Leu Ser Leu Gln His Pro Met Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu
Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Tyr Arg 20 25
30Pro Thr Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Gln Gly Phe Gln
35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile
Tyr 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu Leu Lys Ser Asn Glu Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ser65 70 75 80Ala Gly Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Val Met
Tyr Leu Leu Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro Lys Lys Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr Ala
Lys
Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu 100 105 110Asn Val Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu
Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Ser 115 120 125Ala Gly Gln His Arg Val Val
Val Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Val Ser Val Phe
Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg Gln Val Val145 150 155 160Arg Thr
Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu 165 170
175Thr Val Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp
180 185 190Lys Tyr Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ser Phe Gly
Val Val 195 200 205Gln Met Gly Leu Tyr Ala Leu Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr
Pro Arg Val Pro 210 215 220Pro Ala Lys Glu Val Thr Asp Asp Asp Ala
Ala Ala Asp Gly Thr Phe225 230 235 240Lys Leu Pro Gly Glu His Val
Val Thr Ile Ala Lys Leu Thr Ala Val 245 250 255Pro Ala Val Ser Pro
Gln Leu Gln Glu Glu Ala Lys Pro Ala Asp Asn 260 265 270Gly Thr Thr
Pro Ala Pro Ala Pro Ala Asn Asp Val Gln Leu Asn Ala 275 280 285Glu
Gln Val 29089336PRTSorghum bicolor 89Met Ala Phe Leu Asn Met Glu
Gln Gln Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile
Ser Leu Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val
Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Thr Pro Tyr Val
Val Thr Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Ile Phe Tyr 50 55 60Ala Leu Leu
Lys Ser Gly Ala Glu Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Gly Val65 70 75 80Gly
Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Leu Gly Met Tyr Leu Leu Tyr Ala 85 90
95Pro Lys Ala Ala Arg Val Leu Thr Ala Lys Met Leu Leu Gly Leu Asn
100 105 110Val Gly Val Phe Gly Leu Val Ala Leu Val Thr Met Val Leu
Ser Asn 115 120 125Gly Gly Leu Arg Val Lys Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys
Val Ser Val Ala 130 135 140Leu Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile
Met Arg Gln Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met
Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Val 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Ile
Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Ala Leu Lys Lys Asp Val 180 185 190Phe Val Ala
Ala Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln 195 200 205Met
Ala Leu Tyr Met Ala Tyr Arg Asn Lys Lys Pro Ala Ala Ala Ala 210 215
220Val Ile Met Val Glu Glu Val Lys Leu Pro Ala Glu Gln Tyr Ala
Ser225 230 235 240Lys Glu Val Ala Pro Pro Ala Ala Ala His Glu Gly
Ser Arg Ala Ser 245 250 255Cys Gly Ala Glu Val His Pro Ile Asp Ile
Asp Thr Leu Pro Val Ala 260 265 270Asp Val Gly Arg His His Asp Ser
Gln Ala Val Val Val Ile Asp Val 275 280 285Asp Val Glu Pro Ala Ala
Thr Cys Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala Gly 290 295 300Gly Val Arg Gly
Asp Gly Ala Ala Gly Val Val Thr Ala Gly Pro Glu305 310 315 320Gln
Pro Ala Ala Met Lys Pro Val Asp Met Ala Ile Ala Val Glu Ala 325 330
33590273PRTSorghum bicolor 90Met Ala Gly Gly Leu Phe Ser Met Glu
His Pro Trp Val Ser Ala Phe1 5 10 15Gly Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser
Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val 20 25 30Pro Thr Phe Leu Arg Val Tyr
Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Ser 35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Thr Leu Trp Ile Leu 50 55 60Tyr Ala Val Val Lys
Thr Asn Ser Ser Pro Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala65 70 75 80Phe Gly Cys
Val Val Glu Ala Thr Tyr Ile Leu Leu Tyr Leu Ile Tyr 85 90 95Ala Pro
Arg Ala Ala Arg Leu Arg Ala Leu Ala Phe Phe Phe Leu Leu 100 105
110Asp Val Ala Ala Leu Ala Leu Ile Val Val Val Val Val Val Leu Val
115 120 125Ala Glu Pro His Arg Val Lys Val Leu Gly Ser Ile Cys Leu
Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile
Phe Val Val Ile145 150 155 160Arg Thr Lys Ser Ala Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu 165 170 175Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Ala Trp
Phe Leu Tyr Gly Ile Phe Thr Lys Asp 180 185 190Pro Tyr Val Thr Leu
Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe Phe Gly Cys Ile 195 200 205Gln Met Val
Leu Tyr Cys Cys Tyr Arg Lys Pro Ser Ala Ser Val Val 210 215 220Leu
Pro Thr Thr Thr Asp Ala Ala Ala Thr Glu Met Glu Leu Pro Leu225 230
235 240Ala Ala His Gln Ala Val Ala Pro Val Leu Ala Glu Leu Gln Lys
Leu 245 250 255Glu Glu Ala Met Gly Ser Pro Arg Lys His Gly Gly Val
Val Lys Val 260 265 270Val91313PRTSorghum bicolor 91Met Ile Thr Val
Gly His Pro Val Val Phe Ala Val Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Leu
Ser Phe Leu Val Thr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val
Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val
Val Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55
60Ser Ile Asp Val Leu Leu Leu Ser Ile Asn Thr Ile Ala Cys Val Val65
70 75 80Glu Ser Val Tyr Leu Ala Ile Tyr Leu Thr Tyr Ala Pro Lys Pro
Ala 85 90 95Met Ala Phe Thr Leu Lys Leu Leu Phe Thr Met Asn Met Gly
Leu Phe 100 105 110Gly Ala Met Val Ala Phe Leu Gln Phe Tyr Val Asp
Gly Gln Arg Arg 115 120 125Val Ser Ile Ala Gly Gly Val Gly Ala Ala
Phe Ala Leu Ala Val Phe 130 135 140Val Ala Pro Leu Thr Ile Ile Arg
Gln Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155 160Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe
Trp Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Ser Ala Val 165 170 175Val Trp Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Met Lys Asp Phe Phe Val Ala Met 180 185 190Pro
Asn Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Ala Leu Tyr 195 200
205Phe Val Tyr Arg Asn Arg Asn Pro Lys Gln Asn Gly Ala Val Ser Glu
210 215 220Met Gln Gln Gln Ala Ala Val Val Gln Ala Asp Ala Asp Ala
Lys Lys225 230 235 240Glu Gln Gln Leu Arg Gln Ala His Ala Asp Ala
Gly Ala Asp Gly Glu 245 250 255Ala Val Ala Val Arg Ile Asp Asp Glu
Glu Glu Pro Lys Asn Val Val 260 265 270Val Asp Ile Met Pro Pro Pro
Pro Pro Leu Leu Pro Ala Glu Arg Ala 275 280 285Ser Pro Pro Leu Pro
Leu Pro Pro Pro Pro Ala Met Val Met Met Thr 290 295 300Ala His Gln
Thr Ala Val Glu Val Val305 31092297PRTRicinus communis 92Met Ala
Ile Phe Asn Thr His Asn Pro Ser Val Phe Val Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu
Gly Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Val Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25
30Phe Leu Arg Val Cys Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Phe
35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ser Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr
Ala 50 55 60Ser Leu Lys Ser Asp Ala Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser
Val Gly65 70 75 80Cys Leu Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Thr Leu Phe Ile
Thr Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Gln Ala Arg Ile Thr Thr Leu Lys Ile Leu
Leu Leu Leu Asn Phe 100 105 110Gly Gly Phe Cys Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu
Ser His Phe Leu Ala Lys Gly 115 120 125Ser Glu Arg Ala Thr Ile Leu
Gly Trp Val Cys Val Ile Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Ala Ala
Pro Leu Ser Val Met Arg Ile Val Ile Arg Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser
Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Tyr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170
175Ser Ala Ile Met Trp Leu Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Leu Tyr
180 185 190Ile Ala Val Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Leu Val Phe Gly Val Leu
Gln Met 195 200 205Ile Leu Tyr Val Ile Tyr Lys Asn Val Lys Thr Val
Val Glu Glu Pro 210 215 220Lys Leu Pro Glu His Asn Val Asp Asn Val
Lys Leu Ser Ala Val Ile225 230 235 240Thr Cys Glu Val Gln Gln Glu
Val Cys Ser Gln Ser Gln Pro Asn Gly 245 250 255Asp Asp Gly Ala His
Asn Lys Glu Gln Lys Met His Asp Asn Pro Ala 260 265 270Asn Ala Val
Thr Glu Tyr Gln Arg His Ser Gly Met Asp Ala Ser Ile 275 280 285Ala
Asp Gln Ser Ile Ala Cys Arg Val 290 29593277PRTRicinus communis
93Met Ala Tyr His Leu Ser Leu Glu Phe Leu Phe Gly Val Leu Ala Asn1
5 10 15Ile Ile Ser Ser Met Val Cys Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr
Gln 20 25 30Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys Thr Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val Pro
Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Phe Tyr Ala
Thr Phe Asp 50 55 60Asp Asn Ala Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe
Thr Phe Phe Met65 70 75 80Glu Val Gly Tyr Leu Ser Val Tyr Leu Phe
Tyr Gly Thr Arg Lys Asp 85 90 95Arg Met Leu Thr Thr Lys Leu Val Leu
Phe Phe Asn Val Phe Gly Phe 100 105 110Gly Met Ile Ala Ile Leu Thr
Leu Phe Leu Thr His Gly Arg Lys Arg 115 120 125Val Asp Val Leu Gly
Trp Ile Cys Met Ile Phe Ala Leu Cys Val Phe 130 135 140Val Ala Pro
Leu Gly Ile Met Arg Lys Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155
160Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val
165 170 175Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Phe Leu Lys Lys Asp Ile Tyr Val
Tyr Ile 180 185 190Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Phe Phe Gly Ile Val Gln
Met Ile Leu Tyr 195 200 205Leu Ile Tyr Arg Asn Ser Lys Lys Pro Val
Glu Glu Pro Lys Ser Gln 210 215 220Glu Phe Ser Glu His Ile Val Asp
Val Ala Lys Leu Ser Ala Val Ile225 230 235 240Cys Ser Glu Leu Lys
Thr Met Val Val Ala Lys Leu Asn Asp Asn Gly 245 250 255Asn Glu Val
Val Lys Glu Glu Thr Lys Asn Thr Lys Gln Glu Met Glu 260 265 270Ala
Ser Asn Lys Val 27594279PRTRicinus communis 94Met Ala Phe His Leu
Thr Leu Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Ile Ile Ser Phe
Leu Val Cys Leu Ala Pro Met Pro Thr Phe Tyr Gln 20 25 30Ile Cys Lys
Lys Lys Thr Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile Ala
Leu Phe Ser Ala Thr Leu Trp Leu Phe Tyr Ala Ile Phe Ala 50 55 60Asn
Asp Ala Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Ala Phe Phe Met65 70 75
80Glu Thr Ala Tyr Ile Ala Ile Tyr Leu Phe Tyr Ala Val Lys Lys Asp
85 90 95Arg Leu Phe Thr Thr Lys Leu Val Leu Ser Leu Asn Ile Phe Ala
Phe 100 105 110Gly Ser Ile Cys Val Ile Ala Met Phe Leu Thr His Gly
Gln Lys Arg 115 120 125Val Gln Leu Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Met Val Phe
Ala Leu Cys Val Phe 130 135 140Val Ala Pro Leu Ala Ile Val Arg Lys
Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155 160Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser
Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val 165 170 175Met Trp Phe Phe
Tyr Gly Phe Leu Lys Lys Asp Leu Tyr Val Ala Val 180 185 190Pro Asn
Ile Leu Gly Phe Met Phe Gly Val Leu Gln Met Ile Leu Tyr 195 200
205Leu Ile Tyr Arg Asn Pro Lys Lys Thr Gly Asp Asp Asp Gln Lys Ala
210 215 220Asn Glu Leu Pro Asn Gln His Ser Ile Ile Asp Val Ala Lys
Leu Asn225 230 235 240Thr Arg Val Ser Cys Cys Glu Pro Asn Ala Thr
Thr Val Ala His Ser 245 250 255Arg Asn Asp Arg Glu Glu Gln Gln Thr
Met Gln Ile Asn Arg Glu Asp 260 265 270Lys Asp Ala Thr Asn Thr Val
27595272PRTRicinus communis 95Met Ala Ile Ile Ser Thr His Pro Pro
Leu Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Ile1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Ile Leu
Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Arg Lys
Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu 35 40 45Pro Tyr Leu Val Ala Leu
Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Met Leu Lys Lys Asp
Val Phe Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile
Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ile Met Tyr Ile Ile Tyr Ala Thr 85 90 95Lys Lys
Asn Arg Val Ser Thr Phe Lys Val Leu Thr Ser Met Asn Leu 100 105
110Gly Leu Phe Ala Phe Ile Ile Leu Phe Ser His Phe Leu Val Lys Ser
115 120 125Ser Val Arg Ala Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala Val
Ser Val 130 135 140Cys Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val Ala Gln
Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Asn
Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Ile Met Trp Phe Ala
Tyr Gly Leu Ser Thr Lys Asp Thr Cys 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn
Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln Met 195 200 205Val Leu Tyr
Val Ile Tyr Arg Lys Ala Lys Lys Val Ile Leu Glu Glu 210 215 220Lys
Leu Pro Glu His Leu Lys Thr Ile Val Val Leu Ser Thr Leu Gly225 230
235 240Asn Ser Glu Gln Gln Leu Val Thr Pro Val Gly Ser Leu Leu Ile
Phe 245 250 255Gly Gln Phe Arg Asp Val Ala Thr Cys Arg Arg Phe Gln
Ile Leu Leu 260 265 27096286PRTRicinus communis 96Met Ala Leu Asn
Asp Pro Arg Phe Ile Leu Ala Phe Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Val
Ser Phe Leu Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Trp 20 25 30Arg Ile
Val Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ser
Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Thr Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Thr Leu 50 55
60Lys Glu Asn Ala Ile Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Ile Gly Cys Leu65
70 75 80Ile Glu Gly Ile Tyr Leu Thr Ile Tyr Met Ile Tyr Ala Thr Gln
Thr 85 90 95Ser Arg Val Gln Ile His Phe Lys Leu Leu Ile Leu Phe Asn
Leu Gly 100 105 110Thr Tyr Leu Leu Ile Val Met Leu Ala Ser Glu Leu
Thr His Gly Thr 115 120 125Leu Arg Val Gln Val Val Gly Trp Ile Cys
Ala Val Phe Ser Val Cys 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile
Met Arg Leu Val Ile Lys Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met
Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Cys 165 170 175Ala Ile Ser
Trp Leu Gly Tyr Gly Leu Ala Val Asn Asp Tyr Phe Ile 180 185 190Ala
Ser Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Val Gln Met Val 195 200
205Leu Tyr Met Ile Tyr Lys Asn Lys Lys Asn Glu Ile Leu Pro Thr Ser
210 215
220Thr Ser Gln Glu Leu Ala Val Ser Lys Pro Glu Thr Ser Gln Asp
Arg225 230 235 240Glu Asn Ser Asn Ser Ser Ser Leu Asn Gln Gln Asp
Leu Glu Ala Ala 245 250 255Lys Asp Asp Arg Arg Glu Asn Asn Lys Ala
Val Pro Glu Glu Ala Ser 260 265 270Glu Arg Asn Gly Tyr Arg Ala Thr
Cys Phe Gly Ile Ser Phe 275 280 28597294PRTArabiopsis lyrata 97Met
Ala Leu Thr His Asn Val Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Met Leu Gly1 5 10
15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Val Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Val
20 25 30Arg Ile Cys Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro
Tyr 35 40 45Val Ser Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala
Met Gln 50 55 60Lys Asp Gly Ser Gly Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala
Val Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Val Leu Phe Val
Thr Tyr Ala Asn Lys 85 90 95Lys Thr Arg Ile Ser Thr Leu Lys Val Leu
Gly Leu Leu Asn Phe Leu 100 105 110Gly Phe Ala Ala Ile Val Leu Val
Cys Glu Leu Leu Thr Glu Gly Ser 115 120 125Thr Arg Glu Lys Val Leu
Gly Gly Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala
Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Val Val Val Arg Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser
Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Ile Ser 165 170
175Ala Val Thr Trp Leu Phe Tyr Gly Leu Ala Ile Lys Asp Phe Tyr Val
180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Ala Phe Leu Gly Ala Val Gln
Met Ile 195 200 205Leu Tyr Ile Ile Phe Lys Tyr Tyr Lys Ile Pro Met
Ala Gln Lys Thr 210 215 220Asp Lys Ser Lys Ala Val Ser Asp His Ser
Ile Asp Ile Ala Lys Leu225 230 235 240Thr Thr Val Thr Pro Gly Pro
Ile Ser Asp Ser Ala Val His Gln Pro 245 250 255Pro Leu Ile His Asn
Val Pro Glu Thr Gln Ile Gln Val Thr Glu Val 260 265 270Lys Ser Gln
Asn Ile Thr Asp Pro Lys Asp Gln Ile Asn Lys Asp Val 275 280 285Glu
Asn Gln Ser Gln Val 29098262PRTGlycine max 98Met Val Ser Ile Ser
Asp His Glu Leu Val Leu Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Val
Ser Phe Met Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Thr Ile
Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Ala
Val Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Leu Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Gly Phe 50 55 60Ile
Lys Thr Asn Ala Thr Leu Ile Ile Thr Ile Asn Cys Ile Gly Cys65 70 75
80Val Ile Glu Val Ser Tyr Leu Thr Met Tyr Ile Ile Tyr Ala Pro Arg
85 90 95Lys Gln Lys Ile Ser Thr Leu Val Met Ile Leu Ile Ala Asp Ile
Gly 100 105 110Gly Phe Gly Leu Thr Met Leu Ile Thr Thr Phe Ala Val
Lys Gly Ile 115 120 125Asn Arg Val His Ala Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala
Ile Phe Asn Ile Ala 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met
Arg Arg Val Ile Lys Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Leu Cys 165 170 175Ala Thr Met Trp
Phe Phe Tyr Gly Phe Phe Asp Lys Asp Asp Phe Ile 180 185 190Met Phe
Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile Ser Gln Met Ile 195 200
205Leu Tyr Met Ile Tyr Lys Asn Ser Lys Lys Asn Gly Glu Thr Asn Cys
210 215 220Thr Glu Gln Gln Glu Ser Glu Gly Thr Val Asn Ser Lys Gln
His Ser225 230 235 240Cys Asp Gly Asn Lys Leu Asp Phe Pro Ser Leu
Val Glu Met Lys Glu 245 250 255Asn Gln Leu Asn Gln Val
26099258PRTGlycine max 99Met Ala Ile Ser His Glu Thr Trp Ala Phe
Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Val Phe Leu
Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Ser
Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser
Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Val 50 55 60Lys Lys Asp Ala Ser Leu
Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu Thr
Ile Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Leu Val Tyr Ala Pro Ser 85 90 95Lys Thr Arg
Leu Trp Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Met Leu Asn Val Phe 100 105 110Gly
Phe Gly Gly Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Tyr Leu Thr Thr Gly Ser 115 120
125Lys Arg Leu Ser Val Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Asn Ile Ser
130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Cys Ile Met Lys Arg Val Ile Lys
Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu
Ser Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu
Leu Leu Lys Asp Tyr Tyr Ile 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly
Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val 195 200 205Leu Tyr Leu Val Tyr
Arg Asn Ala Lys Pro Gln Thr Leu Glu Glu Pro 210 215 220Thr Lys Val
Gln Glu Leu Asn Gly His Ile Ile Asp Val Val Lys Pro225 230 235
240Asn His Ala Thr Lys Asn Gly His Val Pro Val Ile Glu Ile Ala Ser
245 250 255Ser Val100283PRTGlycine max 100Met Ala Ile Phe Asn Gly
His Asn His Leu Ala Leu Gly Phe Gly Met1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile
Ser Phe Met Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile
Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu 35 40 45Pro Tyr Leu
Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Ser Leu
Lys Pro Ala Asp Ala Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Leu65 70 75
80Gly Cys Val Ile Glu Ile Val Tyr Ile Ile Met Phe Thr Ile Tyr Ala
85 90 95Thr Lys Asp Ala Arg Asn Leu Thr Val Lys Leu Phe Met Val Met
Asn 100 105 110Val Gly Ser Phe Ala Leu Ile Phe Leu Val Thr Tyr Phe
Ala Met His 115 120 125Gly Ser Leu Arg Val Gln Val Val Gly Trp Val
Cys Val Ser Ile Ala 130 135 140Val Gly Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser
Ile Val Ala Gln Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Asn Val Glu Phe
Met Pro Phe Asn Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Ile Ser Ala Val
Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile 180 185 190Cys Ile
Ala Ile Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Thr Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln 195 200
205Met Leu Leu Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn Gly Lys Thr Asn Asn Lys Glu
210 215 220Val Val Thr Lys Glu Glu His Ala Leu Glu Ala Met Lys Asn
Val Val225 230 235 240Val Val Asn Pro Leu Gly Thr Cys Glu Val Tyr
Pro Val Ile Gly Lys 245 250 255Glu Ile Asn Asn Asn Gly Gln Gly Ile
Glu Gly Ala Glu Glu Lys Glu 260 265 270Lys Gly Val Glu Leu Gly Lys
Glu Cys Pro Val 275 280101272PRTGlycine max 101Met Val Ile Thr His
His Thr Leu Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly Met Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser
Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Ile Tyr
Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Lys
Arg Asp Ala Val Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys Val65 70 75
80Ile Glu Ile Ile Tyr Ile Val Leu Tyr Ile Thr Tyr Ala Thr Arg Asp
85 90 95Ala Arg Asn Leu Thr Ile Lys Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Asn Met Thr
Ser 100 105 110Phe Ala Val Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe Gly Val His
Gly Pro Leu 115 120 125Arg Val Gln Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ser
Ile Ser Val Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val Ala
Gln Val Val Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Asn Leu Ser Phe Thr Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Ile Met Trp Phe
Gly Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile Cys Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro
Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln Met Leu Leu 195 200
205Tyr Thr Ile Tyr Arg Lys Gly Asn Lys Lys Thr Asn Thr Asn Glu Lys
210 215 220Ser Leu Ser Val Lys Pro Leu Lys Asn Ile Ala Val Val Asn
Pro Leu225 230 235 240Gly Thr Gly Glu Val Phe Pro Val Glu Glu Asp
Glu Gln Ala Ala Lys 245 250 255Lys Ser Gln Gly Asp Gly Glu Asp Lys
Lys Ala Glu Asp Cys Leu Val 260 265 270102268PRTGlycine
maxmisc_feature(244)..(244)Xaa can be any naturally occurring amino
acid 102Met Pro Thr His His Ala Ser Ala Ala Ile Phe Gly Ile Ile Gly
Asn1 5 10 15Met Ile Ser Val Met Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe
Tyr Gln 20 25 30Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Cys Thr Asp Gly Phe His Ser Leu
Pro Tyr Leu 35 40 45Leu Ser Leu Met Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr
Ala Phe Leu Lys 50 55 60Ile His Asp Gly Val Val Pro Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ser Ile Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu Leu Ile Tyr Ile Leu Thr
Tyr Ile Lys Tyr Ala His Lys 85 90 95Asp Ala Arg Asn Leu Thr Tyr Thr
Leu Phe Ala Ala Met Asn Ile Ala 100 105 110Phe Leu Thr Leu Val Leu
Ser Ser His Phe Ala Leu His Gly Ser His 115 120 125Arg Val Lys Val
Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Asp Ala Val Ser Leu Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala
Ser Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Ala Lys Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155
160Val Gln Phe Met Pro Phe Tyr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Asn Ala
165 170 175Ile Thr Trp Phe Val Tyr Gly Leu Ser Ile Gln Asp Lys Cys
Ile Tyr 180 185 190Val Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Gly Leu Gly Leu Val
Gln Met Val Leu 195 200 205Tyr Gly Ile Tyr Arg Asn Gly Gly Glu Ser
Glu Lys Glu Gln Ala Leu 210 215 220Ala Glu Gly Ala Ile Asn Ile Val
Val Val Asn Pro Leu Gly Pro Ala225 230 235 240Glu Val Phe Xaa Ile
Ala Glu Glu Val Asp Asp Asp Lys Val Lys Glu 245 250 255Gly Leu Val
Val Asp Gln Glu Lys Asp Ala Lys Asp 260 265103298PRTBrachypodium
distachyon 103Met Ala Ala Ile Gly Asn Pro Trp Val Phe Ala Val Gly
Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Leu Ser Phe Leu Val Ile Leu Ala Pro Val
Pro Thr Phe His 20 25 30Arg Val Tyr Lys Arg Lys Ser Thr Glu Ser Phe
Gln Ser Ala Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ala Met Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Trp
Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Thr Ala Asp Leu Leu Leu Leu Ser Ile
Asn Ala Val Gly Cys Val Val65 70 75 80Glu Thr Ala Tyr Leu Ala Val
Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro Lys Gln Ala 85 90 95Arg Ala Phe Thr Val Lys
Leu Val Phe Val Met Asn Val Ala Leu Tyr 100 105 110Gly Ala Met Val
Ala Phe Leu Gln Leu Tyr Val Arg Asp Gly Asp Arg 115 120 125Arg Val
Ala Ile Ala Gly Gly Val Gly Ala Ala Phe Ala Phe Ala Val 130 135
140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ala Ile Ile Arg Gln Val Ile Arg Thr Lys
Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Leu Pro Phe Trp Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu
Thr Ile Ser Ala 165 170 175Val Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Met
Lys Asp Phe Phe Val Ala 180 185 190Met Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Leu Leu
Phe Gly Leu Ala Gln Met Ala Leu 195 200 205His Leu Val Tyr Lys Asn
Pro Lys Lys Lys Lys Gly Ala Val Ser Glu 210 215 220Ala Gly Gln Ala
Ala Val Ala Ala Asp Gly Glu Lys Gln Asn Gln Leu225 230 235 240Glu
Leu Gln Gln Gln His Gln Gln Ala Ala Ala Ala Thr Ile Asn Ala 245 250
255Asp Asp Ala Glu Asp Ala Ser Lys Val Gln Gln Ser Val Thr Val Val
260 265 270Val Asp Ile Pro Leu Pro Pro Pro Glu Glu His Pro Ala Pro
Met Pro 275 280 285Pro Pro Ile Arg Thr Ala Val Glu Val Val 290
295104299PRTBrachypodium distachyon 104Met Ala Ala Gly Phe Leu Ser
Met Ala His Pro Ala Ile Thr Leu Ser1 5 10 15Gly Ile Ala Gly Asn Val
Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val 20 25 30Thr Thr Phe Val Gln
Val Val Arg Lys Lys Thr Thr Gly Gly Phe Ser 35 40 45Ala Val Pro Tyr
Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Thr Leu Trp Ile Leu 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu
Leu Lys Gly Asn Ser Arg Pro Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Gly65 70 75 80Phe
Gly Cys Gly Val Glu Leu Ala Tyr Val Val Ala Tyr Leu Leu Tyr 85 90
95Ala Pro Arg Lys Ala Arg Leu Arg Ala Leu Ala Tyr Phe Leu Ala Leu
100 105 110Asp Val Ala Ala Phe Ala Ile Val Ala Ala Val Ala Leu Leu
Gly Val 115 120 125Ala Pro Glu His Arg Val Lys Phe Leu Gly Ser Val
Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser
Ile Ile Phe Lys Val Ile145 150 155 160Lys Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe
Met Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Cys Leu 165 170 175Val Leu Ser Ala Val
Ala Trp Phe Cys Tyr Gly Tyr Phe Thr Lys Asp 180 185 190Pro Tyr Val
Met Tyr Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe Phe Ser Cys Val 195 200 205Gln
Met Gly Leu Tyr Phe Tyr Tyr Arg Arg Pro Ser Asn Ala Ala Val 210 215
220Leu Pro Thr Thr Ala Asp Gly Ala Thr Gly Gly Gly Ala Val Gln
Ala225 230 235 240Gln Val Ile Glu Leu Pro Pro His Ala Val Ala Ile
Leu Ser Val Ser 245 250 255Asn Ile Pro Ile Leu Gly Met His Lys Ile
Glu Val Met Ala Ala Pro 260 265 270Glu Gln Gln Asp Ala Lys Ala Ala
Asp Ile Val Asp Lys Ala Ala Pro 275 280 285Ala Pro Glu Ala Val Glu
Ile Ala Gly Thr Val 290 295105309PRTBrachypodium distachyon 105Met
Ala Phe Leu Asn Met Glu Gln His Thr Trp Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10
15Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Leu Met Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro
20 25 30Thr Phe Tyr Arg Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln
Ser 35 40 45Thr Pro Tyr Val Val Thr Leu Phe Ser Cys Leu Leu Trp Met
Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Phe Leu Lys Ser Gly Ala Glu Leu Leu Leu Thr Ile
Asn Gly Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Gly Ile Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Ala Met
Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys Ser Ala Arg Leu Leu Thr Ala Lys
Leu Phe Leu Gly Leu Asp 100 105 110Val Gly Leu Phe Gly Leu Ile Ala
Leu Val Thr Met Leu Val Ser Ala 115 120 125Gly Thr Leu Arg Val Gln
Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala Val Ala 130 135 140Leu
Gly Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Ile Arg Leu Val Ile Arg145 150
155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Ile Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu
Val 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Ile Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Leu Leu Lys
Lys Asp Val 180 185 190Phe Val Ala Val Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Val
Phe Gly Val Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ala Leu Tyr Met Ala Tyr Arg Asn
Lys Ser Pro Ala Ile Thr Val 210 215 220Val His Gln Glu Met Lys Leu
Pro Glu His Val Lys Glu Val Thr Thr225 230 235 240Asn Thr Lys Leu
Gly Gly Ala Pro Thr Glu Gly Arg Ile Ser Cys Gly 245 250 255Ala Glu
Val His Pro Ile Asp Val Met Pro Thr Ser Ala Ala Ala Gly 260 265
270Ala Asp Glu Gln Ala Ile Asn Val Glu Glu Ala Ala Ala Gly Arg Asp
275 280 285Asp His Asn Met Leu Arg Pro Glu Gln Val Ile Lys Pro Asp
Met Ala 290 295 300Ile Val Val Glu Val305106300PRTBrachypodium
distachyon 106Met Ala Gly Leu Ser Leu Gln His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala
Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Met Thr Tyr Leu Ala
Pro Leu Ser Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Asn Lys Ser Thr Gln
Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met
Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu Leu Lys Ser Asp Gly Cys Leu Leu
Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Ala Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr
Ile Val Val Tyr Leu Ala Tyr Ala Pro 85 90 95Lys Gln Ala Lys Leu Phe
Thr Ala Lys Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly
Met Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Leu Leu Ser Glu Gly 115 120 125Glu Lys
Arg Val Val Met Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Gly Phe Ser Val 130 135
140Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile Arg Leu Val Val Arg
Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Asn Leu Ser Leu
Ser Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu
Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly
Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Ile Gln Met 195 200 205Gly Leu Tyr Ala Leu Tyr
Arg Asn Ser Thr Pro Arg Pro Val Thr Lys 210 215 220Glu Val Asp Ala
Glu Ser His Asp Gly Ala Ala Pro Lys Val Pro Glu225 230 235 240His
Val Val Asn Ile Gly Lys Leu Gly Ala Val Glu Leu Lys Thr Thr 245 250
255Glu Val Phe Ile His Pro Ala Ile Glu Ser Pro Pro Thr Lys Glu Asn
260 265 270Gly Val Ala His Gly Ala Glu Gln Ser Arg Glu Gly Gly Val
Val Val 275 280 285Glu Lys Val Asp Glu Ala Ser Gln Val Glu Gln Val
290 295 300107292PRTBrachypodium distachyon 107Met Ala Gly Leu Ser
Leu Glu His Pro Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Val
Ile Ser Phe Met Ser Tyr Leu Ala Pro Ile Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Ile Arg
Ile Tyr Lys Ser Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro Tyr
Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Leu
Val Lys Ser Asn Glu Ser Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ala Ala Gly65 70 75
80Cys Val Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Val Val Met Tyr Phe Val Tyr Ala Pro
85 90 95Arg Lys Ala Lys Leu Phe Thr Ala Lys Ile Met Leu Leu Leu Asn
Gly 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly Val Ile Leu Phe Cys Thr Leu Phe Leu
Ala His Gly 115 120 125Glu Lys Arg Val Val Ser Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys
Val Ala Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile
Ile Gly Arg Val Ile Lys Thr145 150 155 160Arg Ser Val Glu Tyr Met
Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Val
Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Ile Lys Asp Lys Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala
Leu Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ser Phe Gly Val Val Gln Met 195 200
205Ala Leu Tyr Met Phe Tyr Met Asn Lys Thr Pro Ile Val Arg Gly Asp
210 215 220Gly Lys Glu Gly Lys Leu Pro Ala Ala Glu Glu His Val Val
Val Asn225 230 235 240Met Ala Lys Leu Gly Gly Gly Ala Thr Pro Asp
Asn Lys Asn Cys Gly 245 250 255Ser Glu Val Tyr Pro Val Glu Val Lys
Ala Leu Pro Lys Ser Cys Ala 260 265 270Ala Gly Val Asp Arg Pro Leu
Val Asp Pro Thr Ala Arg Pro Ala Thr 275 280 285Val Glu Val Val
290108291PRTBrachypodium distachyon 108Met Ala Gly Ala Leu Phe Ser
Met Ala His Pro Trp Ala Ser Ala Phe1 5 10 15Gly Ile Leu Gly Asn Ile
Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Thr 20 25 30Pro Thr Phe Leu Arg
Val Tyr Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Ser 35 40 45Ser Val Pro Tyr
Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Thr Leu Trp Ile Leu 50 55 60Tyr Ala Leu
Val Lys Thr Asn Ser Ser Pro Leu Leu Thr Ile Asn Ala65 70 75 80Phe
Gly Cys Val Val Glu Ala Ala Tyr Ile Val Leu Tyr Leu Val Tyr 85 90
95Ala Pro Arg Pro Ala Arg Leu Arg Thr Leu Ala Ser Phe Leu Leu Leu
100 105 110Asn Val Ala Ala Phe Ser Leu Ile Val Ala Val Thr Val Phe
Leu Val 115 120 125Ala Pro Met His Arg Val Lys Val Leu Gly Ser Ile
Cys Leu Ala Phe 130 135 140Ser Met Ala Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser
Val Ile Phe Val Val Ile145 150 155 160Lys Thr Lys Ser Ala Glu Tyr
Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu 165 170 175Thr Leu Ser Ala Val
Ala Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr Lys Asp 180 185 190Ile Tyr Val
Thr Leu Pro Asn Val Gly Gly Phe Phe Phe Gly Ile Ala 195 200 205Gln
Met Thr Leu Tyr Phe Cys Tyr Arg Lys Pro Gly Thr Ser Ala Leu 210 215
220Val Leu Pro Thr Ser Ile Asp Asp Val Ser Thr Glu Pro Ala Ala
Ser225 230 235 240Ala Ala Ala Asp Gln Glu Val Glu Leu Pro Ala Gly
Thr His Pro Ala 245 250 255Val Ala Met Leu Thr Val Ser Thr Leu Pro
Val Leu Ala Glu Leu Gln 260 265 270Lys Met Glu Gln Glu Ile Gly Thr
Pro Thr Pro Arg Lys Gly Tyr Ile 275 280 285Lys Ala Phe
290109292PRTCucumis sativus 109Met Ala Ile Ser Pro Gln Thr Leu Ala
Phe Val Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Val Phe
Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Lys Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser
Ala Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser
Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Lys Thr Asn Ala Thr
Phe Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Ile Glu Ser
Leu Tyr Ile Leu Leu Phe Ile Ile Tyr Ala Pro Thr Lys 85 90 95Leu Arg
Phe Gln Thr Ala Lys Val Ile Phe Leu Leu Asn Val Leu Gly 100 105
110Phe Gly Leu Met Leu Ala Leu Thr Leu Val Leu Ala Lys Gly Glu Lys
115 120 125Arg Leu Lys Val Leu Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Asn Leu
Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Phe Ile Met Gly Lys Val Ile
Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ala Leu Ser
Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Asn Ala 165 170 175Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Tyr Tyr Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Val
Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Val Ile
Val Lys His Ile Gly Asn Lys Ser Arg Ile Pro Val Lys 210 215 220Asp
Glu Lys Ala Ala Ala Pro Pro Gln Leu His Glu Leu Ser Glu Gln225 230
235 240Ile Ile Asp Ala Val Lys Leu Gly Thr Met Val Cys Thr Glu Leu
Asn 245 250 255Pro Val Pro Val Thr Val Leu Gln Pro Asn Met Asp Val
Val Asp Ala 260 265 270Val Val Glu Ala Val Ile Asp Asn Ile Gln Lys
Lys Lys Asp Gln Asp 275 280 285Ile Ile Thr Asn 290110302PRTCucumis
sativus 110Met Ala Leu Ser Phe Met Asn His Asn Pro Trp Ile Phe Ala
Phe Gly1 5 10 15Leu Leu Gly Asn Ile Phe Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ala
Pro Val Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Ile Arg Val Cys Arg Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu
Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Ile Pro Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Leu
Leu Leu Ile Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ser Thr Leu Asn Ala Asp Glu Phe Phe Leu
Met Thr Ile Asn Ser Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Phe Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr
Ile Ala Leu Tyr Ile Ala Tyr Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys Lys Ala Arg Ile Phe
Thr Val Arg Phe Val Leu Leu Leu Asp 100 105 110Val Val Gly Phe Cys
Ser Ile Leu Val Val Thr Gln Phe Leu Val Lys 115 120 125Arg Ala Tyr
Arg Ala Arg Val Ile Gly Phe Ile Cys Gly Gly Leu Ser 130 135 140Val
Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Lys Arg Val Ile Arg145 150
155 160Thr Arg Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu
Thr 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Val Met Trp Leu Cys Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu
Lys Asp Leu 180 185 190Tyr Val Ala Leu Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe Thr
Phe Gly Met Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ile Leu Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn
Ala Lys Pro Leu Pro Ser Glu 210 215 220Glu Lys Leu Pro Gln His Lys
Ala Asp Ile Glu Thr Gln Ile Val Ile225 230 235 240Thr Ala Thr Pro
Thr Asn Pro Asp Asp His Gln Gly Asp Glu His Gln 245 250 255Asn Gln
Asp Gln Val Ile Asn Val Pro Pro Pro Pro Pro Gln Ser Asn 260 265
270Thr Asn His Ala Pro Ser Val Cys Asn Asn Asn Asp Lys Tyr Cys Met
275 280 285Asp Asn Asn Met Ala Pro Pro Pro Met Val Lys Cys Glu Ala
290 295 300111236PRTCucumis sativus 111Met Asn Gly Leu Ser Val His
Gln Leu Gln Phe Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe
Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Met Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Trp Thr Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Thr Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Val Val Ala
Leu Met Ser Ala Met Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Ala 50 55 60Leu Lys Thr
Asn Ala Tyr Leu Leu Val Ser Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val
Ile Glu Val Ile Tyr Ile Ala Leu Tyr Leu Phe Tyr Ala Pro Lys 85 90
95Lys Gln Lys Ile Phe Thr Leu Lys Leu Phe Ile Ile Phe Asn Leu Gly
100 105 110Phe Ser Gly Val Met Val Gly Gly Thr Met Phe Phe Leu His
Gly Met 115 120 125Lys Arg Thr Asn Ala Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala Ala
Phe Asn Leu Ser 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ser Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Lys
Arg Val Ile Thr Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe
Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser 165 170 175Ala Thr Met Trp Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Phe Phe Ile Lys Asp Leu Phe Ile 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro
Asn Val Val Gly Phe Leu Leu Gly Met Val Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Met
Tyr Ile Tyr Ile Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu His Tyr Thr Thr Pro 210 215
220His Ala Asp Val Leu Gln Ile Phe Ser Leu Leu Ile225 230
235112274PRTCucumis sativus 112Met Lys Gly Leu Ser Val His Gln Leu
Gln Phe Ile Phe Gly Leu Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Met Val
Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Trp Thr Val Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Thr Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln Cys Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Met
Ser Ala Met Leu Leu Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Val 50 55 60Leu Lys Thr Asn Ala
Tyr Leu Leu Ile Ser Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu
Leu Ile Tyr Ile Ala Leu Tyr Phe Tyr Tyr Ala Pro Lys 85 90 95Lys Leu
Lys Ile Phe Thr Leu Lys Leu Leu Met Ile Leu Asn Leu Gly 100 105
110Ser Tyr Gly Val Met Val Gly Gly Thr Met Leu Ile Leu His Gly Asn
115 120 125Lys Arg Thr His Ala Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala Ala Phe Asn
Leu Ala 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ser Pro Leu Ala Ile Met Lys Arg Val
Ile Thr Thr Lys145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Ser Leu
Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser 165 170 175Ala Thr Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr
Gly Phe Phe Ile Lys Asp Leu Phe Ile 180 185 190Ala Leu Pro Asn Ile
Val Gly Phe Leu Leu Gly Met Val Gln Met Ile 195 200 205Met Tyr Met
Ile Tyr Lys Asp Arg Lys Gly Asn Ser Leu Glu Glu Lys 210 215 220Leu
Glu Glu Gly Gly Lys Lys Tyr Glu Val Asp Asp Gln Ser Leu Ser225 230
235 240Lys Tyr Lys Gly Gln Ile Arg Arg Ile Leu Asp Leu Val Leu Glu
Glu 245 250 255Tyr Arg Phe Ser Arg Glu Asn Tyr Asn Ala Leu Asp Val
Val Glu Pro 260 265 270Thr Thr113277PRTCucumis sativus 113Met Thr
Ile Phe His Ser Pro His Leu Leu Val Phe Thr Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu
Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Phe Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro Thr 20 25
30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Trp Gln Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe His Ala Leu
35 40 45Pro Tyr Leu Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Ala Leu Trp Leu Cys Tyr
Ala 50 55 60Phe Leu Lys Thr Asn Thr Phe Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser
Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Val Ile Glu Phe Leu Tyr Phe Ile Val Phe Ile
Val Phe Ala Ala 85 90 95Asn Ser Val Arg Met Leu Thr Ile Arg Ile Phe
Ala Met Met Asn Met 100 105 110Gly Leu Phe Gly Leu Ile Leu Val Ala
Ile His Phe Ile Pro Asn Pro 115 120 125Ser Asn Arg Thr Asp Val Met
Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala Val Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Ala Ala
Pro Leu Ser Ile Leu Arg Gln Val Met Thr Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser
Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170
175Ser Ala Ile Met Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Asn Asp Ile Cys
180 185 190Ile Ala Ile Pro Asn Val Val Gly Phe Ile Leu Gly Leu Leu
Gln Met 195 200 205Val Val Tyr Ala Ile Tyr Arg Lys Arg Lys Ile Val
Ile Met Glu Glu 210 215 220Lys Lys Gln Pro Glu Gln Val Val Leu Lys
Ser Ile Ala Val Ser Glu225 230 235 240Val Phe Ala Met Lys Lys Pro
Asn Gly Asn Asp Ala Gln Leu Lys Glu 245 250 255Val Ile Ile Ile Lys
Gln Glu Ala Gln Glu Asp Asp Lys Leu Ser Cys 260 265 270Asp Lys Ile
Asn Thr 275114291PRTCucumis sativus 114Met Ala Leu Phe Asp Thr His
His Pro Gly Val Phe Ala Phe Gly Leu1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn
Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Met
Arg Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Val 35 40 45Pro
Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55
60Ser Phe Asn Ser Asn Glu Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly65
70 75 80Cys Leu Ile Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Ala Ile Phe Ile Val Phe Ala
Pro 85 90 95Lys Gln Ile Arg Val Ser Thr Leu Arg Phe Val Leu Leu Leu
Asn Phe 100 105 110Gly Gly Phe Cys Ile Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe
Leu Val His Gly 115 120 125Ser Asn Gln Val Lys Val Val Gly Trp Ile
Cys Val Ala Phe Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Thr
Ile Met Arg Leu Val Ile Arg Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Phe
Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Ala Ile
Thr Trp Leu Leu Tyr Gly Val Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile Tyr 180 185 190Val
Ala Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Val Ala Gln Met 195 200
205Ile Leu Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Arg Lys Tyr Glu Ile Ala Ile Ala Lys Glu
210 215 220Met Lys Leu Pro Glu Gln Thr Thr Val Asp Ile Val Met Lys
Gln Lys225 230 235 240Gln Asp Ser Ser Val Glu Ala Ile Glu Val Ile
Ile Lys Thr Asn Ile 245 250 255Glu Glu Ile Glu Leu Ser Asn Gly Asn
Asn Asn Asn Asp Asn Asp Lys 260 265 270His Asn His Lys Thr Leu Glu
Val Ser His Gln Ile Thr Asp His Leu 275 280 285Asn His Val
290115295PRTCucumis sativus 115Met Ala Leu Ser Phe Asn Thr His Asn
Pro Ala Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Leu Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe
Ile Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Met Arg Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Ile Pro Tyr Val Val Ala
Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Ser Phe Asn Pro
Asn Glu Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Leu
Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Ile Val Phe Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys
Gln Ile Arg Val Ser Thr Leu Arg Phe Val Leu Leu Leu Asn 100 105
110Phe Gly Gly Phe Cys Ile Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe Leu Val His
115 120 125Gly Ser Asn Arg Val Lys Val Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Phe Ser 130 135 140Ile Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Thr Ile Ile Arg
Leu Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Tyr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Thr Ser Trp Leu
Leu Tyr Gly Val Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile 180 185 190Tyr Ile Ala Val Pro
Asn Ile Pro Gly Phe Met Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ile Leu
Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Lys Lys Arg Glu Thr Ala Met Glu Met 210 215 220Gln
Leu Pro Gln His Ser Thr Asp Asn Ile Val Ile Val Ser Ala Ala225 230
235 240Thr Asn Ser Asp Lys Gln Lys Gln His Ser Ser Ser Leu Pro Ser
Asn 245 250 255Asn Leu Val Gly Ala Ala Val Asp Asp Asp Asp Val Thr
Thr Thr Thr 260 265 270Lys Asn Gly Ile Asp Pro Ile Asn Asn Leu Glu
Gln Asn His Gln Val 275 280 285Lys Asp Gln Leu Asn His Val 290
295116294PRTCucumis sativus 116Met Ala Leu Ser Phe Asn Thr His Asn
Pro Ala Ala Phe Thr Phe Gly1 5 10 15Leu Leu Gly Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe
Ile Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro 20 25 30Thr Phe Met Arg Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser 35 40 45Ile Pro Tyr Val Val Ala
Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr 50 55 60Ala Ser Phe Asn Pro
Asn Glu Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val65 70 75 80Gly Cys Leu
Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Ile Val Phe Ala 85 90 95Pro Lys
Gln Ile Arg Val Ser Thr Leu Arg Phe Val Leu Leu Leu Asn 100 105
110Phe Gly Gly Phe Cys Ile Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe Leu Val His
115 120 125Gly Ser Asn Arg Val Lys Val Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Ala
Phe Ser 130 135 140Ile Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Thr Ile Ile Arg
Leu Val Ile Arg145 150 155 160Thr Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe
Tyr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr 165 170 175Leu Ser Ala Thr Ser Trp Leu
Leu Tyr Gly Val Phe Leu Lys Asp Ile 180 185 190Tyr Ile Ala Val Pro
Asn Ile Pro Gly Phe Met Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln 195 200 205Met Ile Leu
Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Lys Lys Arg Glu Thr Ala Met Glu Met 210 215 220Gln
Leu Pro Gln His Ser Thr Asp Asn Thr Val Ile Val Ser Ala Ala225 230
235 240Thr Asn Ser Asp Lys Gln Lys Gln His Ser Ser Ser Leu Pro Ser
Asn 245 250 255Asn Leu Val Gly Ala Ala Val Asp Asp Asp Val Thr Thr
Thr Thr Lys 260 265 270Asn Gly Ile Asp Pro Ile Asn Asn Leu Glu Glu
Asn His Gln Val Lys 275 280 285Asp Gln Leu Asn His Val
290117300PRTSolanum lycopersicum 117Met Ala Val Asp Phe Gly His Tyr
Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val
Phe Leu Ser Pro Ile Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Ser Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Ser Thr Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Lys Ser Asn Met
Pro Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Met Phe65 70 75 80Ile Glu
Thr Ile Tyr Val Gly Phe Tyr Leu Phe Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Ala
Arg Val His Thr Ile Lys Met Leu Met Leu Ser Val Val Gly Gly 100 105
110Phe Gly Ala Ile Val Leu Val Thr Glu Phe Leu Phe Lys Gly Val Val
115 120 125Arg Gly Gln Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Ile Phe Ser Leu
Cys Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Gly Ile Val Arg Gln Val Ile
Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Leu Leu Leu Ser
Val Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly
Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile Asn Ile Ala 180 185 190Ala Pro Asn Val Leu
Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile Leu Gln Ile Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Ala Ile
Tyr Ser Lys Lys Glu Lys Ser Ile Ile Lys Glu Gln Lys 210 215 220Leu
Pro Glu Ile Gln Lys Thr Glu Val Ile Val Lys Asp Glu Asn Met225 230
235 240Asn Ala Asn Lys Lys Leu Pro Glu Leu Thr Gln Glu Gln Ile Ile
Asp 245 250 255Ile Val Lys Leu Ala Gly Leu Leu Val Val Thr Asp Lys
Thr Asn Val 260 265 270Ala Thr Cys Pro Asn Asp Thr Asn Cys Gly Val
Lys Ala Val Asn Lys 275 280 285Ile Glu Asn Met Pro Lys Leu Gln Thr
Val Ala Thr 290 295 300118296PRTSolanum lycopersicum 118Met Ala Phe
Ser Ala Asp His Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile
Val Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Thr
Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Thr Ala Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40
45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Leu
50 55 60Lys Thr Asn Thr Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Val
Phe65 70 75 80Val Glu Thr Ile Tyr Val Val Phe Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Ala
Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Ser Arg Val Gln Thr Ile Lys Met Leu Ser Leu Phe
Val Val Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly Ala Ile Ile Leu Val Thr Gln Phe
Leu Phe Lys Gly Val Ile 115 120 125Arg Gly Gln Val Val Gly Trp Ile
Cys Leu Ile Phe Ser Leu Cys Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Gly
Ile Val Arg Lys Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr
Met Pro Leu Leu Leu Ser Val Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Val
Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile Asn Ile Ala 180 185
190Ala Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Val Leu Gln Met Ile Leu
195 200 205Tyr Val Ile Tyr Ser Lys Lys Glu Lys Ala Ile Leu Lys Glu
Gln Lys 210 215 220Leu Pro Glu Ile Gln Lys Gly Glu Val Ile Val Lys
Asp Glu Asn Met225 230 235 240Asn Ala Asp Lys Lys Phe Pro Glu Leu
Thr Gln Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp 245 250 255Ile Val Arg Leu Gly Leu Met
Val Cys Lys Gly Lys Val His Val Ala 260 265 270Thr Cys Pro His Gly
Thr Thr Cys Glu Pro Lys Val Asp Glu Asn Glu 275 280 285Pro Lys Leu
Gln Thr Val Glu Val 290 295119298PRTSolanum lycopersicum 119Met Val
Phe Asn His Trp Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Leu Gly Asn Ile1 5 10 15Val
Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Ile Pro Thr Phe Tyr Asn Ile 20 25
30Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val Val
35 40 45Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu Lys
Ser 50 55 60Asn Met Pro Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Met Phe
Ile Glu65 70 75 80Thr Ile Tyr Val Gly Leu Tyr Leu Leu Tyr Ala Pro
Asn Lys Ala Arg 85 90 95Val His Thr Ile Lys Met Leu Met Leu Ser Val
Val Gly Gly Phe Gly 100 105 110Ala Ile Val Leu Ile Thr Glu Phe Leu
Phe Lys Gly Val Val Arg Gly 115 120 125Gln Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys
Leu Ile Phe Ser Leu Cys Val Phe Val 130 135 140Ala Pro Leu Gly Ile
Val Arg Lys Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser Val Glu145 150 155 160Tyr Met
Pro Leu Leu Leu Ser Val Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Met 165 170
175Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile Asn Ile Ala Ala Pro
180 185 190Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile Leu Gln Ile Val Leu
Tyr Ala 195 200 205Ile Tyr Ser Lys Lys Glu Lys Val Ile Leu Lys Glu
Gln Lys Leu Pro 210 215 220Glu Ile Gln Thr Pro Ala Val Ile Val Lys
Asn Glu Asn Met Met Asn225 230 235 240Thr Thr Lys Lys Leu Pro Glu
Leu Thr Gln Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp Ile 245 250 255Val Lys Leu Gly Leu
Leu Val Cys Ser Asp Lys Thr Gln Val Ala Thr 260 265 270Cys Pro Asn
Asp Thr Asn Cys Gly Val Lys Asp Thr Asn Asn Asn Val 275 280 285Val
Asn Met Pro Lys Leu Gln Thr Val Ala 290 295120282PRTSolanum
lycopersicum 120Met Ala Ile Ala Gly His Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Val
Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Ile Pro
Thr Phe Asn Lys 20 25 30Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Tyr Gln
Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val 35 40 45Ile Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Ile
Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Leu Lys 50 55 60Thr Asn Thr Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ser Phe Gly Met Leu Ile65 70 75 80Glu Thr Ile Tyr Val Ser Leu
Phe Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys Ala 85 90 95Arg Val Asn Thr Val Lys
Met Leu Leu Leu Thr Val Val Gly Gly Phe 100 105 110Gly Ala Ile Ile
Leu Val Thr Gln Phe Leu Phe Lys Gly Val Val Arg 115 120 125Gly Gln
Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Ile Phe Ser Leu Cys Val Phe 130 135
140Val Ala Pro Leu Gly Ile Val Arg Gln Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser
Val145 150 155 160Glu Tyr Met Pro Ile Leu Leu Ser Val Phe Leu Thr
Ile Ser Ala Val 165 170 175Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys
Asp Val Asn Ile Ala Ala 180 185 190Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe
Gly Ile Leu Gln Met Ile Leu Tyr 195 200 205Ala Met Tyr Arg Lys Lys
His Lys Pro Ile Val Asn Val Asn Val Glu 210 215 220Val Gln Asn Pro
Val Ile Ile Leu Asp Asp Asn Lys Lys Ile Pro Glu225 230 235 240Leu
Thr Glu Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp Ile Val Lys Leu Gly Lys Leu Val 245 250
255Cys Ser Gly Lys Ile Gln Met Ala Ser Thr Leu Asn Gln Asn Ala Ser
260 265 270Lys Glu Val Lys Gln Gln Thr Glu Glu Ala 275
280121295PRTSolanum lycopersicum 121Met Thr Thr His Leu Ala Phe Val
Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn Ile Val1 5 10 15Ser Phe Met Val Tyr Leu Ala
Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr Lys Ile Tyr 20 25 30Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu
Gly Phe Gln Ser Val Pro Tyr Val Val Gly 35 40 45Leu Phe Ser Ala Met
Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Leu Lys Pro Asp 50 55 60Thr Thr Leu Leu
Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly Cys Phe Ile Gln Thr65 70 75 80Phe Tyr
Ile Cys Phe Phe Leu Phe Tyr Ala Thr Lys Lys Ala Lys Met 85 90 95Asp
Thr Met Lys Leu Leu Leu Ser Met Asn Val Val Gly Leu Gly Leu 100 105
110Ile Ile Phe Leu Thr Gln Phe Phe Ala Lys Gly Ser Asn Arg Ala Gln
115 120 125Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Ile Phe Ser Phe Cys Val Phe
Val Ala 130 135 140Pro Leu Gly Val Leu Arg Gln Val Ile Arg Thr Lys
Ser Val Glu Tyr145 150 155 160Met Pro Phe Gln Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu
Thr Leu Ser Ala Val Met Trp 165 170 175Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu Leu Arg
Lys Asp Tyr Asn Ile Ala Ile Pro Asn 180 185 190Val Leu Gly Phe Ser
Leu Gly Val Ile Gln Met Thr Leu Tyr Leu Ile 195 200 205Tyr Lys Asn
Ala Lys Lys Val Thr Lys Glu Val Lys Leu Glu Val Thr 210 215 220Glu
Ile Val Ala Asp Asp Lys Glu Leu Lys Leu Ser Glu Glu Ile Leu225 230
235 240Lys Asp Gln Ile Ile Asp Val Val Lys Leu Ser Ala Ile Val Cys
Ser 245 250 255Glu Ile Ile Pro Met Val Thr Gly Asn Glu Leu Lys Asn
Glu Ile Asn 260 265 270Leu Pro Gln Leu Asn Val Ile Ile Asn Glu Asp
Met Met Ile Lys Pro 275 280 285Lys Ala Ile Ile Glu Ala Ser 290
295122297PRTSolanum lycopersicum 122Met Ala Gly Ile Ser Gly His Trp
Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Ile Val
Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Lys Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys
Ser Thr Asp Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe
Ser Ser Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Leu 50 55 60Lys Thr Asn Thr
Thr Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Val Phe65 70 75 80Ile Glu
Thr Ile Tyr Val Gly Phe Tyr Leu Phe Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Asp
Arg Val Gln Thr Ile Lys Met Leu Met Leu Ser Val Val Gly Gly 100 105
110Phe Gly Ala Ile Val Leu Ile Thr Glu
Phe Leu Phe Lys Gly Val Val 115 120 125Arg Gly Gln Ile Val Gly Trp
Ile Cys Leu Ile Phe Ser Leu Cys Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu
Gly Ile Val Lys Gln Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu
Tyr Met Pro Leu Leu Leu Ser Ile Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170
175Val Val Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile Asn Ile Ala
180 185 190Ile Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Leu Gly Ile Leu Gln Met
Val Leu 195 200 205Tyr Val Ile Tyr Asn Lys Lys Glu Lys Ala Ile Leu
Lys Glu Gln Lys 210 215 220Leu Pro Glu Lys Leu Gln Asn His Met Ile
Ile Ser Met Asp Glu Lys225 230 235 240Asn Lys Asn Ser Pro Gly Leu
Thr Glu Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp Ile Val 245 250 255Lys Leu Gly Ser Leu
Ile Ser Ser Gly Lys Ile His Ile Ala Ser Cys 260 265 270Leu His Asp
Ala Met Cys Ala Ser Ala Lys Ile Glu Asn Thr Pro Asn 275 280 285Asn
Leu Glu Thr Val Glu Ala Ile Asn 290 295123276PRTSolanum
lycopersicum 123Met Thr Ser Val Ser His Thr His Pro Leu Val Tyr Thr
Phe Gly Ile1 5 10 15Leu Gly Asn Leu Val Ser Phe Met Val Phe Ile Ala
Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Val Lys Lys Lys Ser Ser Glu
Gly Phe His Ser Leu 35 40 45Pro Tyr Val Val Gly Leu Phe Ser Ala Met
Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala 50 55 60Met Val Lys Thr Asn Val Thr Leu Leu
Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly65 70 75 80Cys Ile Ala Glu Thr Ile Tyr
Val Ala Ile Tyr Phe Thr Tyr Ala Thr 85 90 95Lys Lys Ala Arg Met Lys
Thr Leu Gly Leu Val Leu Leu Leu Asn Phe 100 105 110Gly Val Phe Gly
Leu Ile Leu Phe Leu Thr Gln Ile Leu Cys Gln Gly 115 120 125Thr Lys
Arg Ala Glu Val Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Met Ala Phe Ser Ile 130 135
140Ser Val Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Gly Arg Val Ile Arg
Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Asn Leu Ser Leu
Ala Leu Thr Val 165 170 175Ser Ala Val Met Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Leu
Leu Leu Lys Asp Val Tyr 180 185 190Val Ala Val Pro Asn Ile Pro Gly
Met Ile Leu Gly Val Leu Gln Met 195 200 205Ile Leu Tyr Gly Ile Tyr
Arg Asn Ser Lys Ser Asn Asn Val Ala Thr 210 215 220Glu Lys Glu Leu
Pro Ile Val Val Lys Val Asp Gln Glu Gln Pro Thr225 230 235 240Lys
Val Asn Ser Glu Val Tyr Pro Val Asn Ile Ser Ser Leu Asp Ser 245 250
255Glu Asn Gly Glu Ala Lys Asp Gly Lys Asn Leu Gln Asp Pro Gln Met
260 265 270Asn Ser Gln Val 275124287PRTSolanum lycopersicum 124Met
Ala Gly Phe Ser Asp His Trp Thr Phe Ala Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10
15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Phe Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr
20 25 30Asn Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Tyr Gln Ser Ile Pro
Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala
Phe Leu 50 55 60Lys Thr Asn Thr Thr Leu Leu Val Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe
Gly Cys Phe65 70 75 80Ile Glu Thr Leu Tyr Val Gly Phe Tyr Leu Phe
Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Ala Arg Val Gln Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu
Leu Leu Val Val Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly Ala Ile Ile Leu Ile Thr
Gln Phe Leu Phe Lys Gly Ala Ile 115 120 125Arg Ala Gln Ile Val Gly
Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe Ser Leu Cys Val 130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro
Leu Cys Ile Val Arg Gln Val Ile Lys Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val
Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Leu Leu Ser Val Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170
175Val Met Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Phe Asn Ile Ala
180 185 190Ile Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Ile Phe Gly Ile Leu Gln Met
Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Val Met Tyr Asn Lys Lys Glu Lys Val Val Ile
Lys Glu Gln Asn 210 215 220Leu Pro Glu Leu Lys Asp His Val Ile Ile
Ile Glu Asp Asp Lys Lys225 230 235 240Lys Leu Pro Glu Leu Ser Glu
Glu Gln Ile Ile Asn Ile Ile Lys Leu 245 250 255Gly Ser Leu Val Tyr
Ser Asp Lys Asn Tyr Gly Asn Leu Thr Glu Val 260 265 270Ala Lys Asn
Asp Lys Ala Ile Ser Lys Leu Gln Thr Leu Glu Ala 275 280
285125286PRTSolanum lycopersicum 125Met Pro Leu Phe Thr Thr Leu Gln
Leu Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Ile Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Gly Val Ser Phe Leu
Val Tyr Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Arg Ile Phe Lys Arg
Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Ser Val Ser Leu
Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Tyr Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Tyr 50 55 60Leu Lys Lys Asn
Glu Ile Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Thr65 70 75 80Gly Ile
Gln Leu Ile Tyr Leu Thr Ile Phe Met Ile Tyr Ala Thr Lys 85 90 95Ser
Ala Lys Ile Phe Ala Thr Lys Leu Leu Ile Gly Phe Asn Leu Val 100 105
110Ala Phe Gly Ala Ile Val Gly Leu Thr Tyr Val Phe Ala Asn Glu Asn
115 120 125Asp Leu Arg Ile Ser Ile Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala Val Phe
Ser Val 130 135 140Ser Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Arg
Val Ile Gln Thr145 150 155 160Lys Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Pro
Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile 165 170 175Cys Ala Val Met Trp Phe Phe
Tyr Gly Leu Leu Lys Lys Asp Met Tyr 180 185 190Ile Ala Met Pro Asn
Ile Leu Gly Phe Ser Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met 195 200 205Ile Leu Tyr
Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn Arg Lys Gln Gln Val Leu Pro Asp 210 215 220Leu
Ser Leu Met Asp Leu Lys Glu Ile Ala Ile Asp Met Lys Ala Val225 230
235 240Val Val Glu Ile Ile Gln Glu Asn Val Asp Asp Glu Asn Lys Asn
Lys 245 250 255Ile Asn Lys Gln Glu Glu Val Val Ser Val Asp Glu Lys
Lys Asp Val 260 265 270Glu Tyr Asp Lys Gln Asp Val Ala Leu Thr Thr
Ser Asn Val 275 280 285126310PRTFragaria vesca 126Met Thr Ser Ser
His Ser Pro Leu Ala Phe Ala Phe Gly Ile Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Val
Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val
Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ile
Phe Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Thr Ile Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Ser Leu 50 55
60Lys Ser Asp Glu Met Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Gly Phe Gly Cys Val65
70 75 80Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Ile Ala Met Tyr Ile Thr Tyr Ala Pro Lys
Lys 85 90 95Ala Arg Val Asn Thr Leu Arg Leu Leu Leu Leu Val Asn Phe
Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Cys Leu Ile Leu Phe Leu Ser His Phe Leu Thr
Gln Gly Pro Thr 115 120 125Arg Val Lys Val Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val
Ala Phe Ser Val Ser Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met
Arg Leu Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro
Phe Ser Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Ser Ala 165 170 175Ile Met Trp
Leu Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Leu Tyr Val Ala 180 185 190Ala
Pro Asn Ile Leu Gly Phe Ser Phe Gly Val Val Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200
205Tyr Ala Ala Tyr Arg Asn Lys Lys Thr Val Leu Val Asp Glu Glu Lys
210 215 220Val Pro Glu His Lys Thr Ala Asp Asp Phe Val Lys Gln Ile
Asn Ile225 230 235 240Thr Val Leu Pro Ser Pro Lys Ala Gln Val Gln
Val Lys Glu Glu Ala 245 250 255Val Ser Pro Ala Arg Ala Asp Ser Ser
Asp Glu Ser Ser Asp Asp His 260 265 270Glu Gln Asn Val His Asp Gln
Gln Arg Glu His Val Pro Gln Pro Cys 275 280 285His Val Asp Ala Gln
Gly Ala Asp Leu Ile Ser Lys Gln Val Pro Ala 290 295 300Leu Val Gln
Cys Glu Val305 310127292PRTFragaria vesca 127Met Ala Ile His His
Pro Leu Thr Leu Ala Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn1 5 10 15Ile Ile Ser Phe
Met Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Met Pro Thr Phe Tyr Lys 20 25 30Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Thr Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ala Leu Pro Tyr Ala 35 40 45Val Ala
Leu Phe Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Leu Lys 50 55 60Gln
Asp Ala Thr Phe Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly Cys Val Ile65 70 75
80Glu Thr Val Tyr Leu Ala Ile Phe Leu Phe Tyr Ser Pro Lys Lys Ala
85 90 95Arg Ile Ser Thr Val Lys Phe Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val Leu Gly
Tyr 100 105 110Gly Leu Met Leu Val Leu Thr Leu Phe Leu Ala Lys Gly
Glu Ile Arg 115 120 125Leu Lys Val Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Val Phe
Asn Leu Thr Val Phe 130 135 140Ala Ala Pro Leu Cys Ile Leu Lys Lys
Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser Val145 150 155 160Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Pro
Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Gly Ala Val 165 170 175Met Trp Phe Phe
Tyr Gly Phe Leu Leu Lys Asp Tyr Asn Ile Ala Phe 180 185 190Pro Asn
Ile Leu Gly Phe Met Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met Val Leu Tyr 195 200
205Ile Val Tyr Lys Asn Ala Lys Lys Val Val Leu Leu Glu Glu Pro Ser
210 215 220Lys Val Gln Glu Leu Ser Asp His Ile Ile Glu Val Met Lys
Ile Ser225 230 235 240Thr Met Val Cys Pro Asp Leu Thr Pro Val Val
Leu Gln Pro Asn Asp 245 250 255Ile Asn Ile Asp Leu Ile Glu Val Ile
Pro Leu Asp Pro Asn Asn Val 260 265 270Val Lys Gly Ile Asn Ala Glu
Glu Ser Lys Glu Asp Met Asp Asp Ala 275 280 285Ser Thr Lys Val
290128291PRTFragaria vescamisc_feature(137)..(137)Xaa can be any
naturally occurring amino acid 128Met Ser Met Tyr Asn Ser Gln His
His Leu Ala Phe Ile Phe Val Val1 5 10 15Ile Gly Asp Val Ile Ser Phe
Met Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr 20 25 30Phe Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys
Lys Lys Thr Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu 35 40 45Pro Tyr Leu Val Ala
Leu Phe Gly Ser Thr Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Gly 50 55 60Ile Val Lys Gln
Asn Met Val Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly65 70 75 80Ser Val
Met Glu Thr Leu Tyr Ile Ala Met Tyr Ile Val Tyr Ala Thr 85 90 95Asn
Ala Ser Arg Lys Leu Thr Ile Lys Leu Phe Gly Phe Met Asn Leu 100 105
110Gly Leu Phe Ser Leu Ile Val Val Cys Ile Ser Tyr Ala Val His Ser
115 120 125Glu Tyr Arg Ala Leu Val Leu Gly Xaa Ile Asn Val Ala Val
Thr Ile 130 135 140Cys Ala Ser Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Val Ala Gln
Val Ile Arg Thr145 150 155 160Gly Ser Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Thr
Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu 165 170 175Ser Gly Val Leu Trp Phe Ser
Tyr Gly Met Leu Leu Lys Asp Ile Phe 180 185 190Ile Ala Leu Pro Asn
Gly Leu Gly Phe Val Leu Gly Leu Leu Gln Met 195 200 205Leu Phe Tyr
Ala Ile Tyr Arg Asn Arg Lys Gln Val Thr Val Asp Gln 210 215 220Arg
Asn Lys Leu Pro Ala Pro Glu His Val Thr Asp Thr Val Ile Leu225 230
235 240Ser Ile Ala Thr Ser Glu Val Gln Ser Val Asp Ala Lys Gln Cys
Tyr 245 250 255Asp Tyr Asp Gly Lys Asp Gly Ser Lys Glu Ser Asp Gly
Asp Glu His 260 265 270Glu Lys Cys Val Val Glu Met Val Asp Val Asp
Ala Ser Gly Asp Leu 275 280 285Ala Ser Leu 290129257PRTFragaria
vesca 129Met Ala Tyr Ser Thr Thr Glu Gln Leu Ala Phe Ser Phe Gly
Leu Leu1 5 10 15Gly Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Met Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Met
Pro Thr Phe 20 25 30Tyr Arg Ile Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Ser Glu Gly Phe
Gln Ser Ile Pro 35 40 45Tyr Val Val Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Leu
Leu Tyr Tyr Gly Val 50 55 60Ile Lys Thr Asn Ala Ile Leu Ile Ile Ser
Ile Asn Ala Phe Gly Ile65 70 75 80Val Ile Glu Val Ala Tyr Leu Ile
Phe Tyr Leu Thr Tyr Ala Pro Lys 85 90 95Lys Gln Arg Ile Phe Thr Leu
Asn Leu Ile Leu Leu Val Asn Val Ala 100 105 110Phe Gly Leu Thr Leu
Ala Ala Thr Ile Phe Leu Leu Ser Gly Thr Lys 115 120 125Arg Val Ala
Ala Val Gly Trp Ile Cys Ala Val Phe Asn Ile Ala Val 130 135 140Phe
Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Arg Glu Val Ile Arg Thr Lys Ser145 150
155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Gly Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu Thr Leu Cys
Ala 165 170 175Thr Thr Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Phe Thr Lys Asp Tyr
Tyr Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile
Ala Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Met Val Tyr Arg Asn Ser Gly Lys
Asp His Asp Glu Val Glu Ala 210 215 220Lys Thr Arg Thr Asn Gly Asp
Asp Leu Glu Met Arg Tyr Lys Val Ile225 230 235 240Ser Lys Ser Lys
Thr Thr Asn His Asn Lys Leu Tyr Arg Ser Val Ser 245 250
255Thr130254PRTCicer arietinum 130Met Ser Lys Met Phe Thr Phe Ser
Asp His Glu Met Val Leu Ile Phe1 5 10 15Gly Leu Leu Gly Asn Ile Val
Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Leu 20 25 30Pro Thr Phe Tyr Ser Ile
Cys Lys Lys Lys Thr Ser Glu Gly Phe Gln 35 40 45Ser Ile Pro Tyr Val
Val Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Leu Leu Tyr 50 55 60Tyr Gly Leu Leu
Lys Thr Asn Ala Ile Leu Ile Ile Thr Ile Asn Cys65 70 75 80Ile Gly
Cys Val Ile Glu Val Leu Tyr Leu Ile Ile Tyr Ile Ile Tyr 85 90 95Ala
Pro Arg Lys Leu Lys Ile Ser Thr Leu Ala Leu Ile Leu Val Ala 100 105
110Asp Leu Gly Gly Leu Gly Leu Thr Leu Ile Ile Thr Asn Phe Ile Val
115 120 125Lys Ser Tyr Tyr Arg Val His Ala Val Gly Leu Ile Cys Ala
Ile Phe 130 135 140Asn Ile Ala Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met
Arg Lys Val Ile145 150 155 160Lys Thr Arg Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro
Phe Phe Leu Ser Leu Phe Leu 165 170 175Thr Leu Cys Ala Thr Met Trp
Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Phe Asp Lys Asp 180 185 190Asn Tyr Ile Met Leu
Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe Leu Phe Gly Ile Ser 195 200 205Gln Met Ile
Leu Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Lys Asn Ala Lys Asn Lys Val Glu 210 215 220Ala
Asn Ser Asn Glu Gln Gln Glu Tyr Gly Asp Asp Asp Gly Asn Lys225 230
235 240Glu Asp Phe Pro Ser Ile Val Glu Met Lys Glu Asn Ile Val 245
250131255PRTCicer arietinum 131Met Ala Met Thr Arg
Glu Ser Trp Ala Phe Val Phe Gly Leu Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser
Phe Ala Val Phe Leu Ser Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Leu Ile Phe
Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Gln Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val
Ala Leu Phe Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Ile Tyr Tyr Ala Phe Val 50 55 60Lys
Arg Glu Ala Ala Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile Asn Thr Phe Gly Ile65 70 75
80Val Val Glu Ser Cys Tyr Leu Ile Val Phe Leu Ile Tyr Ala Thr Lys
85 90 95Lys Ser Arg Leu Ser Thr Ile Lys Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Asn Val
Phe 100 105 110Gly Phe Gly Ala Met Leu Leu Ser Thr Leu Tyr Leu Ala
Lys Gly Ala 115 120 125Lys Arg Leu Ala Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu
Val Phe Asn Ile Thr 130 135 140Val Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Phe Ile Ile
Ser Arg Val Ile Arg Thr Arg145 150 155 160Ser Val Glu Tyr Met Pro
Phe Phe Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Ile Asn 165 170 175Ala Val Met Trp
Phe Phe Tyr Gly Leu Leu Leu Lys Asp Tyr Tyr Val 180 185 190Ala Leu
Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe Val Phe Gly Ile Ile Gln Met Val 195 200
205Met Tyr Leu Ile Tyr Arg Asn Ala Thr Pro Val Pro Leu Asp Gly Pro
210 215 220Val Lys Gly Gln Glu Leu Ser Gly Gly His Ile Val Asp Val
Val Lys225 230 235 240Ile Gly Ser Asp Pro Asn Arg Gly Gly Gly Ala
Val Ser Lys Val 245 250 255132302PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic
amino acid sequence 132Met Gly Ala Val Gly Ser Pro Trp Ala Phe Leu
Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Val Ser Phe Leu Val Tyr Leu Ser
Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Val Phe Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Gly
Gly Phe Ser Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu Val Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met
Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Met Leu 50 55 60Thr Thr Gly Ser Phe Leu Leu
Ile Ser Ile Asn Gly Ala Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Ile Glu Ser Val Tyr
Val Val Val Tyr Val Ala Tyr Ala Pro Arg Lys 85 90 95Ala Lys Leu Arg
Thr Ala Lys Leu Ile Gly Leu Met Asp Val Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly
Ile Val Leu Leu Val Thr His Val Leu Val His Gly Ser Lys 115 120
125Arg Val Gln Ile Val Gly Trp Val Cys Leu Ala Phe Ser Met Cys Val
130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile Arg Arg Val Ile Gln Ser
Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Leu Phe
Leu Thr Val Cys Ala 165 170 175Thr Met Trp Leu Ala Tyr Gly Leu Leu
Lys Lys Asp Tyr Cys Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe
Val Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met Gly Leu 195 200 205Tyr Val Phe Tyr Arg
Asn Arg Lys Pro Val Ile Phe Asp Pro Glu Asp 210 215 220Lys Leu Arg
Ala Pro Glu Gln Met Lys Ser Ile Val Ile Leu Ser Thr225 230 235
240Ile Pro Thr Ser Glu Val His Pro Val Asp Ala Lys His Cys Asp Gly
245 250 255Asn Asp Gly Glu Asp Val Asp Gly Lys Asp Gly Asn Lys Glu
Gly Asp 260 265 270Gly Asp Glu His Glu Lys Cys Val Val Val Leu Val
Asp Met Asp Ala 275 280 285Ser Gly Glu Leu Gln Leu Lys Ser Asp Glu
Pro Cys Val Glu 290 295 300133288PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic
amino acid sequence 133Met Ala Met Asn His Ser Thr Leu Ala Phe Val
Phe Gly Leu Ile Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Val Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ser
Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val Cys Lys Ser Lys Ser Ala Glu
Gly Tyr His Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Met Ala Leu Phe Ser Cys Met
Leu Trp Ile Phe Tyr Gly Phe Val 50 55 60Thr Ser Gly Asp Phe Leu Leu
Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Val Gly Cys Leu65 70 75 80Ile Glu Ser Val Tyr
Val Ile Val Phe Met Ile Tyr Ala Pro Arg Lys 85 90 95Ala Arg Ile Arg
Thr Ala Arg Leu Leu Leu Leu Leu Asp Ile Gly Leu 100 105 110Phe Gly
Ile Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr Leu Val Leu Thr His Gly Asp Lys 115 120
125Arg Val Val Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Leu Gly Phe Asn Val Ala Val
130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Val Ala Lys Val Val Lys Ser
Arg Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Phe Ser Leu Ser Leu Phe
Leu Thr Val Cys Ala 165 170 175Val Ala Trp Phe Phe Tyr Gly Phe Leu
Leu Lys Asp Tyr Asn Val Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Ile Ile Gly Leu
Val Leu Gly Ile Leu Gln Met Ile Leu 195 200 205Tyr Phe Met Tyr Met
Asn Lys Thr Pro Val Ala Ser Gln Val Lys Glu 210 215 220Gly Lys Glu
Ala Trp Lys Ala Pro Ala Glu Asp His Val Val Val Ile225 230 235
240Asn Val Gly Lys Ala Asp Lys Ser Ser Cys Ala Glu Val Arg Pro Val
245 250 255Thr Glu Met Ala Gly Ala Val Asp Val Pro Arg Arg Cys Ala
Ala Glu 260 265 270Ala Ala Ala Ala Pro Gly Val Asp Phe Ala Arg Ser
Val Asn Val Val 275 280 285134333PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic
amino acid sequence 134Met Ala Met Asn His Ser Thr Leu Ala Phe Val
Phe Gly Met Ile Gly1 5 10 15Asn Ile Ile Ser Phe Ile Val Phe Leu Ser
Pro Leu Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Val Phe Lys Lys Lys Thr Ser Glu
Gly Tyr His Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Val Val Ala Leu Phe Ser Ser Met
Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Leu Val 50 55 60Lys Ser Gly Ser Phe Leu Leu
Ile Thr Ile Asn Ser Phe Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Val Glu Ser Val Tyr
Val Val Met Phe Val Leu Tyr Ala Pro Arg Lys 85 90 95Ala Arg Val Ser
Thr Leu Arg Met Ile Leu Leu Leu Val Ile Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly
Leu Ile Leu Leu Leu Thr His Leu Leu Ser His Gly Pro Leu 115 120
125Arg Val Gln Val Ile Gly Trp Val Cys Leu Gly Phe Asn Ile Ser Val
130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Ile Met Ala Lys Val Ile Gln Thr
Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Leu Ser Leu Ser Leu Phe
Leu Thr Val Cys Ala 165 170 175Ile Ala Trp Phe Ala Tyr Gly Phe Phe
Leu Lys Asp Tyr Asn Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Ile Gly Leu
Val Leu Gly Ile Val Gln Met Leu Leu 195 200 205Tyr Met Ile Tyr Arg
Asn Lys Lys Pro Ala Ala Ala Ala Val Ile Met 210 215 220Val Glu Glu
Val Lys Leu Pro Ala Glu Gln Tyr Ala Ser Lys Glu Val225 230 235
240Ala Pro Pro Ala Ala Ala His Glu Gly Ser Arg Ala Ser Cys Gly Ala
245 250 255Glu Val His Pro Ile Asp Ile Asp Thr Leu Pro Val Ala Asp
Val Gly 260 265 270Arg His His Asp Ser Gln Ala Val Val Val Ile Asp
Val Asp Val Glu 275 280 285Pro Ala Ala Thr Cys Ala Ala Ala Ala Ala
Ala Ala Gly Gly Val Arg 290 295 300Gly Asp Gly Ala Ala Gly Val Val
Thr Ala Gly Pro Glu Gln Pro Ala305 310 315 320Ala Met Lys Pro Val
Asp Met Ala Ile Ala Val Glu Ala 325 330135296PRTArtificial
SequenceSynthetic amino acid sequence 135Met Gly Ala Val Gly Ser
Pro Trp Ala Phe Leu Phe Gly Val Ile Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Val Ser Phe
Leu Val Tyr Leu Ala Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Arg Val Cys Lys
Lys Lys Thr Thr Gln Gly Phe His Ser Leu Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ile Met Ala
Leu Leu Ser Ala Met Leu Trp Leu Phe Tyr Gly Phe Val 50 55 60Lys Thr
Gly Glu Leu Leu Leu Ile Ser Ile Asn Gly Phe Gly Cys Phe65 70 75
80Ile Glu Thr Val Tyr Leu Val Leu Phe Met Ile Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys
85 90 95Ala Lys Val Ser Thr Leu Arg Ile Ile Gly Leu Leu Asn Phe Gly
Val 100 105 110Phe Gly Ile Ile Leu Leu Val Thr His Phe Leu Thr Lys
Ala Glu Lys 115 120 125Arg Val Val Ile Leu Gly Trp Val Cys Val Ala
Phe Ser Ile Cys Val 130 135 140Phe Ala Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Met Arg
Val Val Val Lys Ser Arg Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe
Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Leu Cys Ala 165 170 175Thr Met Trp Phe
Phe Tyr Gly Leu Phe Leu Lys Asp Tyr Cys Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro
Asn Thr Val Gly Leu Thr Phe Gly Val Ile Gln Met Val Leu 195 200
205Tyr Val Phe Tyr Ser Lys Lys Glu Lys Ala Ile Leu Lys Glu Gln Lys
210 215 220Leu Pro Glu Ile Gln Lys Gly Glu Val Ile Val Lys Asp Glu
Asn Met225 230 235 240Asn Ala Asp Lys Lys Phe Pro Glu Leu Thr Gln
Glu Gln Ile Ile Asp 245 250 255Ile Val Arg Leu Gly Leu Met Val Cys
Lys Gly Lys Val His Val Ala 260 265 270Thr Cys Pro His Gly Thr Thr
Cys Glu Pro Lys Val Asp Glu Asn Glu 275 280 285Pro Lys Leu Gln Thr
Val Glu Val 290 295136292PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic amino acid
sequence 136Met Gly Ala Val Gly Ser Pro Trp Ala Phe Ile Phe Gly Val
Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Ile Ser Phe Leu Val Phe Leu Ala Pro Leu Pro
Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Val Tyr Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Glu Gly Phe Ser
Ser Val Pro Tyr 35 40 45Ile Met Ala Leu Leu Ser Cys Met Leu Trp Leu
Phe Tyr Ala Leu Leu 50 55 60Thr Thr Asn Ser Leu Leu Leu Ile Thr Ile
Asn Ser Ala Gly Cys Leu65 70 75 80Ile Glu Thr Ile Tyr Val Ile Leu
Tyr Phe Ile Tyr Ala Pro Lys Lys 85 90 95Ala Lys Ile Phe Thr Ala Lys
Met Val Leu Leu Leu Asn Ile Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly Val Val Leu
Leu Leu Thr Val Phe Leu Thr Lys Ala Glu Lys 115 120 125Arg Val Gln
Ile Ile Gly Trp Ile Cys Val Gly Phe Ala Ile Ala Val 130 135 140Phe
Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile Ala Lys Val Ile Gln Thr Lys Ser145 150
155 160Val Glu Phe Met Pro Leu Thr Leu Ser Phe Phe Leu Thr Val Ser
Ala 165 170 175Val Val Trp Phe Leu Tyr Gly Ile Leu Thr Lys Asp Lys
Tyr Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Thr Leu Gly Phe Leu Leu Gly Leu
Ala Gln Met Gly Leu 195 200 205Tyr Ala Phe Tyr Lys Lys Arg Glu Thr
Ala Met Glu Met Gln Leu Pro 210 215 220Gln His Ser Thr Asp Asn Ile
Val Ile Val Ser Ala Ala Thr Asn Ser225 230 235 240Asp Lys Gln Lys
Gln His Ser Ser Ser Leu Pro Ser Asn Asn Leu Val 245 250 255Gly Ala
Ala Val Asp Asp Asp Asp Val Thr Thr Thr Thr Lys Asn Gly 260 265
270Ile Asp Pro Ile Asn Asn Leu Glu Gln Asn His Gln Val Lys Asp Gln
275 280 285Leu Asn His Val 290137287PRTArtificial SequenceSynthetic
amino acid sequence 137Met Gly Ala Val Gly Ser Pro Trp Ala Phe Leu
Phe Gly Val Leu Gly1 5 10 15Asn Val Val Ser Phe Leu Val Tyr Leu Ser
Pro Val Pro Thr Phe Tyr 20 25 30Gln Val Phe Lys Lys Lys Ser Thr Gly
Gly Phe Ser Ser Ile Pro Tyr 35 40 45Leu Val Ala Leu Leu Ser Ala Met
Leu Trp Leu Tyr Tyr Ala Met Leu 50 55 60Thr Thr Gly Ser Phe Leu Leu
Ile Ser Ile Asn Gly Ala Gly Cys Val65 70 75 80Ile Glu Ser Val Tyr
Val Val Val Tyr Val Ala Tyr Ala Pro Arg Lys 85 90 95Ala Lys Leu Arg
Thr Ala Lys Leu Ile Gly Leu Met Asp Val Gly Gly 100 105 110Phe Gly
Ile Val Leu Leu Val Thr His Val Leu Val His Gly Ser Lys 115 120
125Arg Val Gln Ile Val Gly Trp Val Cys Leu Ala Phe Ser Met Cys Val
130 135 140Phe Val Ala Pro Leu Ser Val Ile Arg Arg Val Ile Gln Ser
Lys Ser145 150 155 160Val Glu Tyr Met Pro Phe Thr Leu Ser Leu Phe
Leu Thr Val Cys Ala 165 170 175Thr Met Trp Leu Ala Tyr Gly Leu Leu
Lys Lys Asp Tyr Cys Ile Ala 180 185 190Leu Pro Asn Val Leu Gly Phe
Val Phe Gly Ile Ala Gln Met Gly Leu 195 200 205Tyr Val Phe Tyr Lys
Tyr Cys Lys Thr Ser Pro His Leu Gly Glu Lys 210 215 220Glu Val Glu
Ala Ala Lys Leu Pro Glu Val Ser Leu Asp Met Leu Lys225 230 235
240Leu Gly Thr Val Ser Ser Pro Glu Pro Ile Ser Val Val Arg Gln Ala
245 250 255Asn Lys Cys Thr Cys Gly Asn Asp Arg Arg Ala Glu Ile Glu
Asp Gly 260 265 270Gln Thr Pro Lys His Gly Lys Gln Ser Ser Ser Ala
Ala Ala Thr 275 280 28513836DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
138taatgtcgac atgaacatcg ctcacactat cttcgg 3613939DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 139tatgagctct taaacttgaa ggtcttgctt tccattaac
3914036DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 140taatgtcgac atggatgttt
ttgctttcaa tgcttc 3614136DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
141tatgagctct cacacgtaag aaacaatcaa aggctc 3614237DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 142taatgtcgac atgggtgata aacttcgatt atccatc
3714337DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 143tatgagctct tagatcgatg
aggcattgtt agaattc 3714441DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
144taatgtcgac atggttaacg ctacagttgc gagaaacatt g
4114538DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 145tatgagctct caagctgaaa
ctcgtttagc ttgtccac 3814640DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
146taatgtcgac atgacggacc cccacaccgc ccggacgatc 4014740DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 147tatgagctct caagcctggc caagttcgat
tccagcattc 4014843DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 148taatgtcgac
atggtgcatg aacagttgaa tcttattcgg aag 4314941DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 149tatgagctct caaacgccgc taactctttt
gtttaaatat g 4115038DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
150taatgtcgac atggtgtttg cacatttgaa ccttcttc 3815140DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 151tatgagctct taaacattgt taggttcttg
gttggtattc 4015241DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 152taatgtcgac
atgttcctca aggttcatga aattgctttt c 4115336DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 153tatgagctct cacttcattg gcctcaccga tccttc
3615439DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 154taatgtcgac atgagtctct
tcaacactga aaacacatg 3915536DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
155tatgagctct catgtagctg ctgcggaaga ggactg 3615639DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 156taatgtcgac atggctctct tcgacactca taacacatg
3915738DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 157tatgagctct caagtagttg
cagcactgtt tctaactc 3815841DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
158ggaattccat atggctctaa ctaacaattt atgggcattt g
4115941DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 159taatgtcgac ttaaacttga
ctttgtttct ggacatcctt g 4116040DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
160taatgtcgac atgggagtca tgatcaatca ccatttcctc
4016136DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 161tatgagctct caaacggttt caggacgagt agcctc
3616239DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 162taatgtcgac atggcagagg
caagtttcta tatcggagt 3916338DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA
163tatgagctct taagagagga gaggttcaac acgtgatg 3816420DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 164gtaaaacgac cagtcttaag 2016517DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 165caggaaacag ctatgac 1716621DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 166tgctgtactt gcttggtatt g
2116718DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 167ggaccagacc agacaacc
18168909DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 168atgggtgctg
ttggttctcc ttgggctttc ctttttggtg tgttgggtaa tgttgtttct 60ttcttggttt
atttgtctcc tgttcctact ttctaccaag ttttcaagaa aaagagtaca
120ggaggttttt cttcaattcc ttacttggtt gctcttttgt ctgcaatgct
ttggttgtat 180tacgctatgc ttactacagg atcattcctc ctcatatcta
ttaacggagc aggttgtgtg 240atcgaatcag tttatgttgt ggtttatgtt
gcttacgcac caagaaaggc taagttgagg 300accgcaaaat tgattggact
catggatgtt ggaggttttg gtatcgttct tttggtgaca 360catgttcttg
tgcacggatc aaagagagtt caaattgtgg gttgggtttg tttggctttt
420tctatgtgcg ttttcgtggc acctctctca gtgatcagaa gggttataca
gagtaaatct 480gtggagtaca tgccttttac tctctcttta ttccttacag
tttgtgctac catgtggttg 540gcttatggac tcttaaaaaa ggattactgc
atagctttac ctaatgtgct tggatttgtt 600ttcggtattg cacaaatggg
tctttatgtg ttttacagaa acaggaagcc tgttatcttc 660gatccagaag
ataaattaag agcacctgag cagatgaagt ctatagttat tctctcaacc
720atacctacta gtgaagtgca tccagttgat gctaaacact gtgatggaaa
tgatggtgaa 780gatgttgatg gaaaagatgg taacaaggag ggagatggag
atgaacatga gaagtgcgtg 840gttgtgctcg tggatatgga tgctagtgga
gagttacagt tgaagtctga tgaaccttgt 900gtggaatga
909169867DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 169atggctatga
accactctac tctcgctttt gttttcggat tgatcggtaa tatcgtttct 60ttcttagttt
tcctcagtcc tgtgcctact ttctacagag tttgtaagag taaatctgct
120gaaggttatc attcaatacc ttacgttatg gctcttttta gttgcatgtt
gtggatcttt 180tacggattcg ttacctctgg agattttctt ttgataacta
tcaatagtgt gggatgtttg 240attgagtctg tgtatgttat tgtgtttatg
atctatgctc caagaaaggc aagaattagg 300acagctaggc tcttactttt
gctcgatatc ggacttttcg gtattatcct ccttttgact 360cttgttttga
cacacggaga taaaagagtt gtgataattg gatggatctg tctcggtttt
420aacgttgctg tgttcgctgc acctctttct gttgtggcaa aggttgtgaa
atcaaggagt 480gttgaattca tgccattctc tctctcatta tttcttaccg
tttgcgctgt ggcatggttt 540ttctatggat tcctcttaaa ggattacaat
gttgctttgc ctaacatcat aggattggtg 600ctcggtatcc tccaaatgat
actctacttc atgtacatga ataagacacc tgttgcttca 660caggtgaagg
aaggaaaaga ggcatggaaa gctccagcag aggatcatgt tgtggttatt
720aacgttggaa aggctgataa atcttcatgc gcagaagtta gacctgtgac
cgagatggct 780ggagcagttg atgtgccaag aaggtgtgca gcagaagcag
cagcagcacc tggagtggat 840ttcgcaagga gtgtgaatgt tgtttga
8671701002DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 170atggctatga
accactctac tctcgctttt gtgtttggta tgatcggaaa tattatctct 60tttatcgtgt
ttttgtctcc actccctact ttctaccaag tgttcaagaa aaagacaagt
120gaaggatatc attctgttcc ttacgttgtg gctcttttct cttcaatgct
ttggttgtat 180tacgctttgg ttaaaagtgg atcttttctt ttgattacca
tcaattcatt cggttgtgtt 240gtggagagtg tgtatgttgt gatgtttgtt
ctctacgctc ctagaaaggc aagggtgagt 300acattgagaa tgatcctctt
acttgttata ggaggtttcg gacttatctt gctcttaacc 360catcttttgt
cacacggtcc actcagggtg caagttatag gatgggtttg tttaggtttt
420aacatttctg tgttcgttgc tcctttgtca attatggcaa aagtgatcca
gaccaagtct 480gttgaattca tgccactctc attaagtctt ttcttgactg
tttgcgctat tgcatggttc 540gcttatggat ttttccttaa ggattacaac
atagctttgc ctaacgttat tggactcgtg 600ttaggtatcg ttcaaatgct
cctctacatg atctacagaa ataagaagcc tgctgcagct 660gcagtgataa
tggttgaaga ggtgaaactt ccagctgaac agtacgcatc taaggaggtt
720gctcctccag ctgcagctca tgaaggatct agagcttcat gtggtgcaga
ggttcaccct 780atagatattg atacattgcc agttgctgat gtgggaaggc
atcacgattc acaggctgtt 840gtggttatcg atgtggatgt tgagccagca
gctacttgcg ctgcagcagc tgcagctgca 900ggaggtgtta gaggagatgg
tgctgctggt gtggttacag ctggtcctga acaacctgct 960gctatgaaac
ctgtggatat ggctattgct gtggaggcat ga 1002171891DNAArtificial
SequenceSynthetic DNA 171atgggtgctg tgggtagtcc ttgggctttt
ctcttcggtg ttattggtaa tgttgtgtct 60ttcctcgtgt atctcgctcc tgttccaact
ttctacagag tttgtaagaa aaagactaca 120caaggattcc atagtttgcc
ttatattatg gctcttttgt ctgcaatgtt gtggctcttt 180tacggattcg
ttaagaccgg tgaacttctc cttatatcta ttaacggatt tggttgcttc
240atcgaaactg tgtatcttgt tctttttatg atatacgctc caaaaaaggc
aaaagtttca 300actcttagaa ttatcggatt gctcaacttt ggagtgttcg
gtataattct ccttgttacc 360cacttcttaa ctaaagctga gaagagggtt
gtgattcttg gttgggtgtg tgttgcattt 420tcaatctgcg tgttcgctgc
acctttgagt gttatgagag ttgtggttaa atctagatca 480gttgaataca
tgccttttac tctctctttc tttcttacac tctgtgctac catgtggttt
540ttctatggat tattccttaa ggattactgc atagcattgc ctaatactgt
gggactcaca 600tttggtgtta tccagatggt gttgtatgtt ttctactcaa
aaaaggagaa ggctattctc 660aaggaacaaa agcttcctga gatacagaaa
ggtgaagtga ttgttaagga tgaaaacatg 720aacgctgata agaagttccc
agaacttaca caagagcaga tcatagatat cgtgaggttg 780ggactcatgg
tttgtaaagg aaaggtgcat gttgctacct gcccacacgg aaccacctgt
840gaacctaaag ttgatgagaa cgaaccaaag ttgcagactg ttgaagtgtg a
891172879DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 172atgggtgctg
ttggtagtcc ttgggctttt atctttggtg tgttgggtaa tgtgatttct 60ttcttggtgt
tccttgctcc tcttcctaca ttctaccaag tttacaagaa aaagtcaacc
120gaaggattct cttcagtgcc ttatatcatg gctcttttga gttgtatgtt
atggcttttc 180tatgcactcc tcactacaaa ctctcttttg ctcataacta
ttaactcagc tggttgcctt 240attgagacaa tctatgttat tttgtacttc
atctacgctc caaaaaaggc aaagattttc 300actgctaaga tggttctcct
tttgaacatt ggaggtttcg gagttgtgct cttacttact 360gttttcttga
caaaagctga aaagagagtt caaattatcg gatggatatg tgtgggtttt
420gctattgcag ttttcgtggc tcctctcagt gttattgcaa aagtgatcca
gacaaagtct 480gttgagttta tgccattgac cctctcattt ttccttactg
tgagtgctgt tgtgtggttc 540ttatatggaa tccttaccaa ggataagtac
atagcattgc ctaatacact cggatttttg 600ctcggtttag ctcagatggg
tctttatgca ttctacaaaa agagggaaac tgctatggag 660atgcaacttc
ctcagcattc aactgataat atcgttatag tgagtgctgc aacaaactct
720gataaacaaa agcagcacag ttcttcattg ccatctaata acctcgttgg
agctgcagtg 780gatgatgatg atgttaccac tacaaccaaa aacggtatag
atccaatcaa caacctcgaa 840cagaatcatc aagtgaaaga tcagttaaac cacgtttga
879173864DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 173atgggtgctg
tgggttctcc ttgggctttt ctctttggtg ttctcggtaa tgtggtttct 60tttcttgtgt
atttgagtcc tgttccaaca ttctaccaag ttttcaagaa aaagtcaacc
120ggaggttttt cttcaatacc ttacttggtt gctcttttga gtgcaatgct
ttggttgtat 180tacgctatgc tcactacagg atctttcctc ctcatatcta
ttaacggagc tggttgtgtt 240atcgagtctg tgtatgttgt ggtttatgtt
gcttacgcac caagaaaggc taagttgagg 300accgcaaaat taatcggact
tatggatgtt ggaggttttg gtatagtgct tttggttaca 360catgtgcttg
ttcacggtag taagagagtg caaattgttg gttgggtgtg tttggctttt
420agtatgtgcg tgttcgttgc acctctctct gttataagaa gagttattca
gtcaaaaagt 480gttgaataca tgccttttac tctctcatta ttccttaccg
tgtgtgctac tatgtggttg 540gcttatggac tcttaaaaaa ggattactgc
attgctttgc ctaacgttct cggatttgtg 600ttcggtatcg ctcaaatggg
actttatgtt ttctataagt actgcaagac atctcctcat 660cttggtgaaa
aagaggttga agctgcaaag ttaccagagg tgtctcttga tatgttgaaa
720ctcggaactg ttagttctcc tgaaccaatc tcagtggtta gacaggctaa
taagtgtaca 780tgcggtaacg atagaagggc agagatagaa gatggtcaaa
cacctaagca cggaaagcag 840tcaagttcag cagcagcaac atga
864174909DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 174atgggagcag
tcggttcgcc gtgggccttt ttgttcggag ttcttggtaa tgtggtctcg 60tttctcgtgt
atctctcacc cgttcctacg ttctaccagg tgttcaagaa gaagtccact
120ggcgggttct ccagcatccc gtatctggtg gctctcctgt ctgcaatgct
ctggctgtac 180tatgccatgc ttaccacagg atcgttcctt ttgatcagta
ttaacggcgc ggggtgcgtt 240attgagtcag tctacgtggt cgtttacgtc
gcctatgcac caagaaaggc aaagctcagg 300accgcaaagc tgatcggact
tatggacgtg ggaggtttcg gtattgtcct cctggttaca 360cacgtgctcg
tccatggcag caagcgggtg cagatcgtcg ggtgggtttg cctggccttc
420tcaatgtgtg tttttgtggc gccgctttcg gtcatccgca gggttattca
atctaagtca 480gtcgaataca tgccattcac cctttccttg tttctcaccg
tttgcgctac aatgtggctg 540gcatacggcc ttttgaagaa ggattattgt
atcgctttgc ctaacgtgct cggcttcgtc 600tttgggattg cacagatggg
cctctacgtt ttctatcgga atagaaagcc ggtcatcttt 660gacccagagg
ataagttgag ggctcccgaa cagatgaagt ccatcgtcat tctcagcacg
720attcctactt ctgaggtgca ccccgtcgac gcgaagcatt gcgacggcaa
cgatggggag 780gacgtggatg gaaaggatgg taataaggaa ggagacggcg
acgagcacga aaagtgtgtg 840gtcgttttgg tggatatgga tgccagcggg
gaattgcagt tgaagagtga tgaaccctgt 900gtggagtga
909175879DNAArtificial SequenceSynthetic DNA 175atgggggcag
tgggttcgcc ttgggccttt atttttgggg tcctcggcaa tgtgatttcc 60tttctggttt
tcctggctcc tcttcctacg ttctaccagg tttacaagaa gaagtccact
120gagggctttt ccagcgtgcc gtacattatg gccctcctgt cctgcatgtt
gtggctcttc 180tatgcgcttt tgaccacaaa ctcactcctg cttatcacca
ttaattcggc cggatgtctc 240atcgaaacaa tctacgtgat cctgtacttc
atctacgctc caaagaaggc aaagatcttt 300acggcgaaga tggtgttgct
cctgaacatc ggcgggttcg gcgtggtcct tttgctcacg 360gtctttctga
ctaaggctga gaagcgcgtg cagatcattg gctggatttg cgtcgggttc
420gccatcgcgg tctttgttgc cccgctcagt gttattgcga aggtcatcca
aacaaagtct 480gtcgaattca tgccactgac ccttagcttc tttctcacag
tttctgctgt tgtgtggttc 540ttgtacggca ttctcacgaa ggacaagtat
atcgcactgc cgaacactct tggattcctg 600cttggtttgg ctcaaatggg
gctctacgca ttttataaga agagggagac cgcgatggaa 660atgcagctcc
ctcaacactc aaccgacaac atcgtgattg tcagtgccgc gacaaattcc
720gataagcaga agcaacattc ttcatcgctg cccagcaaca atcttgtcgg
agctgcagtt 780gacgatgacg atgtcacgac taccacaaag aatggtatcg
acccaatcaa taacctggag 840caaaaccatc aagtgaagga ccaactgaat catgtgtga
879
D00001

D00002

D00003

D00004

D00005

D00006

D00007

D00008

D00009

D00010

D00011

D00012

D00013
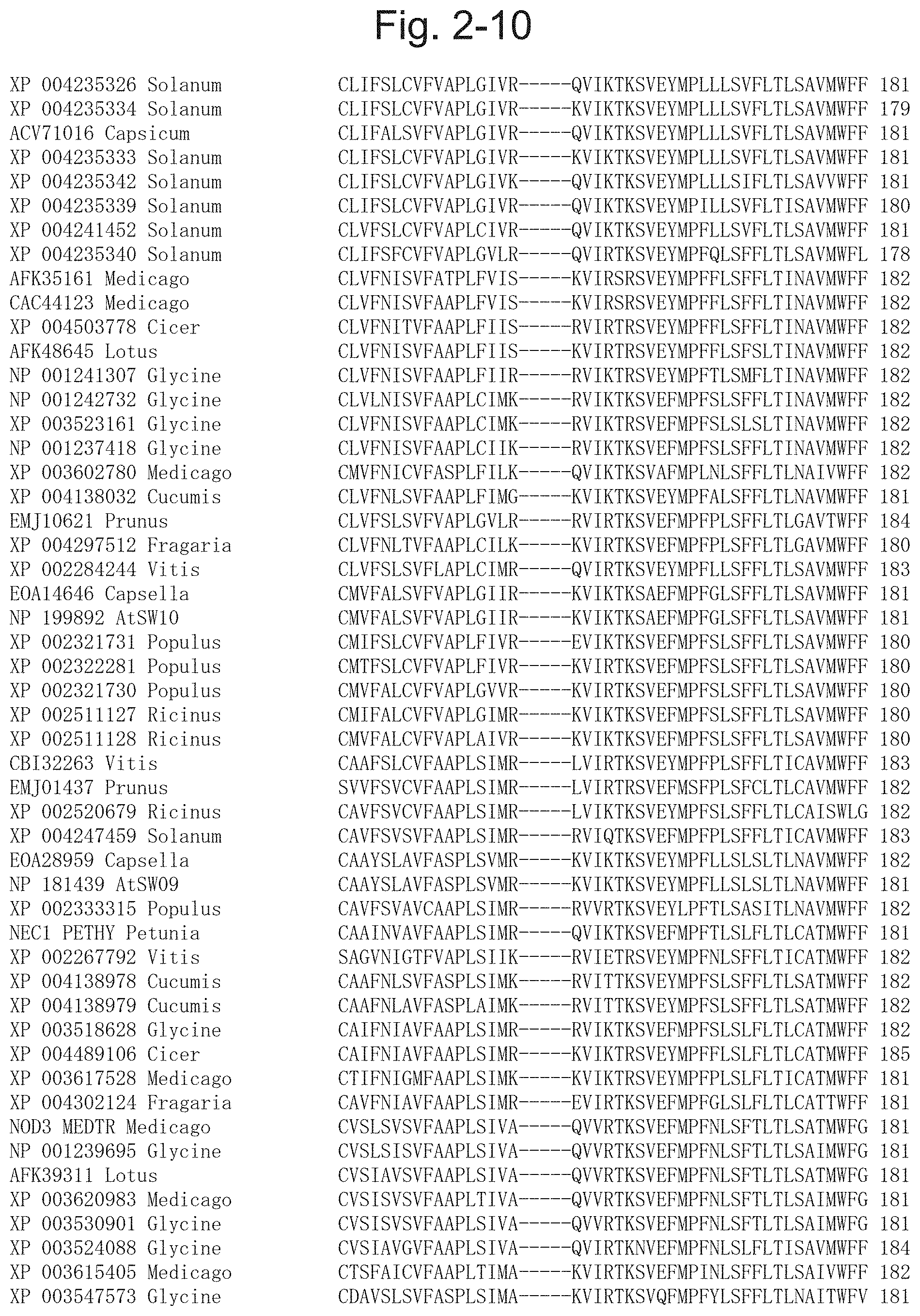
D00014

D00015

D00016

D00017
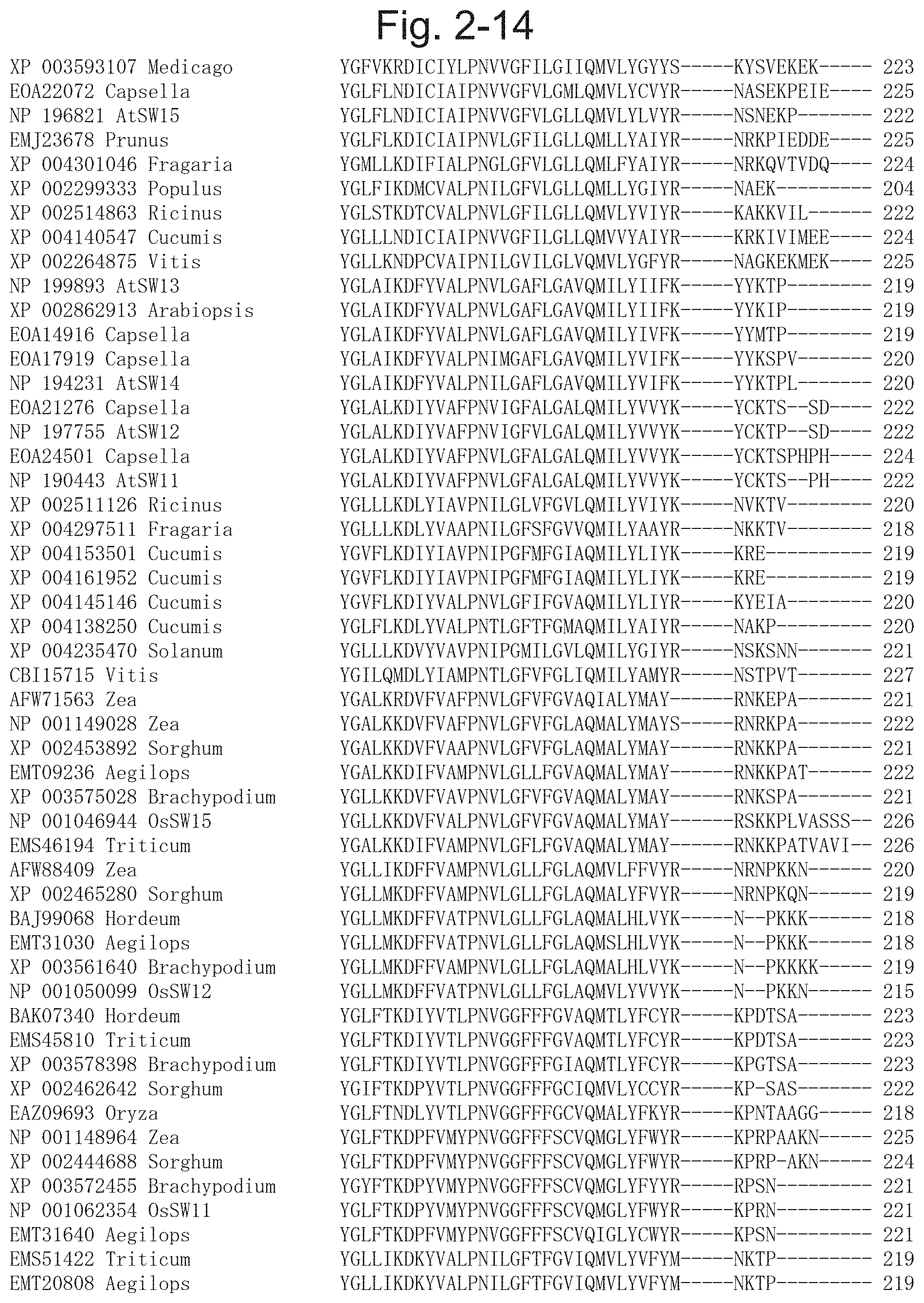
D00018

D00019

D00020
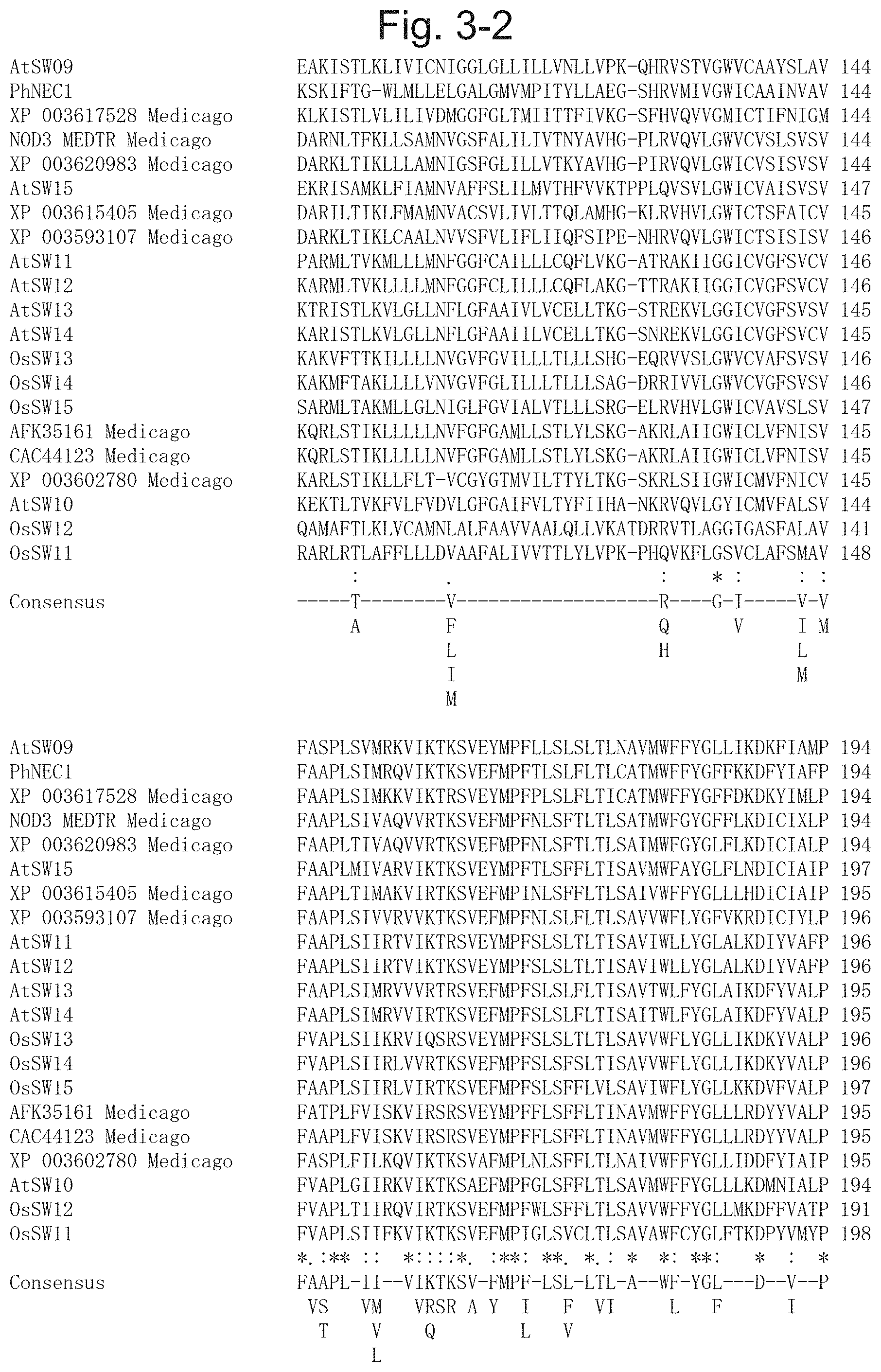
D00021

D00022

D00023

D00024
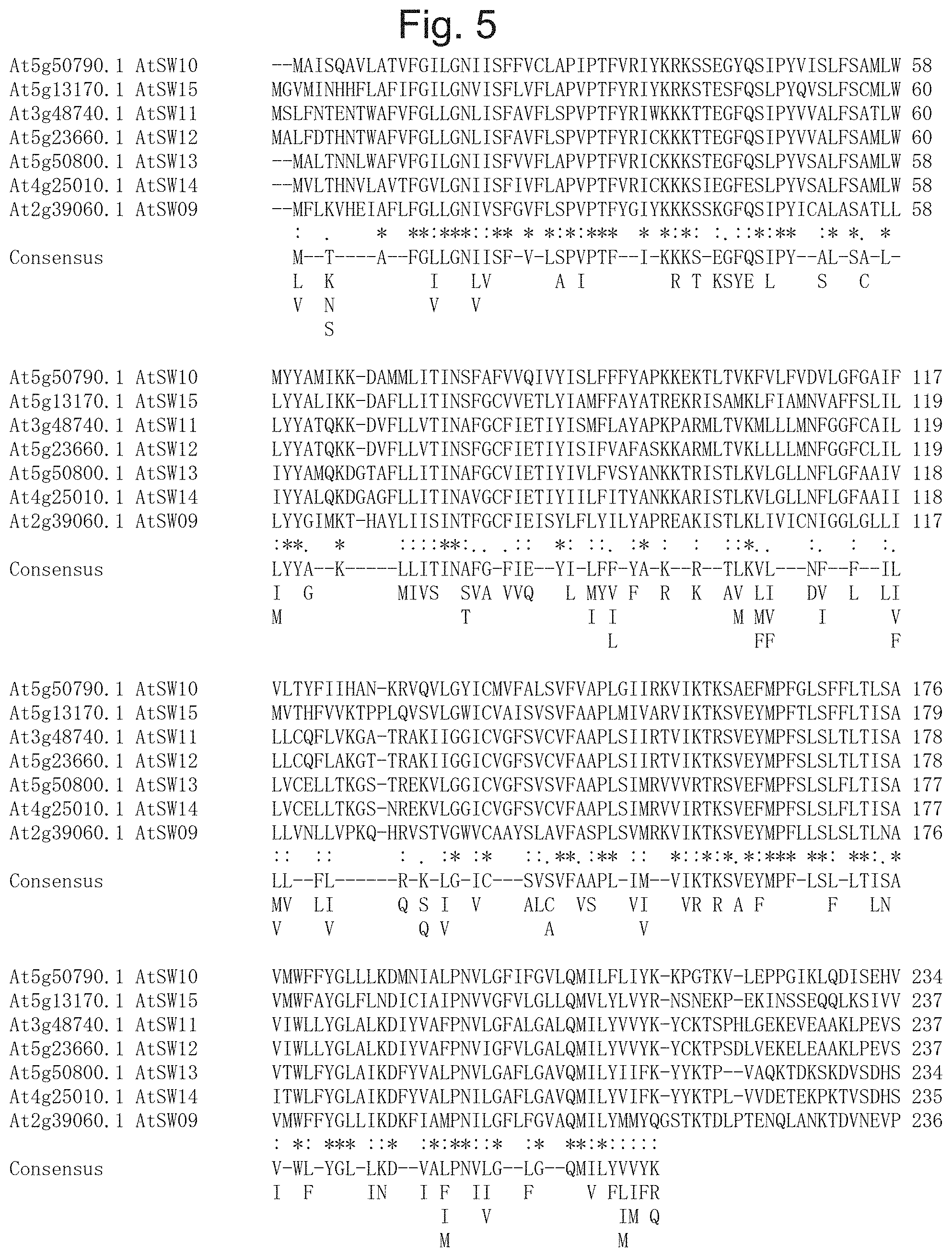
D00025

D00026

D00027
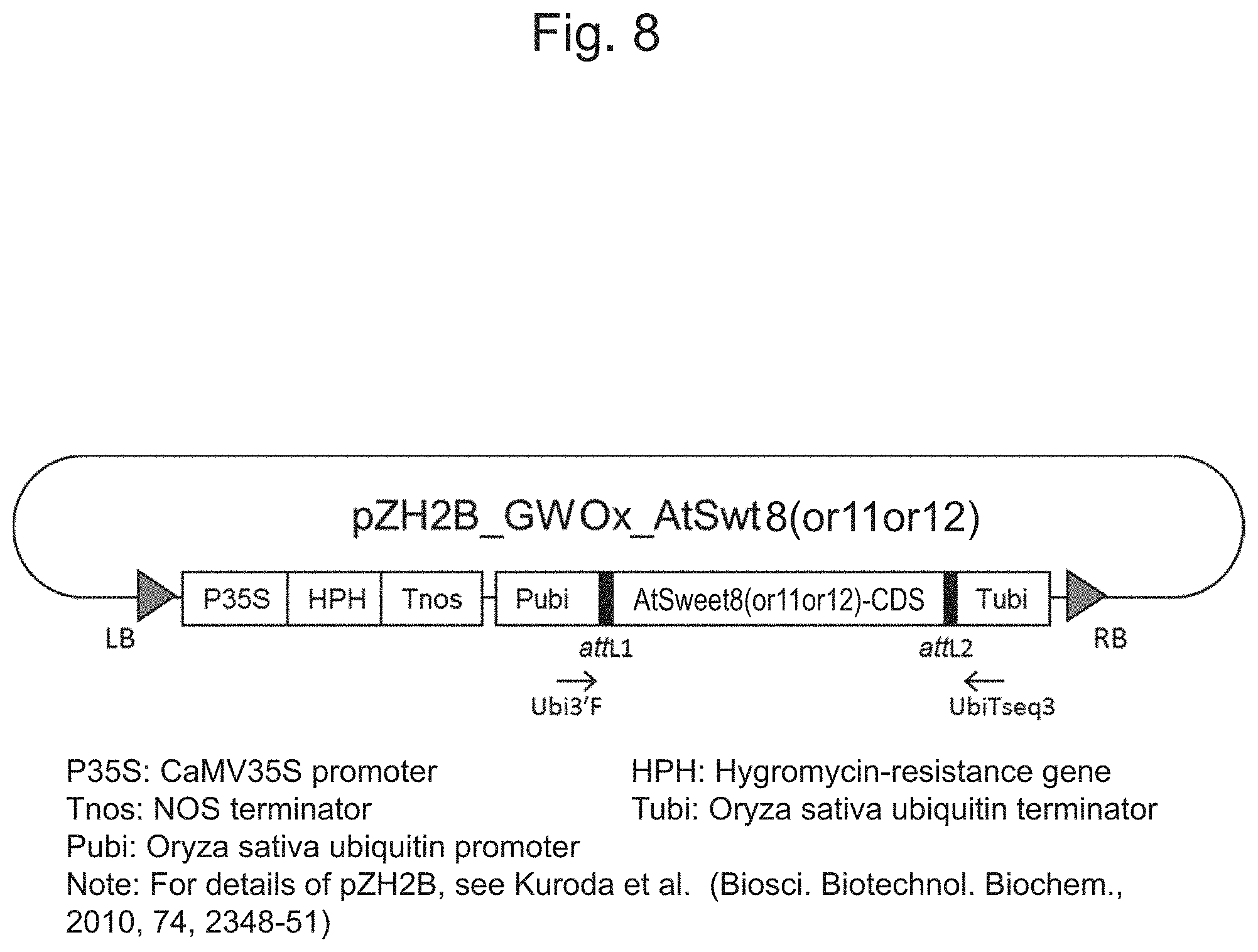
D00028

S00001
XML
uspto.report is an independent third-party trademark research tool that is not affiliated, endorsed, or sponsored by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) or any other governmental organization. The information provided by uspto.report is based on publicly available data at the time of writing and is intended for informational purposes only.
While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information displayed on this site. The use of this site is at your own risk. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
All official trademark data, including owner information, should be verified by visiting the official USPTO website at www.uspto.gov. This site is not intended to replace professional legal advice and should not be used as a substitute for consulting with a legal professional who is knowledgeable about trademark law.