Novel Compositions And Methods
WENNOGLE; Lawrence P.
U.S. patent application number 16/090142 was filed with the patent office on 2020-01-23 for novel compositions and methods. This patent application is currently assigned to INTRA-CELLULAR THERAPIES, INC.. The applicant listed for this patent is INTRA-CELLULAR THERAPIES, INC.. Invention is credited to Lawrence P. WENNOGLE.
| Application Number | 20200022981 16/090142 |
| Document ID | / |
| Family ID | 59966433 |
| Filed Date | 2020-01-23 |







View All Diagrams
| United States Patent Application | 20200022981 |
| Kind Code | A9 |
| WENNOGLE; Lawrence P. | January 23, 2020 |
NOVEL COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS
Abstract
The invention provides methods for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more disorders associated with dementia comprising administering to a patient in need thereof, a therapeutically effective amount of (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand and (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand and (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor.
| Inventors: | WENNOGLE; Lawrence P.; (Hillsborough, NJ) | ||||||||||
| Applicant: |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assignee: | INTRA-CELLULAR THERAPIES,
INC. New York NY |
||||||||||
| Prior Publication: |
|
||||||||||
| Family ID: | 59966433 | ||||||||||
| Appl. No.: | 16/090142 | ||||||||||
| Filed: | March 28, 2017 | ||||||||||
| PCT Filed: | March 28, 2017 | ||||||||||
| PCT NO: | PCT/US17/24575 PCKC 00 | ||||||||||
| 371 Date: | September 28, 2018 |
Related U.S. Patent Documents
| Application Number | Filing Date | Patent Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62314314 | Mar 28, 2016 | |||
| Current U.S. Class: | 1/1 |
| Current CPC Class: | A61K 31/519 20130101; A61K 45/06 20130101; A61P 25/28 20180101; A61K 31/5383 20130101; A61P 25/16 20180101; A61K 31/4985 20130101; A61P 25/18 20180101; A61K 31/4985 20130101; A61K 2300/00 20130101; A61K 31/519 20130101; A61K 2300/00 20130101; A61K 31/5383 20130101; A61K 2300/00 20130101 |
| International Class: | A61K 31/519 20060101 A61K031/519; A61K 31/4985 20060101 A61K031/4985 |
Claims
1. A method for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more disorders associated with dementia comprising administering to a patient in need thereof, a therapeutically effective amount of (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand and (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor.
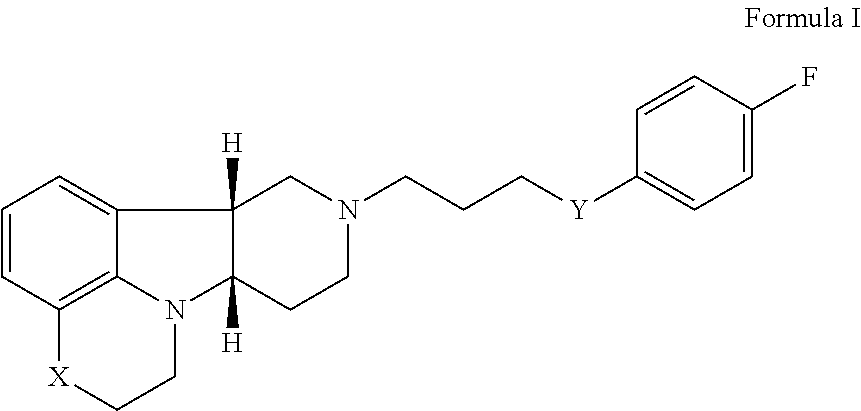
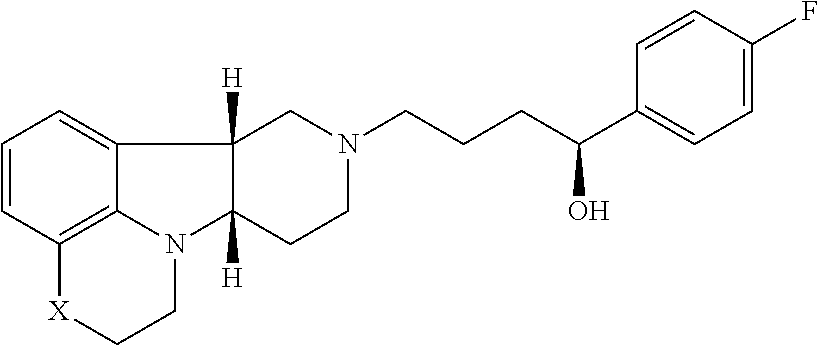
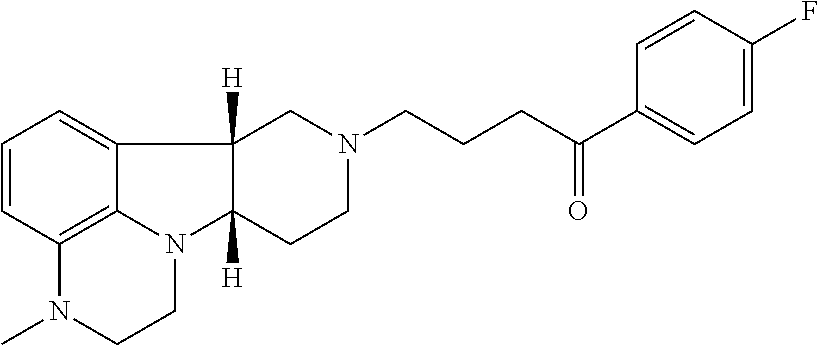
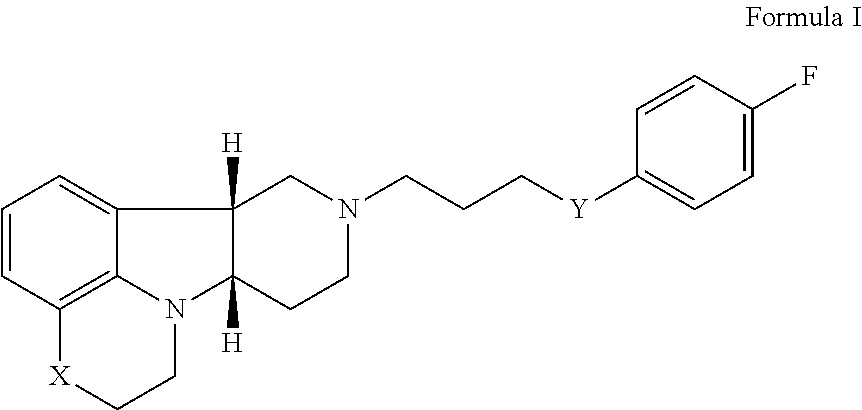
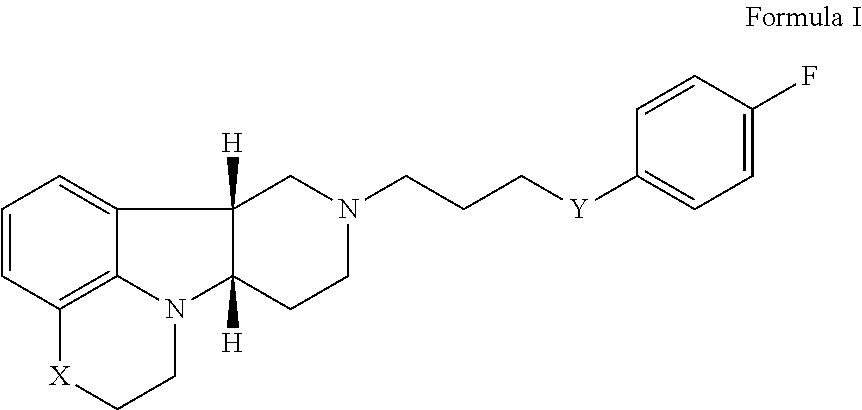
2. The method of claim 1, wherein the 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand is a compound of Formula I: ##STR00023## wherein: X is --N(H)--, --N(CH.sub.3)-- or --O--; Y is --C(.dbd.O), --C(H)(OH) or --C(H)(OR.sub.1); R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl, optionally saturated or unsaturated and optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy, wherein such compound hydrolyzes to form the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid, in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form.
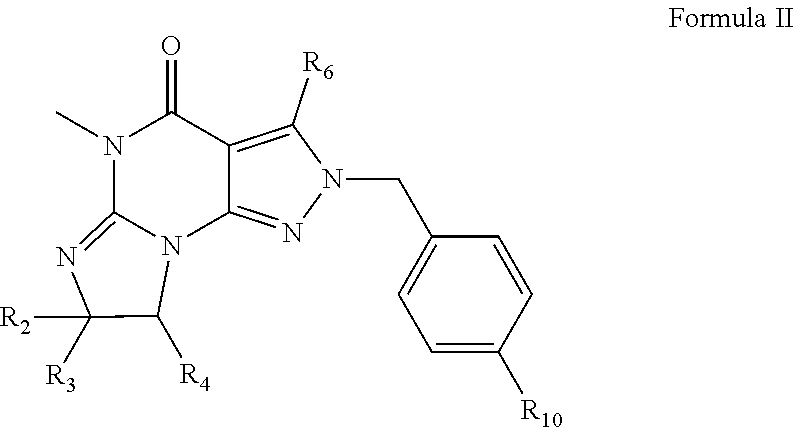
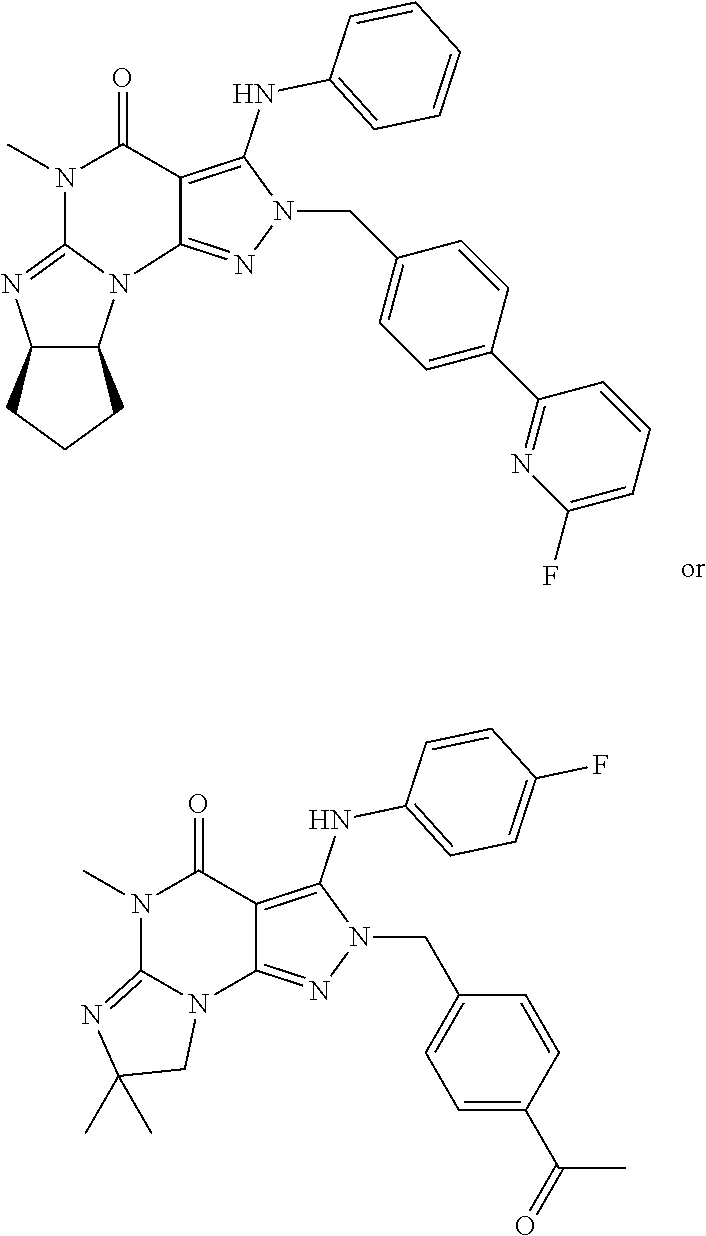
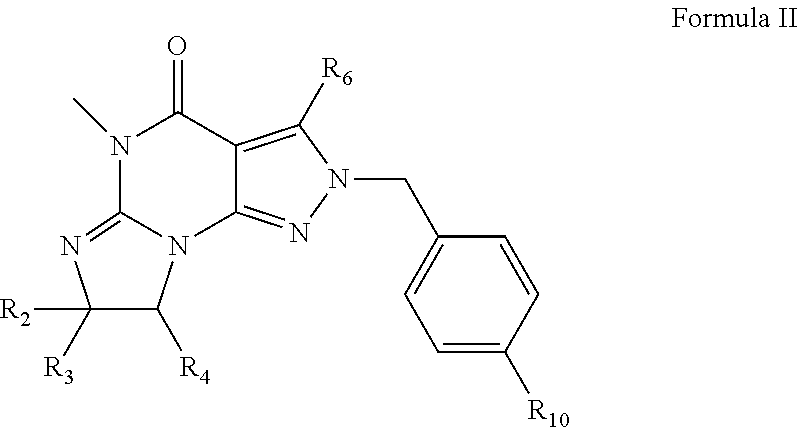
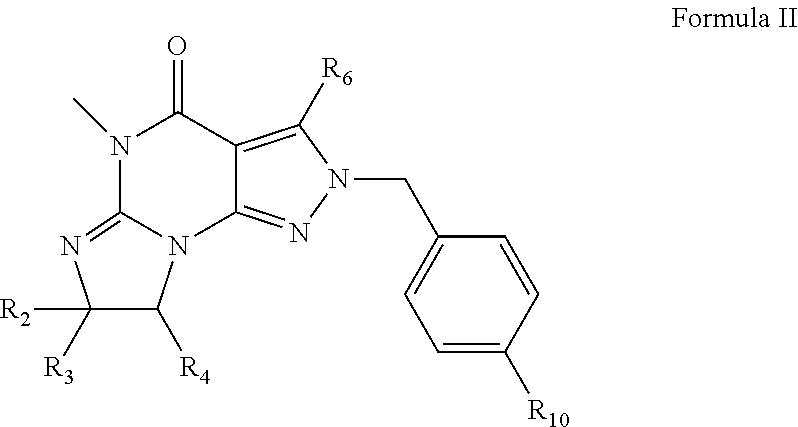
3. The method of claim 1 wherein the PDE1 inhibitor is a compound according to Formula II ##STR00024## wherein R.sub.2 is H and R.sub.3 and R.sub.4 together form a tri- or tetra-methylene bridge; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.3 are each methyl and R.sub.4 is H; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.4 are H and R.sub.3 is isopropyl; R.sub.6 is optionally halo-subsitututed phenylamino or optionally halo-subsitututed benzylamino; R.sub.10 is optionally halo-subsitututed phenyl, optionally halo-subsitututed pyridyl, or thiadiazolyl; in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein the Compound of Formula I is ##STR00025## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
5. The method of claim 1, wherein the Compound of Formula II is ##STR00026## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
6. The method of claim 1, wherein the method comprises administration of a pharmaceutical composition comprising effective amounts of both a Compound of Formula I and a Compound of Formula II.
7. The method of claim 1, wherein the daily dosage of the Compound of Formula 1 is 1 mg to 10 mg.
8. The method of claim 1 wherein the daily dosage of the Compound of Formula 1I is 0.1 mg to 10 mg.
9. The method of claim 1 wherein the Compound of Formula I is: ##STR00027## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, administered in a daily dose of 1 mg to 10 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent; and the Compound of Formula II is: ##STR00028## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, administered in a daily dose of 0.5 mg to 10 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent.
10. The method of claim 9, wherein the compound of Formula I is in tosylate salt form administered in a daily dose equivalent to 1 to 5 mg of free base and the compound of Formula II is in monophosphate salt form administered in a daily dose equivalent to 0.5 to 2 mg of free base.
11. The method of claim 10, wherein the method comprises once daily administration of a unit dosage for oral administration, comprising the compound of Formula I in tosylate salt form in an amount equivalent to 1 to 5 mg of free base, the compound of Formula II in monophosphate salt form in an amount equivalent to 0.5 to 2 mg of free base, and a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier.
12. The method of claim 1, wherein the one or more disorders associated with dementia are selected from disorders associated with mild to severe cognition impairment and dementing illnesses including senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down syndrome, elderly depression, Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome, corticobasal degenerations, and prion disease.
13. The method of claim 1, wherein the disorders associated with dementia include one or more of behavioral or mood disturbances, psychosis, depression and/or sleep disturbances.
14. The method of claim 1, comprising enhancing cognition in a patient with dementia.
15. The method of claim 1, wherein the disorder is Alzheimer's disease or symptoms thereof.
16. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand and (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor.
17. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 wherein the 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand is a compound of Formula I: ##STR00029## wherein: X is --N(H)--, --N(CH.sub.3)-- or --O--; Y is --C(.dbd.O), --C(H)(OH) or --C(H)(OR.sub.1); R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl, optionally saturated or unsaturated and optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy groups, wherein such compound hydrolyzes to form the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid, in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form.
18. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 wherein the PDE1 inhibitor is a compound according to Formula II ##STR00030## wherein R.sub.2 is H and R.sub.3 and R.sub.4 together form a tri- or tetra-methylene bridge; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.3 are each methyl and R.sub.4 is H; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.4 are H and R.sub.3 is isopropyl; R.sub.6 is optionally halo-subsitututed phenylamino or optionally halo-subsitututed benzylamino; R.sub.10 is optionally halo-subsitututed phenyl, optionally halo-subsitututed pyridyl, or thiadiazolyl; in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
19. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 wherein the Compound of Formula I is ##STR00031## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
20. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 wherein the Compound of Formula II is ##STR00032## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
21. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 further comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier.
22. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 in the form of a tablet, capsule, or transdermal patch.
23. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 comprising a Compound of Formula I and a Compound of Formula II in a bioerodable matrix.
24. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 16 in unit dosage form wherein the Compound of Formula I is: ##STR00033## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, in an amount of 1 mg to 10 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent; and the Compound of Formula II is: ##STR00034## in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, in an amount of 0.5 mg to 10 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent.
25. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 24 in the form of a tablet or capsule for oral administration comprising the compound of Formula I in tosylate salt form in an amount equivalent to 1 to 5 mg of free base, the compound of Formula II in monophosphate salt form in an amount equivalent to 0.5 to 2 mg of free base, and a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier.
26. The method of claim 1 comprising administration of the composition according to claim 16.
27. (canceled)
28. (canceled)
Description
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001] This application claims priority to and the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No. 62/314,314, filed Mar. 28, 2016, the contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety.
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0002] The present invention relates to use of (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand, for example a substituted heterocycle fused gamma-carbolines as described herein, in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form, and (ii) a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1 (PDE1) inhibitor, for example a 7,8-dihydro-imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazolo[4,3-e]pyrimidin-4-one compounds, in combination (sequentially or simultaneously, or in the form of a fixed dose combination for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more disorders associated with dementia (including behavioral or mood disturbances (e.g., agitation/aggression), psychosis, depression and/or sleep disturbances), or enhancing cognition, for example in schizophrenia or dementia.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0003] Dementia is a disorder characterized by the loss of cognitive abilities affecting memory, reasoning, judgment and behavior. At an early stage of dementia, people may experience mild cognitive impairment (MCI, also known as incipient dementia, or isolated memory impairment) which is cognitive impairment beyond that expected based on the age and education of the individual, but which is not significant enough to interfere with their daily activities. Studies suggest that these individuals tend to progress to probable Alzheimer's disease at a rate of approximately 10% to 15% per year. Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia and is an irreversible, progressive neurodegenerative disease that disrupts memory, perception, reasoning, judgment, information processing, emotional behavior, personality as well as social and occupational functions. Of date, 5.4 million of Americans are believed to be living with Alzheimer's and nearly 36 million people worldwide are believed to be living with this disease or other dementias.
[0004] Currently, there is no cure or standard of treatment for dementia. Available treatments are palliative and symptomatic in nature aiming to manage and slow the progression of the cognitive manifestation of the disease. Drugs approved in the United States for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, which are also used to treat dementia in general include acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., Tacrine, rivastigmine (Exelon), donepezil (Aricept), and galantamine (Razadyne, formerly called Reminyl)) and NMDA receptor antagonist (e.g., memantine (Namenda)). While these drugs improve mental function (such as memory, attention, social interaction, reasoning ability, language ability, and ability to perform activities of daily living), they often cause side effects including stomach upset, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, fatigue, difficulty falling or staying asleep or excess sleepiness, depression, bradycardia and other side effects. In addition, these drugs do not treat affective symptoms and/or other behavior disruptions such as mood swing, agitation, aggressive/assaultive behavior and paranoia which are common in dementias. In fact, some studies have shown that memantine, a drug approved for Alzheimer's disease and often used for dementias in general, may have some adverse effects on neuropsychiatric functioning, particularly agitation/aggression, delusions or hallucinations. These untreated and sometimes aggravated behavioral disruptions often prevent the patients from integrating back into society, causing further distress to the caregivers and eventually leading to the patients' institutionalization. To control aggression and psychosis in dementia, particularly in Alzheimer's disease, antipsychotic drugs are used. However, antipsychotic drugs such as haloperidol, risperidone and quetiapine are associated with serious side effects including extrapyramidal side effects (akinesia or akathisia), bone marrow suppression, seizure, orthostatic hypotension, insomnia, sedation, somnolence and weight gain. Many atypical antipsychotic agents also have a higher risk of heart failure. Therefore, the use of these antipsychotic agents in combination with anticholinesterase inhibitor or NMDA receptor antagonist is undesirable.
[0005] In addition to behavior and mood disturbances, many dementia patients, particularly those at a more serious stage of the disease also commonly experience sleep disturbances wherein the patients either have difficulty falling asleep, maintaining sleep or experience changes in their sleep-wake cycle/pattern. These patients may also feel restless or agitated in the late afternoon or early evening (often called "sundowning"). In fact, studies have shown evidence that a loss in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) neuronal population coincides with Alzheimer's patients' stage of dementia. This loss of SCN neuronal population appears to be causative in the observed disturbances in melantonin rhythm which may underlie accompanying sleep disturbances. While agents such as temazepam (Restoril), zolpidem (Ambien), or zaleplon (Sonata), or sedating antidepressants, such as trazodone (Desyrel, Molipaxin), may be useful in managing insomnia, failure of these drugs to improve sleep quality in addition to the associated risk of falling due to drowsiness and psychomotor impairment caused by these agents render them undesirable for dementia, particularly Alzheimer's patients.
[0006] Particularly in later stages of dementia, patients may suffer psychosis. While psychosis is often associated with schizophrenia in young people, people with dementia may, as the disease progresses, exhibit a spectrum of behaviors from agitation to positive symptoms of psychosis such as paranoia, delusions and hallucinations. The patients may also suffer negative symptoms such as emotional withdrawal, passive social withdrawal, and stereotyped thinking, and symptoms of general psychopathology including active social avoidance, anxiety, tension, and somatic concerns. These negative symptoms are often accompanied by depression, cognitive dysfunction and insomnia. Collectively, these residual phase symptoms are not well-treated by many antipsychotic drugs currently available on the market and therefore are usually most apparent when the more dramatic positive or active phase symptoms have been brought under control by antipsychotic medications.
[0007] There remains an urgent need for an effective therapeutic regime for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia and disorders associated thereof, particularly to alleviate behavioral/mood disturbances (e.g., agitation, aggressive/assaultive behavior) and sleep disturbances in patients suffering from dementia or psychosis associated with dementia.
[0008] Substituted heterocycle fused gamma-carbolines are known to be 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligands, useful in treating central nervous system disorders. These compounds have been disclosed in U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,548,493; 7,238,690; 6,552,017; 6,713,471; U.S. RE39680, and U.S. RE39679, as novel compounds useful for the treatment of disorders associated with 5-HT2A receptor modulation such as obesity, anxiety, depression, psychosis, schizophrenia, sleep disorders, sexual disorders, migraine, conditions associated with cephalic pain, and social phobias. PCT/US08/03340 and U.S. Pat. No. 7,081,455 also disclose methods of making substituted heterocycle fused gamma-carbolines and uses of these gamma-carbolines as serotonin agonists and antagonists useful for the control and prevention of central nervous system disorders such as addictive behavior and sleep disorders. WO 2009/145900 and WO 2013/155506, each incorporated herein by reference, disclose use of specific substituted heterocycle fused gamma-carbolines for the treatment of a combination of psychosis and depressive disorders as well as sleep, depressive and/or mood disorders in patients with psychosis or Parkinson's disease and for the treatment or prophylaxis of disorders associated with dementia, particularly behavioral or mood disturbances such as agitation, irritation, aggressive/assaultive behavior, anger, physical or emotional outbursts and psychosis and sleep disorders associated with dementia.
[0009] PDE1 is a Ca.sup.2+-calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase (CaM-PDE), which can downregulate intracellular cAMP and cGMP signaling by hydrolyzing these cyclic nucleotides to their respective inactive 5'-monophosphates (5'AMP and 5'GMP). PDE1 plays a critical role in mediating signal transduction in brain cells, particularly within an area of the brain known as the basal ganglia or striatum. For example, NMDA-type glutamate receptor activation and/or dopamine D2 receptor activation result in increased intracellular calcium concentrations, leading to activation of effectors such as calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) and calcineurin and to activation of PDE1, resulting in reduced cAMP and cGMP. Dopamine D1 receptor activation, on the other hand, leads to activation of calcium dependent nucleotide cyclases, resulting in increased cAMP and cGMP. These cyclic nucleotides in turn activate protein kinase A (PKA; cAMP-dependent protein kinase) and/or protein kinase G (PKG; cGMP-dependent protein kinase) that phosphorylate downstream signal transduction pathway elements such as DARPP-32 (dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein) and cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB). Inhibition of PDE1 can thus potentiate the effect of a dopamine D1 agonist by protecting cGMP and cAMP from degradation, and likewise can inhibit dopamine D2 receptor signaling pathways, by inhibiting PDE1 activity. WO 2014/145617, incorporated herein by reference, e.g., for its disclosure of PDE1 inhibitors, describes the use of PDE1 inhibitors as neuroprotective agents and/or neural regenerative agents, e.g. to prevent the development of a CNS disease or disorder in an individual at risk for the development of a CNS disease or disorder. By facilitating increased levels of intracellular cAMP and/or cGMP, PDE1 inhibitors can initiate the transcription of genes that are necessary for overcoming myelin inhibition of regeneration after nerve injury and promoting neurite outgrowth and/or axonal regeneration in the case of a CNS disease, disorder, or injury, thus encouraging axonal regeneration and/or neuroprotection while simultaneously decreasing or lessening damage associated with chronically elevated intracellular calcium levels, which can lead to calmodulin activation of PDE 1.
[0010] New methods of treating and improving the quality of life in patients having dementia and slowing the progression of dementia are urgently needed.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0011] The invention provides a method of treating dementia (including associated disorders such as behavioral or mood disturbances (e.g., agitation/aggression), psychosis, depression and/or sleep disturbances), and/or enhancing cognition, for example in patients suffering from schizophrenia or dementia, comprising administering an effective amount of (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand, for example a substituted heterocycle fused gamma-carbolines as described herein, in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form, together with (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor, as described herein. The 5-HT2A/D2 ligand promotes quality of sleep and reduces agitation, while the PDE1 inhibitor promotes cognitive function. The administration may be sequential or simultaneous. The invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition, e.g., for use in such a method, comprising (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand and (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0012] Administration of a PDE1 inhibitor as described herein will enhance cognition and also act to increase levels of intracellular cAMP and initiate the transcription of genes that are necessary for overcoming the inhibition of axonal regeneration and promoting neurite outgrowth and/or axonal regeneration thus inhibiting the neurodegenerative process. For instance, increased intracellular cAMP, such as would result from PDE1 inhibition, leads to increased activity of cAMP-dependent proteins, such as protein kinase C (PKC).
[0013] Another benefit of the administration of a PDE1 inhibitor of the invention is an increase in intracellular cGMP. This increase in intracellular cGMP may lead to an increase in the activity of PKG, preventing a further rise in intracellular calcium levels. Thus, it is believed that the administration of a PDE1 inhibitor could have the dual benefit of, for example, playing a beneficial role in axonal regeneration (and/or neuroprotection) while simultaneously decreasing the deleterious effects that may be associated with elevated intracellular calcium levels.
[0014] The 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand is a compound which antagonizes serotonin-2A (5-HT2A) receptor, and/modulates dopamine receptor signaling at the level of key intra-cellular phosphoproteins and therefore is useful for the treatment of not only acute symptoms, but also residual symptoms of pyschosis, particularly schizophrenia. At dopamine D2 receptors, these compounds have dual properties and act as both post-synaptic antagonists and pre-synaptic partial agonists. They also stimulate phosphorylation of glutamatergic NMDA NR2B, or GluN2B, receptors in a mesolimbic specific manner. It is believed that this regional selectivity in the brain areas thought to mediate the efficacy of antipsychotic drugs, together with serotonergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic interactions, may result in antipsychotic efficacy for positive, negative, affective and cognitive symptoms associated with schizophrenia. The compounds also exhibit serotonin reuptake inhibition, providing antidepressant activity for the treatment of schizoaffective disorder, co-morbid depression, and/or as a stand-alone treatment for major depressive disorder. The 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligands as described are also useful for the treatment of bipolar disorder and other psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders, particularly behavioral disturbances associated with dementia, autism and other CNS diseases. These features may be able to improve the quality of life of patients with schizophrenia and enhance social function to allow them to more fully integrate into their families and their workplace. At a low-dose, the Thus, the combination of the PDE1 inhibitor with a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand will be particularly useful, e.g., in the treatment of dementia or psychosis (e.g., schizophrenia) and disorders associated thereof. At lower doses, they are useful in treating sleep, aggression and agitation. At a high-dose, they can treat acute exacerbated and residual schizophrenia, bipolar disorders, and mood disorders.
[0015] As 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand compounds used in the current disclosure are effective in treating not just acute symptoms, but also residual symptoms of psychosis, their combination with a PDE1 inhibitor disclosed herein, which is believed to provide a neuroprotective effect, is useful in the treatment of a wide range of symptoms and disorders associated with dementia or psychosis such as schizophrenia.
[0016] Therefore, in a particular embodiment, the invention provides a method (Method I) for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more disorders associated with dementia (e.g., disorders associated with mild to severe cognition impairment and dementing illnesses including senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down syndrome, elderly depression, Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome, corticobasal degenerations, and prion disease; and further including behavioral or mood disturbances (e.g., agitation/aggression), psychosis, depression and/or sleep disturbances, as well as enhancing cognition, for example in schizophrenia or dementia) comprising administering to a patient in need thereof, a therapeutically effective amount of [0017] (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand, for example a compound of Formula I:
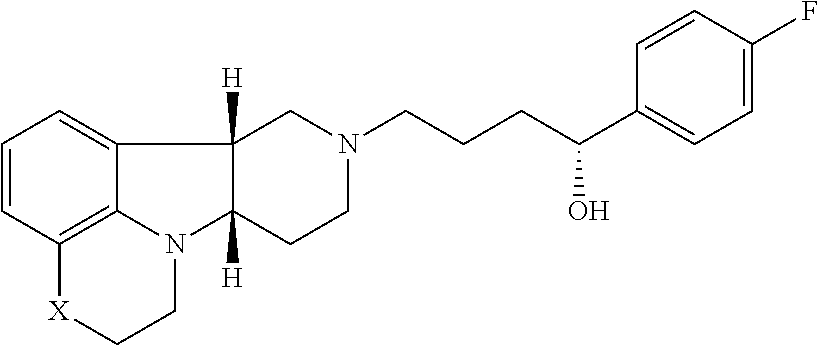
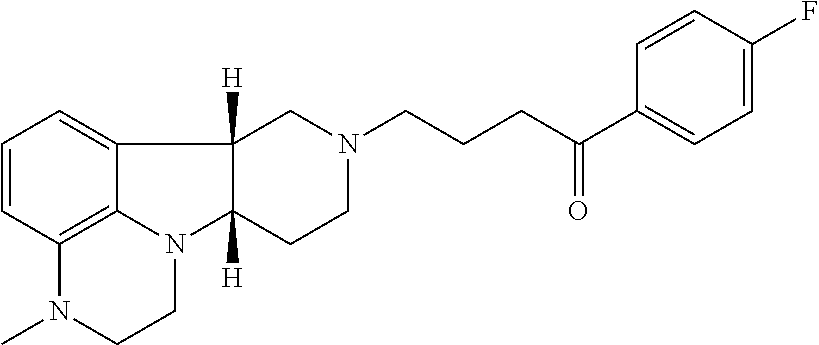
[0017] ##STR00001## [0018] wherein: [0019] X is --N(H)--, --N(CH.sub.3)-- or --O--; [0020] Y is --C(.dbd.O)--, --C(H)(OH)-- or --C(H)(OR.sub.1)--; [0021] R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl (e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.1-5alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.6-15alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.16-21alkyl), preferably said alkyl is a straight chain, optionally saturated or unsaturated and optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy (e.g., ethoxy) groups, for example R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.6alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.7alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.11alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.13alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.15alkyl wherein such compound hydrolyzes to form the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid, e.g., the compound hydrolyzes to form the hydroxy compound on the one hand and octanoic acid, decanoic acid, dodecanoic acid, tetradecanoic acid or hexadecanoic acid on the other hand), in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form; and [0022] (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor, for example a compound according to Formula II
[0022] ##STR00002## [0023] wherein [0024] R.sub.2 is H and R.sub.3 and R.sub.4 together form a tri- or tetra-methylene bridge [pref. with the carbons carrying R.sub.3 and R.sub.4 having the R and S configuration respectively]; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.3 are each methyl and R.sub.4 is H; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.4 are H and R.sub.3 is isopropyl [pref. the carbon carrying R.sub.3 having the R configuration]; [0025] R.sub.6 is (optionally halo-subsitututed) phenylamino or (optionally halo-subsitututed) benzylamino; [0026] R.sub.10 is (optionally halo-subsitututed) phenyl, (optionally halo-subsitututed) pyridyl (for example 3-fluoropyrid-2-yl), or thiadiazolyl (e.g., 1,2,3-thiadiazol-4-yl); in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
[0027] For example, Method 1 may be as follows: [0028] 1.1. Method I, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --N(H)--, --N(CH.sub.3)-- or --O--; [0029] 1.2. Method I or 1.1, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --N(H); [0030] 1.3. Method I or 1.1, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --N(CH.sub.3)--; [0031] 1.4. Method I or 1.1, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --O--; [0032] 1.5. Method I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(.dbd.O)--, --C(H)(OH)-- or --C(H)(OR.sub.1)--; [0033] 1.6. Method I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(.dbd.O)--; [0034] 1.7. Method I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(H)(OH)--; [0035] 1.8. Method I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(H)(OR.sub.1)--; [0036] 1.9. Method I or 1.8, wherein R.sub.1 in the compound of Formula I is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl (e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.1-5alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.6-15alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.16-21alkyl), preferably said alkyl is a straight chain, optionally saturated or unsaturated and optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy (e.g., ethoxy) groups, for example R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.6alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.7alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.11alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.13alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.15alkyl wherein such compound hydrolyzes to form the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid, e.g., the compound hydrolyzes to form the hydroxy compound on the one hand and octanoic acid, decanoic acid, dodecanoic acid, tetradecanoic acid or hexadecanoic acid on the other hand); e.g., wherein R.sub.1 in the compound of Formula I is --C(O)--C.sub.6-15alkyl, e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl; or wherein R.sub.1 in the compound of Formula I is --C(O)--C.sub.1-5alkyl, e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.3alkyl. [0037] 1.10. Method I or any of 1.1-1.5 or 1.7, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0037] ##STR00003## [0038] 1.11. Method I or any of 1.1-1.5 or 1.7, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
##STR00004##
[0039] 1.12. Any foregoing Method 1, or 1.1-1.3, 1.5, or 1.9 wherein the Compound of Formula I is
##STR00005## [0040] 1.13. Method 1.12 wherein the Compound of Formula 1 is in the form of the tosylate salt. [0041] 1.14. Method 1.12 wherein the Compound of Formula 1 is in the form of the free base. [0042] 1.15. Any foregoing Method wherein, in the Compound of Formula II, R.sub.6 is phenylamino or 4-fluorophenylamino. [0043] 1.16. Any foregoing Method wherein, in the Compound of Formula II, R.sub.10 is 3-fluoropyrid-2-yl or methylcarbonyl. [0044] 1.17. Any foregoing Method wherein, in the Compound of Formula II, R.sub.6 is phenylamino or 4-fluorophenylamino and R.sub.10 is 3-fluoropyrid-2-yl or methylcarbonyl. [0045] 1.18. Any foregoing Method wherein the Compound of Formula II is
[0045] ##STR00006## [0046] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form. [0047] 1.19. Method 1.16 wherein the Compound of Formula II is in the form of the monophosphate salt. [0048] 1.20. Any foregoing Method, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0048] ##STR00007## [0049] in free of pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, e.g., tosylate salt form; and the Compound of Formula II is:
[0049] ##STR00008## [0050] in free of pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, e.g., monophosphate salt form. [0051] 1.21. Any foregoing Method comprising administration of a pharmaceutical composition comprising effective amounts of both a Compound of Formula I and a Compound of Formula II. [0052] 1.22. Any foregoing method wherein the daily dosage of the Compound of Formula 1 is 1 mg to 10 mg. [0053] 1.23. Any foregoing method wherein the daily dosage of the Compound of Formula 1I is 0.1 mg to 10 mg. [0054] 1.24. Any foregoing method wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0054] ##STR00009## [0055] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, administered in a daily dose of 1 mg to 10 mg, e.g., 2 mg to 7 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent; [0056] and the Compound of Formula II is:
[0056] ##STR00010## [0057] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, administered in a daily dose of 0.5 mg to 10 mg, e.g. 0.5 to 2 mg, or 1 to 5 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent. [0058] 1.25. Method 1.21 wherein the compound of Formula 1 is in tosylate salt form administered in a daily dose equivalent to 1 to 5 mg of free base, the compound of Formula II is in monophosphate salt form administered in a daily dose equivalent to 0.5 to 2 mg of free base. [0059] 1.26. Any foregoing Method wherein the compound of Formula I and/or of Formula II is deuterated, e.g., wherein the deuterium:protium ratio at a specified position in the molecule is significantly higher, e.g., at least 2.times., for example at least 10.times. higher, than the natural isotope ratios. [0060] 1.27. Any foregoing Method wherein the Compound of Formula I is a Compound of Formula 1 as described in WO 2015/154025, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference, e.g., wherein the --CH.sub.2- adjacent to X and/or Y is --CHD- or --CD2-. [0061] 1.28. Method 1.22 wherein the method comprises once daily administration of a unit dosage for oral administration, for example a tablet or capsule, comprising the compound of Formula I in tosylate salt form in an amount equivalent to 1 to 5 mg of free base, the compound of Formula II in monophosphate salt form in an amount equivalent to 0.5 to 2 mg of free base, and a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier. [0062] 1.29. Any foregoing method wherein the disorders associated with dementia are disorders associated with Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, Mulitple sclerosis, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down syndrome, Eldery depression, Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome, corticobasal degenerations, and prion disease. [0063] 1.30. Any foregoing method wherein the disorders associated with dementia are disorders associated with mild cognition impairment and dementing illnesses including senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies and vascular dementia. [0064] 1.31. Any foregoing method wherein the disorders associated with dementia are disorders associated with senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies and vascular dementia. [0065] 1.32. Any foregoing method wherein the disorders associated with dementia are disorders associated with Alzheimer's disease. [0066] 1.33. Any foregoing method wherein the disorders associated with dementia are disorders associated with mild cognition impairment. [0067] 1.34. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder associated with dementia to be treated is selected from the group consisting of (1) behavioral or mood disorders such as agitation/irritation, aggressive/assaultive behavior, anger, physical or emotional outbursts; (2) psychosis; (3) depression; and (4) sleep disorders in patients suffering from dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0068] 1.35. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder to be treated is psychosis in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0069] 1.36. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder to be treated is depression in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0070] 1.37. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder to be treated is behavioral or mood disorders such as agitation/irritation, aggressive/assaultive behavior, anger, physical or emotional outbursts in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0071] 1.38. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder to be treated is sleep disorders in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0072] 1.39. Any of Method I et seq. wherein the disorder to be treated is sleep maintenance insomnia, frequent awakenings, and waking up feeling unrefreshed in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0073] 1.40. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder to be treated is sleep maintenance insomnia in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0074] 1.41. Any of Method I et seq. wherein the disorder to be treated is advanced sleep-phase syndrome in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0075] 1.42. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder to be treated is delayed sleep-phase syndrome in a patient with dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0076] 1.43. Any foregoing method wherein the disorder associated with dementia is selected from behavioral or mood disturbances (e.g., agitation/aggression), psychosis, depression and/or sleep disturbances. [0077] 1.44. Any foregoing method comprising enhancing cognition, for example in schizophrenia or dementia. [0078] 1.45. Any foregoing method further comprising administering one or more additional therapeutic agents useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. [0079] 1.46. The foregoing method wherein the therapeutic agent useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease is a cholinesterase inhibitor (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) or an N-Methyl D-Asparate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form; [0080] 1.47. The foregoing method wherein the cholinesterase inhibitor (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) is selected from the group consisting of Tacrine, rivastigmine (Exelon), donepezil (Aricept), and galantamine (Razadyne, formerly called Reminyl)) in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form; [0081] 1.48. The foregoing method wherein the cholinesterase inhibitor (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) is donepezil in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form; [0082] 1.49. Any foregoing method wherein the patient additionally receives a NMDA receptor antagonist, e.g., memantine in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form; [0083] 1.50. Any foregoing method further comprising administering one or more additional therapeutic agents useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease, wherein the therapeutic agent useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease is a combination of a cholinesterase inhibitor (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) and an N-Methyl D-Asparate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form. [0084] 1.51. The foregoing method wherein the one or more therapeutic agent(s) useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease or symptoms thereof is a combination of donepezil and memantine in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form. [0085] 1.52. Any foregoing method further comprising administering one or more therapeutic agents useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease further comprises administering one or more therapeutic agents selected from antidepressant compounds, compounds that modulate GABA activity (e.g., enhances the activity and facilitates GABA transmission), a GABA-B agonist, a serotonin-2 antagonist/reuptake inhibitor (SARIs), an orexin receptor antagonist, an H3 agonist, a noradrenergic antagonist, a galanin agonist, a CRH antagonist, human growth hormone, a growth hormone agonist, estrogen, an estrogen agonist, a neurokinin-1 drug, and an antipsychotic agent, e.g., an atypical antipsychotic agent, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
[0086] In another aspect, the invention provides a pharmaceutical composition (Composition 1) [e.g., for the prophylaxis or treatment of one or more disorders associated with dementia (e.g., disorders associated with mild to severe cognition impairment and dementing illnesses including senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down syndrome, elderly depression, Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome, corticobasal degenerations, and prion disease, e.g., for use in any of Methods 1 et seq.], comprising [0087] (i) a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand, for example a compound of Formula I:
[0087] ##STR00011## [0088] wherein: [0089] X is --N(H)--, --N(CH.sub.3)-- or --O--; [0090] Y is --C(.dbd.O), --C(H)(OH) or --C(H)(OR.sub.1); [0091] R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl (e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.1-5alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.6-15alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.16-21alkyl), preferably said alkyl is a straight chain, optionally saturated or unsaturated and optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy (e.g., ethoxy) groups, for example R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.6alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.7alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl, --C(O)-C.sub.11alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.13alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.15alkyl wherein such compound hydrolyzes to form the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid, e.g., the compound hydrolyzes to form the hydroxy compound on the one hand and octanoic acid, decanoic acid, dodecanoic acid, tetradecanoic acid or hexadecanoic acid on the other hand), [0092] in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form; and [0093] (ii) a PDE1 inhibitor, for example a compound according to Formula II
[0093] ##STR00012## [0094] wherein [0095] R.sub.2 is H and R.sub.3 and R.sub.4 together form a tri- or tetra-methylene bridge [pref. with the carbons carrying R.sub.3 and R.sub.4 having the R and S configuration respectively]; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.3 are each methyl and R.sub.4 is H; or R.sub.2 and R.sub.4 are H and R.sub.3 is isopropyl [pref. the carbon carrying R.sub.3 having the R configuration]; [0096] R.sub.6 is (optionally halo-subsitututed) phenylamino or (optionally halo-subsitututed) benzylamino; for example, phenylamino or 4-fluorophenylamino; [0097] R.sub.10 is methylcarbonyl, (optionally halo-subsitututed) phenyl, (optionally halo-subsitututed) pyridyl (for example 3-fluoropyrid-2-yl), or thiadiazolyl (e.g., 1,2,3-thiadiazol-4-yl); [0098] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
[0099] For example, Composition 1 includes, inter alia, the following embodiments: [0100] 1.1. Composition I, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --N(H)--, --N(CH.sub.3)-- or --O--; [0101] 1.2. Composition I or 1.1, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --N(H); [0102] 1.3. Composition I or 1.1, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --N(CH.sub.3)--; [0103] 1.4. Composition I or 1.1, wherein X in the compound of Formula I is --O--; [0104] 1.5. Composition I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(.dbd.O), --C(H)(OH) or --C(H)(OR.sub.1); [0105] 1.6. Composition I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(.dbd.O); [0106] 1.7. Composition I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(H)(OH); [0107] 1.8. Composition I or any of formulae 1.1-1.4, wherein Y in the compound of Formula I is --C(H)(OR.sub.1); [0108] 1.9. Composition I or 1.8, wherein R.sub.1 in the compound of Formula I is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl (e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.1-5alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.6-15alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.16-21alkyl), preferably said alkyl is a straight chain, optionally saturated or unsaturated and optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy (e.g., ethoxy) groups, for example R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.6alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.7alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl, --C(O)--C.sub.11alkyl, --C(O)-C.sub.13alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.15alkyl wherein such compound hydrolyzes to form the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid, e.g., the compound hydrolyzes to form the hydroxy compound on the one hand and octanoic acid, decanoic acid, dodecanoic acid, tetradecanoic acid or hexadecanoic acid on the other hand); e.g., wherein R.sub.1 in the compound of Formula I is --C(O)--C.sub.6-15alkyl, e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl; or wherein R.sub.1 in the compound of Formula I is --C(O)--C.sub.1-5alkyl, e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.3alkyl. [0109] 1.10. Composition I or any of 1.1-1.5 or 1.7, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0109] ##STR00013## [0110] 1.11. Composition I or any of 1.1-1.5 or 1.7, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0110] ##STR00014## [0111] 1.12. Composition I or any of 1.1-1.5 or 1.7, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0111] ##STR00015## [0112] 1.13. Composition I or any of 1.1, 1.3, 1.5 or 1.7, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0112] ##STR00016## [0113] 1.14. Composition I or any of 1.1, 1.3, 1.5 or 1.6, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0113] ##STR00017## [0114] 1.15. Composition 1.14 wherein the Compound of Formula I is in the form of the tosylate salt. [0115] 1.16. Any foregoing Composition wherein, in the Compound of Formula II, R.sub.6 is phenylamino or 4-fluorophenylamino. [0116] 1.17. Any foregoing Composition wherein, in the Compound of Formula II, R.sub.10 is 3-fluoropyrid-2-yl or methylcarbonyl. [0117] 1.18. Any foregoing Composition wherein, in the Compound of Formula II, R.sub.6 is phenylamino or 4-fluorophenylamino and R.sub.10 is 3-fluoropyrid-2-yl or methylcarbonyl. [0118] 1.19. Any foregoing Composition wherein the Compound of Formula II is
[0118] ##STR00018## [0119] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form. [0120] 1.20. Any foregoing Composition wherein the Compound of Formula II is in the form of the monophosphate salt. [0121] 1.21. Any foregoing Composition, wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0121] ##STR00019## [0122] in free of pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, e.g., tosylate salt form; and the Compound of Formula II is:
[0122] ##STR00020## [0123] in free of pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, e.g., monophosphate salt form. [0124] 1.22. Any foregoing Composition comprising effective amounts of both a Compound of Formula I and a Compound of Formula II. [0125] 1.23. Any foregoing Composition in unit daily dosage form comprising 1 mg to 60 mg, e.g. 1 mg to 10 mg, e.g. 2 mg to 7 mg of the Compound of Formula 1. [0126] 1.24. Any foregoing Composition in unit daily dosage form comprising 0.1 mg to 10 mg e.g., lmg to 5 mg, of the Compound of Formula II, [0127] 1.25. Any foregoing Composition further comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier. [0128] 1.26. Any foregoing Composition in the form of a tablet. [0129] 1.27. Any foregoing Composition in the form of a capsule. [0130] 1.28. Any foregoing Composition in the form of a transdermal patch. [0131] 1.29. Any foregoing composition wherein the Compound of Formula I and the Compound of Formula II are in a bioerodable matrix, e.g., a bioerodable copolymer, for example poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), e.g., for administration by injection to form a depot. [0132] 1.30. Any foregoing Composition in unit dosage form wherein the Compound of Formula I is:
[0132] ##STR00021## [0133] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, in an amount of 1 mg to 10 mg, e.g., 2 mg to 7 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent; [0134] and the Compound of Formula II is:
[0134] ##STR00022## [0135] in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form, in an amount of 0.5 mg to 10 mg, e.g. 1 to 5 mg, the dosage calculated as the free base equivalent. [0136] 1.31. Composition 1.30 in the form of a tablet or capsule for oral administration comprising the compound of Formula I in tosylate salt form in an amount equivalent to 1 to 5 mg of free base, the compound of Formula II in monophosphate salt form in an amount equivalent to 0.5 to 2 mg of free base, and a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier. [0137] 1.32. Any foregoing Composition wherein the compound of Formula I and/or of Formula II is deuterated, e.g., wherein the deuterium:protium ratio at a specified position in the molecule is significantly higher, e.g., at least 2.times., for example at least 10.times. higher, than above the natural isotope ratios. [0138] 1.33. Any foregoing Composition wherein the Compound of Formula I is a Compound of Formula 1 as described in WO 2015/154025, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference, e.g., wherein the --CH.sub.2- adjacent to X and or Y is --CHD- or --CD2-, wherein D signifies a deuterium hydrogen.
[0139] Any foregoing Composition for use in any of Methods 1, et seq. The disclosure further provides the use of a compound of Formula I as hereinbefore described in combination with a compound of Formula II as hereinbefore described, for use in the manufacture of a medicament, e.g., according to any of Composition 1, et seq., for use in any of Methods 1 et seq.
[0140] The 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand for use in the foregoing Methods and Compositions may for example be a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand compound as disclosed in any of the following: U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,548,493; 7,238,690; 6,552,017; 6,713,471; U.S. RE39680, U.S. RE39679; for example as disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 8,598,119, or WO 2011/133224 or WO 2015/154025, for example, a Compound of Formula I as described above. The compounds of Formula I and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and salt crystals may be made using the methods as described and exemplified in any of the following patents or applications: U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,548,493; 7,238,690; 6,552,017; 6,713,471; U.S. RE39680; U.S. RE39679; PCT/US08/03340; U.S. application Ser. No. 10/786,935; WO 2009/114181 and WO 2011/133224, the contents of each of which are incorporated by reference in their entirety.
[0141] The Compounds of Formula I as hereinbefore described have a selective receptor profile wherein at low doses, e.g., 5-10 mg, they fully saturate the 5-HT2A receptors and only partially occupy (e.g. 5%-15% occupancy) the dopamine D2 receptors, and also bind to dopamine D2 receptors more extensively and to serotonin reuptake transporter (SERT) at a higher dose. Therefore the Compounds of the Invention are effective in treating one or more disorders associated with dementia, e.g., one or more disorders associated with mild cognition impairment and dementing illnesses including senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down syndrome, elderly depression, Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome, corticobasal degenerations, and prion disease, particularly behavioral/mood disturbances (e.g., agitation, aggressive/assaultive behavior) and sleep disorders, which are inadequately treated by the current marketed drugs for dementia and Alzheimer's disease, as well as treating psychosis and depressive disorders in patients suffering from dementia.
[0142] The PDE1 inhibitor may for example be a PDE1 inhibitor compound as disclosed in any of the following: WO 2006/133261, WO 2007/025103, WO 2007/143705, WO 2009/075784, WO 2009/073210, WO 2010/065153, WO 2010/065148, WO 2010/065151, WO 2010/065149, WO 2010/065147, WO 2010/065152, WO 2011/043816, WO 2011/153129, WO 2011/153135, WO 2011/153136, WO 2011/153138, WO 2012/171016, WO 2013/192556, WO 2014/151409, WO 2014/205354, or WO 2014/145617, for example as disclosed in WO 2009/075784, the contents of each of which are incorporated by reference herein in their entireties. For example, the PDE1 inhibitor may be a compound of Formula II as hereinbefore described.
[0143] The combinations as disclosed (i.e., of Compounds of Formula I and Formula II as hereinbefore described) may be administered simultaneously, separately or sequentially with one or more other active agents to treat dementia or dementing illnesses as hereinbefore described, particularly Alzheimer's disease or symptoms thereof.
[0144] The second or further therapeutic agents useful for the prophylaxis or treatment of dementia as hereinbefore described, particularly Alzheimer's disease, e.g., as described in Method 1 and 2 above, include but are not limited to a cholinesterase inhibitor and/or N-Methyl D-Asparate (NMDA) receptor antagonist.
[0145] Cholinesterase inhibitors, e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, are known in the art and/or are described e.g., in U.S. Pat Nos. 4,895,841; and 4,948,807, the contents of each of which are incorporated by reference in their entirety. Preferred cholinesterase inhibitors to be used with the compound of the present invention include donepezil, rivastignmine, galantamine and tacrine.
[0146] NMDA receptor antagonists are also known in the art and are described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,061,703, the contents of which are incorporated by reference in their entirety. Preferred NMDA receptor antagonist to be used with the compound of the present invention is memantine.
[0147] Unlike dopamine receptor antagonists, Compounds of Formula I normalize brain dopamine activity, particularly in the prefrontal cortex. The Compounds of Formula I bind to 5-HT2A and dopamine D.sub.2 receptors. Compounds of Formula I also exhibit nanomolar binding affinity for SERT compared to known antidepressants. Therefore, the compounds of Formula I are useful for the treatment of (1) behavioral or mood disorders such as agitation/irritation, aggressive/assaultive behavior, anger, physical or emotional outbursts; (2) psychosis; (3) depression; and (4) sleep disorders in patients suffering from dementia, particularly Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, in addition to the therapeutic agents useful for the treatment of dementia, the methods of the invention as hereinbefore described may optionally further comprises one or more therapeutic agents selected from antidepressant compounds, compounds that modulate GABA activity (e.g., enhances the activity and facilitates GABA transmission), a GABA-B agonist, a 5-HT modulator (e.g., a 5 -HT.sub.1A agonist, a 5-HT2A antagonist, a 5-HT2A inverse agonist, etc.), a melatonin agonist, an ion channel modulator (e.g., blocker) , a serotonin-2 antagonist/reuptake inhibitor (SARIs), an orexin receptor antagonist, an H3 antagonist, a noradrenergic antagonist, a galanin agonist, a CRH antagonist, human growth hormone, a growth hormone agonist, estrogen, an estrogen agonist, a neurokinin-1 drug, and an antipsychotic agent, e.g., an atypical antipsychotic agent, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form. In such methods, the therapeutic agents may be adjunctive to the compounds of the invention. As used herein the term "adjunctive" refers to any treatment that is used in conjunction with another to increase the chance of cure, or to increase the first treatment's efficacy. In other words, adjunctive therapy acts as an aid to the primary treatment. The combinations of the invention can include mixtures of the combined drugs, as well as two or more separate compositions of the drugs, which individual compositions can be, for example, co-administered together to a patient at the same of different times.
[0148] The antidepressant useful for the invention may be selected from amitriptyline, amoxapine, bupropion, citalopram, clomipramine, desipramine, doxepin, duloxetine, escitaloprame, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, imipramine, isocarboxazid, maprotiline, mirtazapine, nefazodone, nortriptyline, paroxetine, phenelzine sulfate, protiptyline, sertraline, tranylcypromine, trazodone, trimipramine, and velafaxine, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form. In certain embodiment, the antidepressant(s) is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). In a further embodiment, the SSRI compound is selected from the group consisting of citalopram , escitalopram oxalate, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine maleate, paroxetine, sertraline, and dapoxetine, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
[0149] The dosages for combined therapy with a compound of Formula I, a compound of Formula II, and a further therapeutic agent can be the same as or lower than the approved dosage for the drug, the clinical or literature test dosage or the dosage used for the drug as a monotherapy. In a specific embodiment, the dosages of a compound of Formula I of Formula II, and/or the additional therapeutic agents are lower than when used in a monotherapy.
[0150] The term "GABA" refers to gamma-aminobutyric acid. The GABA compounds are compounds which bind to the GABA receptor, and include, but are not limited to one or more of doxepin, alprazolam, bromazepam, clobazam, clonazepam, clorazepate, diazepam, flunitrazepam, flurazepam, lorazepam, midazolam, nitrazepam, oxazepam, temazapam, triazolam, indiplon, zopiclone, eszopiclone, zaleplon, Zolpidem, gabaxadol, vigabatrin, tiagabine, EVT 201 (Evotec Pharmaceuticals) or estazolam.
[0151] 5HT.sub.2A antagonists include ketanserin, risperidone, eplivanserin, volinanserin (Sanofi-Aventis, France), pruvanserin, pimavanserin (ACP-103), MDL 100907 (Sanofi-Aventis, France), HY10275 (Eli Lilly), APD125 (Arena Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, Calif.), AVE8488 (Sanofi-Aventis, France) and pizotifen.
[0152] 5HT.sub.1A agonists include repinotan, sarizotan, eptapirone, buspirone and MN-305 (MediciNova, San Diego, Calif.).
[0153] Melatonin agonists include melatonin, ramelteon (ROZEREM.RTM., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Japan), VEC-162 (Vanda Pharmaceuticals, Rockville, Md.), PD-6735 (Phase II Discovery) and agomelatine.
[0154] Ion channel blockers such as lamotrigine, gabapentin or pregabalin.
[0155] Orexin receptor antagonists include orexin, a 1,3-biarylurea, SB-334867-a (GlaxoSmithKline, UK), GW649868 (GlaxoSmithKline) and a benzamide derivative, for example.
[0156] Serotonin-2 antagonist/reuptake inhibitors (SARI) include Org 50081 (Organon--Netherlands), ritanserin, nefazodone, serzone and trazodone.
[0157] Neurokinin-1 drugs include Casopitant (GlaxoSmithKline).
[0158] Specific examples of additional therapeutic agents useful for the current invention include modafinil, armodafinil, doxepin, alprazolam, bromazepam, clobazam, clonazepam, clorazepate, diazepam, flunitrazepam, flurazepam, lorazepam, midazolam, nitrazepam, oxazepam, temazapam, triazolam, indiplon, zopiclone, eszopiclone, zaleplon, zolpidem, gabaxadol, vigabatrin, tiagabine, EVT 201 (Evotec Pharmaceuticals), estazolam, ketanserin, risperidone, eplivanserin, volinanserin (Sanofi-Aventis, France), pruvanserin, pimavanserin (ACP-103), pizotifen, MDL 100907 (Sanofi-Aventis, France), HY10275 (Eli Lilly), APD125 (Arena Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, Calif.), AVE8488 (Sanofi-Aventis, France), repinotan, sarizotan, eptapirone, buspirone, MN-305 (MediciNova, San Diego, Calif.), melatonin, ramelteon (ROZEREM.RTM., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Japan), VEC-162 (Vanda Pharmaceuticals, Rockville, Md.), PD-6735 (Phase II Discovery), agomelatine, lamotrigine, gabapentin, pregabalin, orexin, a 1,3-biarylurea, SB-334867-a (GlaxoSmithKline, UK), GW649868 (GlaxoSmithKline), a benzamide derivative, Org 50081 (Organon--Netherlands), ritanserin, nefazodone, serzone, trazodone, Casopitant (GlaxoSmithKline), amitriptyline, amoxapine, bupropion, citalopram, clomipramine, desipramine, doxepin, duloxetine, escitaloprame, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, imipramine, isocarboxazid, maprotiline, mirtazapine, nefazodone, nortriptyline, paroxetine, phenlzine sulfate, protiptyline, sertraline, tranylcypromine, trazodone, trimipramine, velafaxine, chlorpromazine, haloperidol, droperidol, fluphenazine, loxapine, mesoridazine molidone, perphenazine, pimozide, prochlorperazine promazine, thioridazine, thiothixene, trifluoperazine, clozapine, aripiparazole, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, ziprasidone and paliperidone, asenapine, lurasidone, iloperidone and cariprazine, in free or pharmaceutically acceptable salt form.
[0159] If not commercially available, starting materials for these processes may be made using techniques similar or analogous to the synthesis of known compounds. All references cited herein are hereby incorporated in their entirety by reference.
[0160] The words "treatment" and "treating" are to be understood accordingly as embracing prophylaxis and treatment or amelioration of symptoms of disease and/or treatment of the cause of the disease. In particular embodiment, the word "treatment" and "treating" refers to prophylaxis or amelioration of symptoms of the disease.
[0161] The term "patient" may include a human or non-human patient.
[0162] The term "dementia" is intended to refer to a condition or disorder characterized by the loss of cognitive ability affecting memory, thinking, language, judgment and behavior. Early symptoms of dementia may include difficulty performing tasks that require some thought (balancing a checkbook, playing games (such as bridge); learning new information; getting lost on familiar routes; having language difficulties (difficulties in finding name of familiar objects); losing interest in things previously enjoy; losing social skills. More severe symptoms of dementia include change in sleep patterns, often waking up at night; difficulty performing basic tasks such as brushing teeth or preparing a meal; forgetting details about current events; having hallucinations, violent behavior, delusions, depression, agitation; difficulty reading or writing; having poor judgment or loss of ability to recognize danger; losing the ability to recognize family members or understand language. The term "dementia" refers to any of the dementing illnesses as described herein regardless of etiology and therefore shall include but not limited to mild or severe cognition impairment and dementing illnesses such as senile dementia, Alzheimer's disease, Pick's disease, frontotemporal dementia, parasupranculear palsy, dementia with Lewy bodies, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Down syndrome, elderly depression, Wernicke-Korsakoff's syndrome, corticobasal degenerations, and prion disease. In a particular embodiment, dementia refers to mild cognitive impairment. In another embodiment, dementia refers to Alzheimer's disease.
[0163] The term "disorder associated with dementia" means common co-morbid psychiatric disorders or conditions associated with dementia, which include but not limited to (1) behavioral or mood disorders such as agitation/irritation, aggressive/assaultive behavior, anger, physical or emotional outbursts; (2) psychosis; (3) depression; and (4) sleep disorders. In particular embodiment of the invention, the disorders associated with dementia are disorders associated Alzheimer's disease.
[0164] The term "mild cognitive impairment" or "mild cognition impairment" (MCI, also known as incipient dementia, or isolated memory impairment) is cognitive impairment beyond that expected based on the age and education of the individual, but which is not significant enough to interfere with their daily activities. Symptoms of MCI include difficulty performing more than one task at a time, solving problems or making decisions, forgetting recent events or conversations and taking longer to perform more difficult mental activities.
[0165] If not otherwise specified or clear from context, the following terms herein have the following meanings:
[0166] "Alkyl" as used herein is a saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon moiety, e.g., one to twenty-one carbon atoms in length, which may be linear or branched (e.g., n-butyl or tert-butyl), preferably linear, unless otherwise specified. For example, "C.sub.1-21 alkyl" denotes alkyl having 1 to 21 carbon atoms. In one embodiment, alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more hydroxy or C.sub.1-22alkoxy (e.g., ethoxy) groups. In another embodiment, alkyl contains 1 to 21 carbon atoms, preferably straight chain and optionally saturated or unsaturated, for example R.sub.1 is an alkyl chain containing 1 to 21 carbon atoms, preferably 6-15 carbon atoms, 16-21 carbon atoms, e.g., so that together with the --C(O)-- to which it attaches, e.g., when cleaved from the compound of Formula I, forms the residue of a natural or unnatural, saturated or unsaturated fatty acid.
[0167] The 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand, for example a substituted heterocycle fused gamma-carbolines as described herein and/or the PDE1 inhibitor for use in the Methods and Compositions of the disclosure may be in free, pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug form. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts include, for example, the tosylate salts in the case of Compounds of Formula 1, the phosphate salts in the case of Compounds of Formula II, and other salts as described above. Where dosages or amounts of a salt are given by weight, e.g., milligrams per day or milligrams per unit dose, the dosage amount of the salt is given as the weight of the corresponding free base, unless otherwise indicated.
[0168] The 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A/D2 receptor ligand and/or the PDE1 inhibitor may in some cases also exist in prodrug form. A prodrug form is compound which converts in the body to the active compound. For example compounds which contain hydroxy or carboxy substituents may form physiologically hydrolysable and acceptable esters. As used herein, "physiologically hydrolysable and acceptable ester" means esters which are hydrolysable under physiological conditions to yield acids (in the case of compounds which have hydroxy substituents) or alcohols (in the case of compounds which have carboxy substituents) which are themselves physiologically tolerable at doses to be administered. For example, wherein Y of the compound of Formula I is --C(H)(OR.sub.1), and R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl, e.g., --C(O)--C.sub.3alkyl or --C(O)--C.sub.9alkyl, these compounds may hydrolyze under physiological condition to yield a compound of Formula I wherein Y is --C(H)(OH) on the one hand and C.sub.1-21alkyl-C(O)OH, e.g., C.sub.3alkyl--C(O)OH or C.sub.9alkyl-C(O)OH on the other hand. As will be appreciated the term thus embraces conventional pharmaceutical prodrug forms. Wherein a prodrug (e.g., the compound of formula (I) wherein R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl) is used, the dosage amount is calculated based on the amount of the compound of formula (I) wherein Y is --C(.dbd.O)-- or --CH(OH)--, in free base form.
[0169] The term "simultaneously" when referring to a therapeutic use means administration of two or more active ingredients at or about the same time by the same route of administration.
[0170] The term "separately" when referring to a therapeutic use means administration of two or more active ingredients at or about the same time by different route of administration.
[0171] The phrase "disorder(s) associated with Alzheimer's disease" includes, but is not limited to (1) behavioral or mood disorders such as agitation/irritation, aggressive/assaultive behavior, anger, physical or emotional outbursts; (2) psychosis; (3) depression; and (4) sleep disorders in patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease.
[0172] Dosages employed in practicing the present invention will of course vary depending, e.g. on the particular disease or condition to be treated, the particular active compounds used, the mode of administration, and the therapy desired. Unless otherwise indicated, an amount of an active compound for administration (whether administered as a free base or as a salt form) refers to or is based on the amount of the compound in free form (i.e., the calculation of the amount is based on the amount of active moiety in free form, not taking into account the weight of the counter ion in the case of a salt). Wherein a prodrug (e.g., the compound of formula (I) wherein R.sub.1 is --C(O)--C.sub.1-21alkyl) is used, the dosage amount is calculated based on the amount of the compound of formula (I) wherein Y is C(.dbd.O) in free base form. Compounds of the Invention may be administered by any suitable route, including orally, intra-muscularly, subcutaneously, parenterally or transdermally, but are preferably administered orally. Compounds of the Invention may be administered by any suitable route, including orally, parenterally or transdermally, but are preferably administered orally.
[0173] For the avoidance of doubt, any disclosure of a numerical range, e.g., "up to X" amount is intended to include the upper numerical limit X. Therefore, a disclosure of "up to 60 mg" is intended to include 60 mg.
[0174] Pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds of the Invention may be prepared using conventional diluents or excipients and techniques known in the galenic art. Thus oral dosage forms may include tablets, capsules, solutions, suspensions and the like.
* * * * *























XML
uspto.report is an independent third-party trademark research tool that is not affiliated, endorsed, or sponsored by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) or any other governmental organization. The information provided by uspto.report is based on publicly available data at the time of writing and is intended for informational purposes only.
While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information displayed on this site. The use of this site is at your own risk. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
All official trademark data, including owner information, should be verified by visiting the official USPTO website at www.uspto.gov. This site is not intended to replace professional legal advice and should not be used as a substitute for consulting with a legal professional who is knowledgeable about trademark law.