Crystalline Forms Of Selective S1p1 Receptor Modulator And Preparation Method Thereof
Chen; Minhua ; et al.
U.S. patent application number 16/065350 was filed with the patent office on 2019-11-14 for crystalline forms of selective s1p1 receptor modulator and preparation method thereof. This patent application is currently assigned to Crystal Pharmatech Co., Ltd.. The applicant listed for this patent is Crystal Pharmatech Co., Ltd.. Invention is credited to Minhua Chen, Jiaoyang Li, Xiaoyu Zhang, Yanfeng Zhang.
| Application Number | 20190345120 16/065350 |
| Document ID | / |
| Family ID | 59089139 |
| Filed Date | 2019-11-14 |
| United States Patent Application | 20190345120 |
| Kind Code | A1 |
| Chen; Minhua ; et al. | November 14, 2019 |
CRYSTALLINE FORMS OF SELECTIVE S1P1 RECEPTOR MODULATOR AND PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF
Abstract
The present disclosure relates to crystalline Form 1, Form 2, Form 3 of Ponesimod, a selective S1P1 receptor modulator, and preparation methods thereof. The X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 18.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 14.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 11.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree.; the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 3.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree.; the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 12.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 5.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. The crystalline forms in present disclosure not only have better stability but also have higher solubility compared with the prior art forms, they are more suitable for the formulation development of Ponesimod.
| Inventors: | Chen; Minhua; (Suzhou, CN) ; Zhang; Yanfeng; (Suzhou, CN) ; Li; Jiaoyang; (Suzhou, CN) ; Zhang; Xiaoyu; (Suzhou, CN) | ||||||||||
| Applicant: |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assignee: | Crystal Pharmatech Co.,
Ltd. Suzhou, Jiangsu CN Crystal Pharmatech Co., Ltd. Suzhou, Jiangsu CN |
||||||||||
| Family ID: | 59089139 | ||||||||||
| Appl. No.: | 16/065350 | ||||||||||
| Filed: | December 23, 2016 | ||||||||||
| PCT Filed: | December 23, 2016 | ||||||||||
| PCT NO: | PCT/CN2016/111689 | ||||||||||
| 371 Date: | June 22, 2018 |
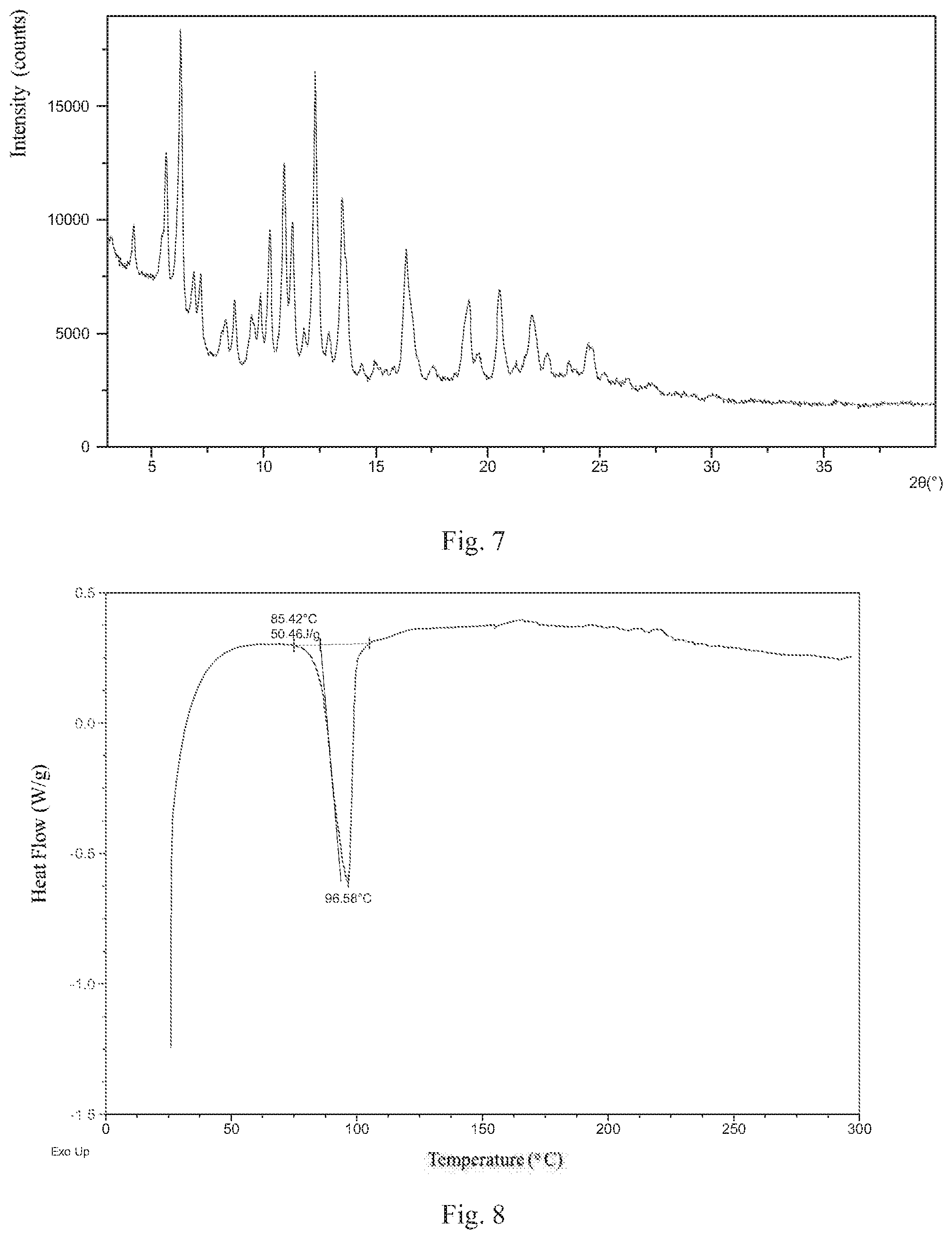
| Current U.S. Class: | 1/1 |
| Current CPC Class: | A61P 17/06 20180101; C07D 277/42 20130101; C07B 2200/13 20130101 |
| International Class: | C07D 277/42 20060101 C07D277/42; A61P 17/06 20060101 A61P017/06 |
Foreign Application Data
| Date | Code | Application Number |
|---|---|---|
| Dec 25, 2015 | CN | 201510993103.7 |
Claims
1. A crystalline Form 2 of Ponesimod, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern (CuK.alpha. radiation) shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 3.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 6.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
2. The crystalline Form 2 according to claim 1, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern further shows one or more characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 5.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 10.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 7.0.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
3. The crystalline Form 2 according to claim 1, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern further shows one or more characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 13.7.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 7.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 11.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
4. The crystalline Form 2 according to claim 1, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 is substantially as depicted in FIG. 4.
5. A preparation method of Form 2 according to claim 1, wherein the method comprises: mixing Ponesimod with esters to obtain a suspension, and stirring the suspension at a temperature of 0-50.degree. C., isolating solids to obtain Form 2.
6. The preparation method according to claim 5, wherein said ester is isopropyl acetate or ethyl acetate or a combination thereof.
7. A crystalline Form 3 of Ponesimod, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern (CuK.alpha. radiation) shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 12.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 5.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
8. The crystalline Form 3 according to claim 7, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern further shows one or more characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 13.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 11.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
9. The crystalline Form 3 according to claim 7, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern further shows one or more characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 10.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 16.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 20.5.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
10. The crystalline Form 3 according to claim 7, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 is substantially as depicted in FIG. 7.
11. A preparation method of Form 3 according to claim 7, wherein the method is method 1) or method 2): method 1) comprising mixing Ponesimod with esters and firstly heating the mixture to obtain a clear solution, and then cooling until solids are precipitated out, isolating the solids to obtain Form 3; method 2) comprising mixing Ponesimod with ethers to obtain a suspension and stirring the suspension at a temperature of 40-60.degree. C., isolating solids to obtain Form 3.
12. The preparation method according to claim 11, wherein in method 1), said ester is isopropyl acetate or ethyl acetate or a combination thereof; in method 2), said ether is methyl tert-butyl ether.
13. The preparation method according to claim 11, wherein in the method 1), said mixture is heated to 40-80.degree. C. in the heating process; said mixture is cooled to -5.degree. C.-5.degree. C. in the cooling process.
14. A crystalline Form 1 of Ponesimod, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern (CuK.alpha. radiation) shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 18.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 14.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 11.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
15. The crystalline Form 1 according to claim 14, wherein the X-ray powder diffraction pattern further shows one or more of characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 16.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 22.7.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 26.0.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., and 13.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
16. A preparation method of Form 1 according to claim 14, wherein the method comprises: dissolving Ponesimod into cyclic ethers to obtain a solution, and then adding alkanes into the solution until solids are precipitated out and Form I is obtained.
17. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Ponesimod and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein said Ponesimod is Form 2 according to claim 1.
18. The pharmaceutical composition according to claim 17, wherein the pharmaceutical composition is used for treatment of psoriasis.
19. (canceled)
20. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Ponesimod and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein said Ponesimod is Form 3 according to claim 7.
21. A pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Ponesimod and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein said Ponesimod is Form 1 according to claim 14.
Description
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0001] The present disclosure relates to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, particularly relates to novel crystalline forms of Ponesimod, a selective S1P1 receptor modulator and preparation method thereof.
BACKGROUND
[0002] It is generally known that crystalline forms greatly affect drug's quality. Different crystalline forms may have remarkable difference in appearance, solubility, melting point, dissolution profile, bioavailability and so on, thus affect drug's stability, bioavailability and efficacy. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop novel and more suitable crystalline forms for drug development.
[0003] Ponesimod (Compound I) is a selective S1P1 receptor modulator developed by Actelion. The drug achieved positive results in phase II mid-stage study for the treatment of moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis, and will be studied in phase III for the treatment of psoriasis.
##STR00001##
[0004] At present, CN100567275 C discloses a preparation method of Compound I in example 85, which is amorphous according to disclosure of CN102177144 B. Additionally CN102177144 B discloses Form A, Form C, Form III and Form II of Compound I. Studies show that Form III has poor crystallinity, and will transform to Form II at room temperature; Form II is difficult to repeat and contains a certain amount of propionic acid; thermodynamic stability of Form A is inferior to Form C. Compared with them all, Form C is suitable for drug development, but its solubility is unsatisfactory.
SUMMARY
[0005] To solve the problems of prior art, the objective of the present disclosure is to provide novel crystalline forms of Ponesimod with better properties than Form C in prior art, and these novel crystalline forms are designated as Form 1, Form 2, and Form 3.
[0006] The present disclosure also provides the preparation method and use of Form 1, Form 2, and Form 3.
[0007] The X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 of present disclosure shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 18.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 14.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 11.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0008] Furthermore, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 further shows one or more characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 16.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 22.7.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. Preferably, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 16.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 22.7.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0009] Furthermore, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 further shows one or more characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 26.0.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 13.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. Preferably, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 shows diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 26.0.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 13.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
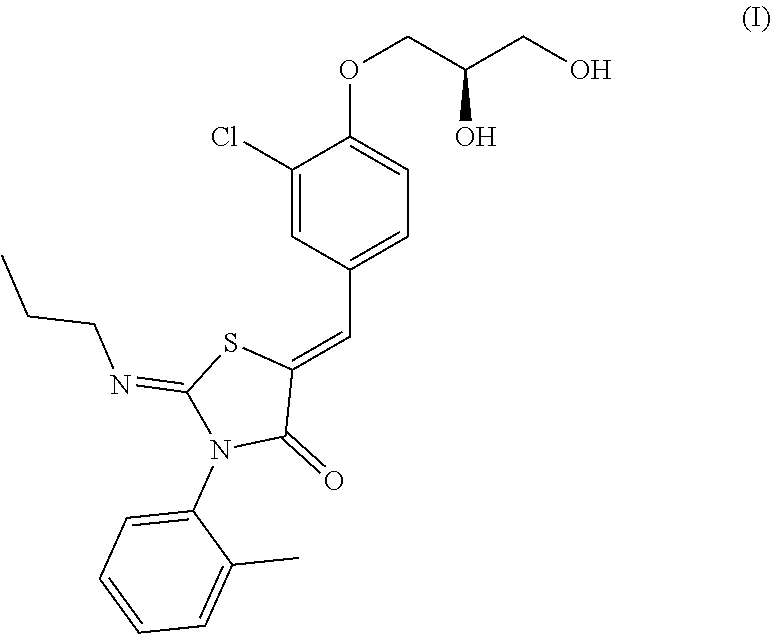
[0010] According to a specific and preferred aspect of the present disclosure, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 1 is substantially as depicted in FIG. 1.
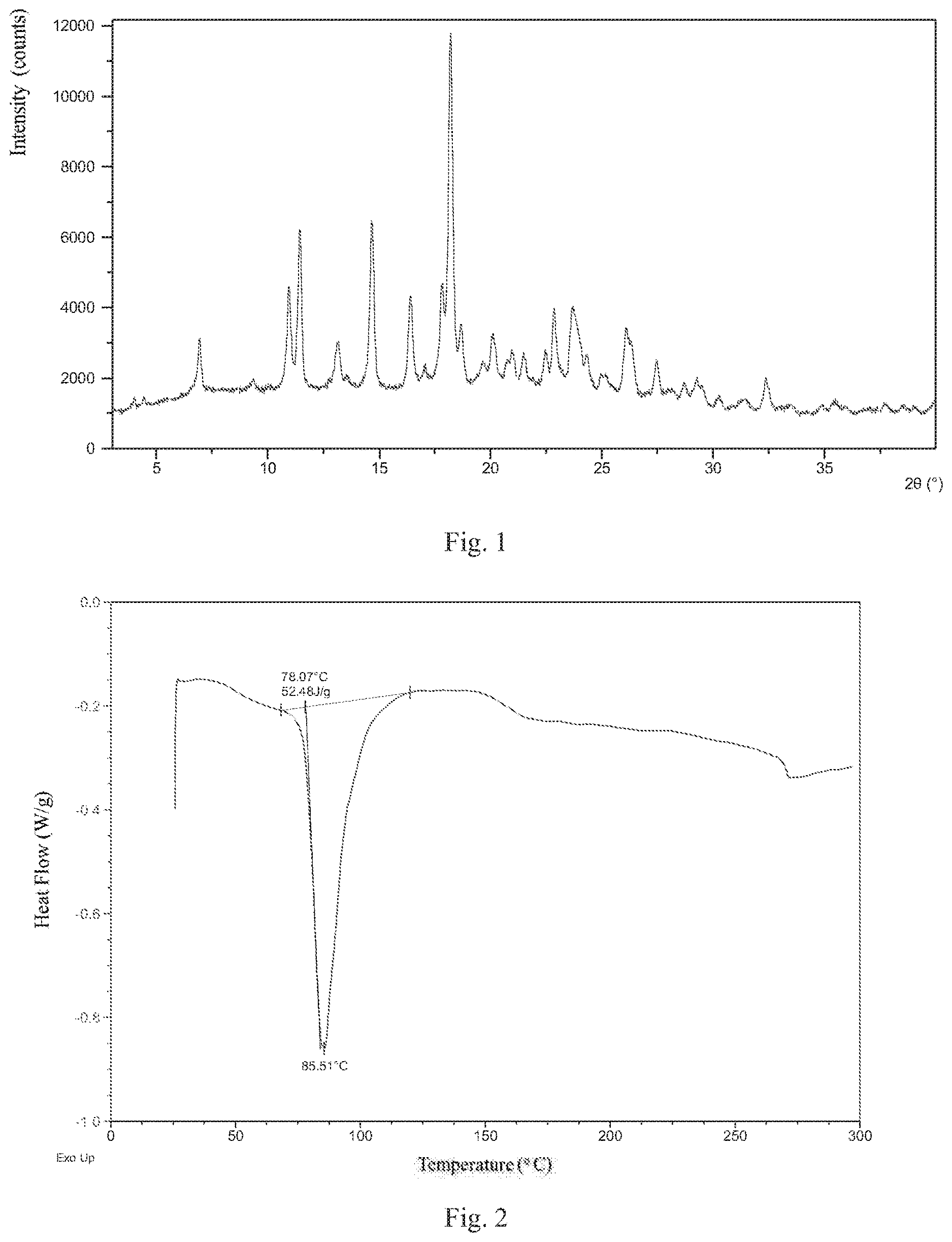
[0011] Preferably, Form 1 of present disclosure shows an endothermic peak when heated to around 78.degree. C. (onset temperature), and the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curve is substantially as depicted in FIG. 2.
[0012] Preferably, Form 1 of present disclosure shows 7.1% weight loss when heated to 100.degree. C., and the thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) curve is substantially as depicted in FIG. 3.
[0013] The preparation method of Form 1 comprises: dissolving Ponesimod into cyclic ethers to obtain a solution, and then adding alkanes into the solution until solid is precipitated out and Form 1 is obtained.
[0014] Furthermore, said cyclic ethers include, but not limited to one or more solvents selected from tetrahydrofuran, 1, 4-dioxane and the like. Preferably, said cyclic ether is 1, 4-dioxane. Said alkanes include, but not limited to one or more solvents selected from n-hexane, n-heptane and the like. Preferably, said alkane is n-heptane.
[0015] The X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 of the present disclosure shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 3.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.1.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0016] Furthermore, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 further shows one or more diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 5.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 10.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 7.0.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. Preferably, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 shows diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 5.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 10.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 7.0.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0017] Furthermore, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 further shows one or more diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 13.7.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 7.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 11.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. Preferably, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 shows diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 13.7.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 7.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 11.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
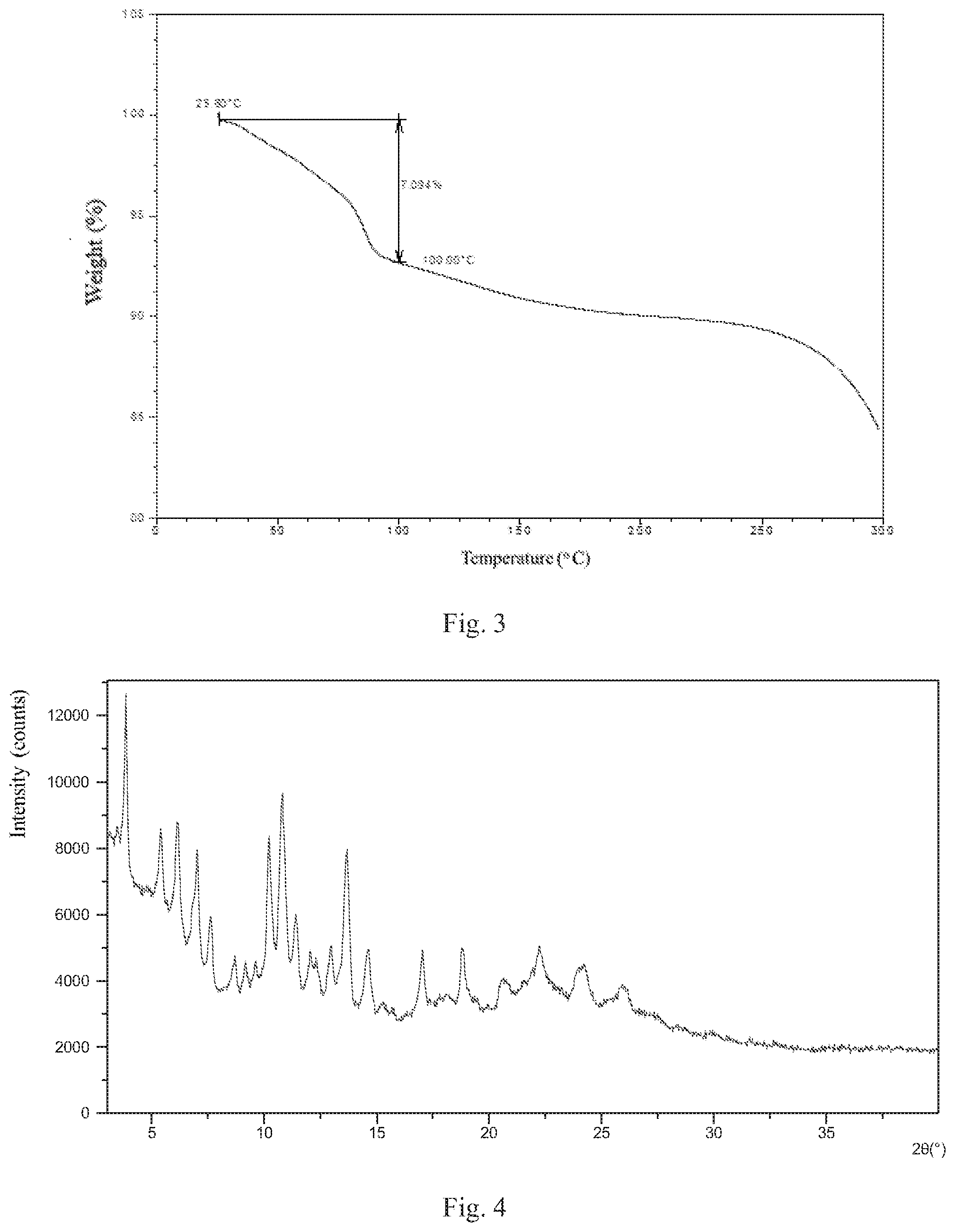
[0018] According to a specific and preferred aspect of the present disclosure, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 2 is substantially as depicted in FIG. 4.
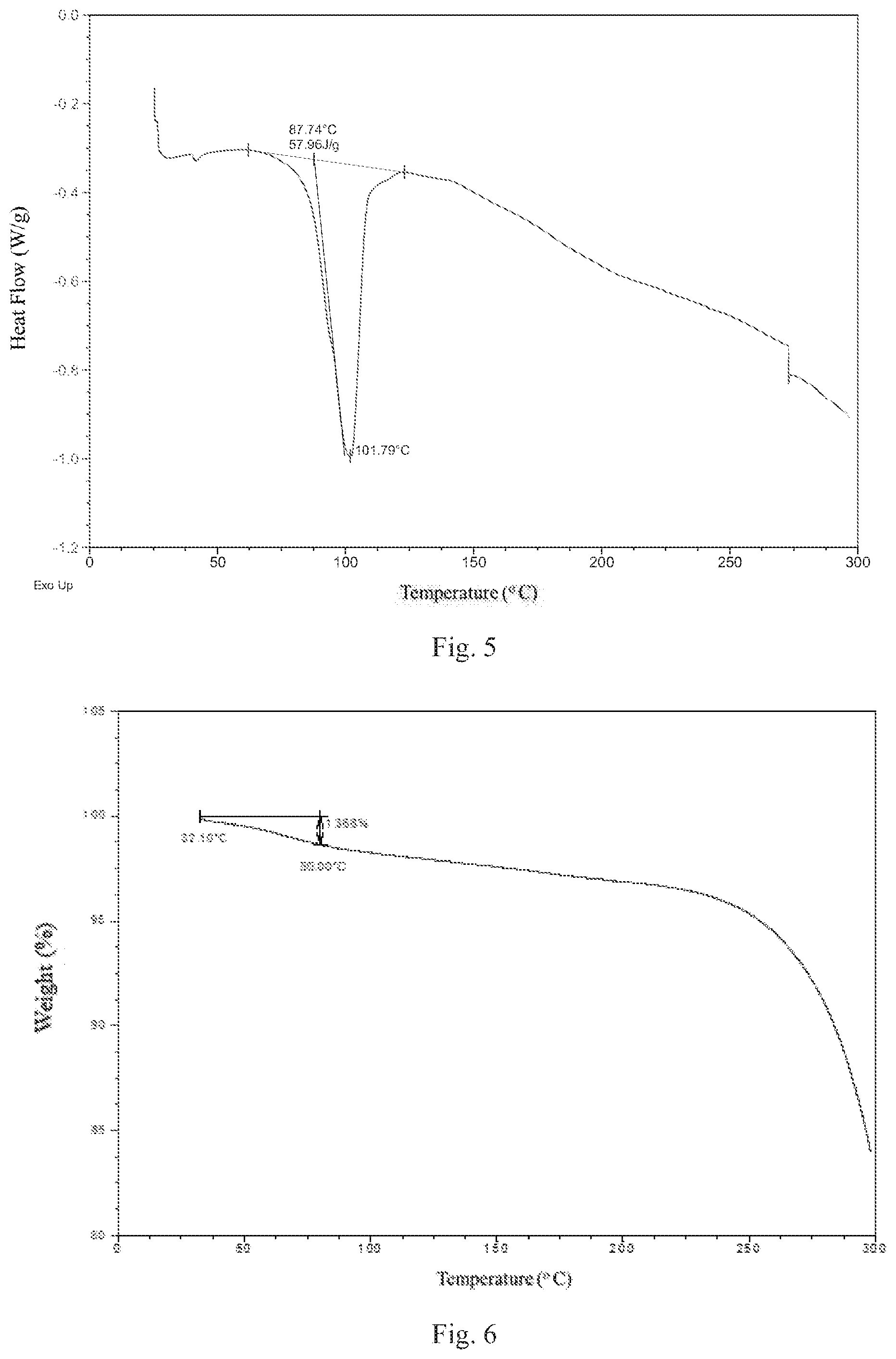
[0019] Preferably, Form 2 of the present disclosure shows an endothermic peaks when heated to around 88.degree. C. (onset temperature), and the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curve is substantially as depicted in FIG. 5.
[0020] Form 2 of the present disclosure shows 1.4% weight loss when heated to 80.degree. C., and the thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) curve is substantially as depicted in FIG. 6.
[0021] The preparation method of Form 2 comprises: mixing Ponesimod with esters to obtain a suspension, and stirring the suspension at a temperature of 0-50.degree. C., isolating solid to obtain Form 2 of Ponesimod.
[0022] Furthermore, said esters include, but not limited to one or more solvents selected from isopropyl acetate, ethyl acetate and the like. Preferably, said ester is isopropyl acetate or ethyl acetate.
[0023] Preferably, the preparation method of Form 2 comprises stirring the suspension at room temperature.
[0024] The X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 of the present disclosure shows characteristic peaks at 2theta values of 12.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 6.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 5.6.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0025] Furthermore, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 shows one or more diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 13.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 11.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. Preferably, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 shows diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 10.8.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 13.4.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 11.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0026] Furthermore, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 shows one or more diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 10.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 16.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 20.5.degree..+-.0.2.degree.. Preferably, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 shows diffraction peaks at 2theta values of 10.2.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 16.3.degree..+-.0.2.degree., 20.5.degree..+-.0.2.degree..
[0027] According to a specific and preferred aspect of the present disclosure, the X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Form 3 is substantially as depicted in FIG. 7.
[0028] Preferably, Form 3 of the present disclosure shows an endothermic peak when heated to around 85.degree. C. (onset temperature), and the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curve is substantially as depicted in FIG. 8.
[0029] Form 3 can be prepared by any one of the following preparation methods: [0030] 1) mixing Ponesimod with esters, heating the mixture to obtain a clear solution, cooling until solid is precipitated out, isolating the solid to obtain Form 3. Said esters include, but not limited to isopropyl acetate, ethyl acetate and the like. Preferably the ester is isopropyl acetate or ethyl acetate; said mixture is heated to 40-80.degree. C. in the heating process, more preferably 50-80.degree. C., most preferably 50-60.degree. C.; said mixture is preferably cooled to -5.degree. C.-5.degree. C. in the cooling process, more preferably about 4.degree. C. [0031] 2) mixing Ponesimod with ethers to obtain a suspension and stirring the suspension at a temperature of 40-60.degree. C., isolating the solid to obtain Form 3. Said ethers include, but not limited to methyl tert-butyl ether.
[0032] Form 1, Form 2, Form 3 or their mixture in any ratio can be used as a selective S1P1 receptor modulator for preparing drugs for treatment of psoriasis.
[0033] The present disclosure also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising Form 1, Form 2, Form 3 or their mixture in any ratio. Furthermore, the pharmaceutical composition can be used for treatment of psoriasis, including but not limited to treatment of moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis and the like.
[0034] By carrying out the above-mentioned technical solution, the present disclosure has the following advantages over prior art:
[0035] Form 1, Form 2 and Form 3 of Ponesimod in the present disclosure are surprisingly discovered, which have better stability and solubility than Form C in prior art. The present disclosure provides new and better choices for the formulation development of Ponesimod, and is of great significance to drug development.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
[0036] FIG. 1 shows an XRPD pattern of Form 1;
[0037] FIG. 2 shows a DSC curve of Form 1;
[0038] FIG. 3 shows a TGA curve of Form 1;
[0039] FIG. 4 shows an XRPD pattern of Form 2;
[0040] FIG. 5 shows a DSC curve of Form 2;
[0041] FIG. 6 shows a TGA curve of Form 2;
[0042] FIG. 7 shows an XRPD pattern of Form 3;
[0043] FIG. 8 shows a DSC curve of Form 3;
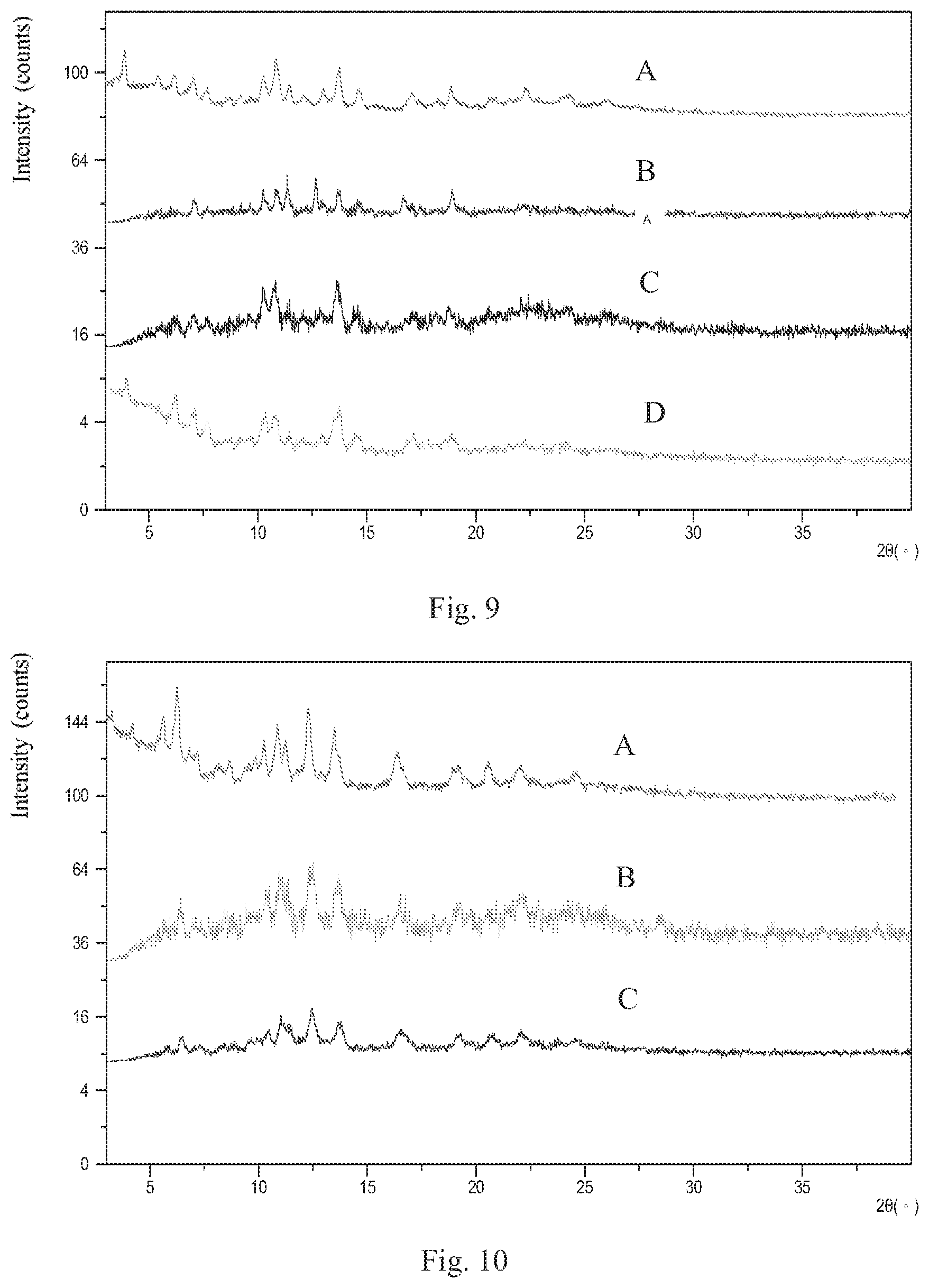
[0044] FIG. 9 shows an XRPD overlay pattern of Form 2 before and after storage (A is the sample before storage, B is the sample after stored under 25.degree. C./60% RH for 6 months, C is the sample after stored under 40.degree. C./75% RH for 6 months, D is the sample after stored under 80.degree. C. for 3 months);
[0045] FIG. 10 shows an XRPD overlay pattern of Form 3 before and after storage (A is the sample before storage, B is the sample after stored under 25.degree. C./60% RH for 6 months, C is the sample after stored under 40.degree. C./75% RH for 6 months).
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE DISCLOSURE
[0046] The present disclosure will be further explained by the specific examples, but the present disclosure is not limited to the following examples. The experimental conditions not specified are general conditions. Starting material of Ponesimod used in the preparation method is amorphous prepared by known method in prior art (for example, the method disclosed in CN100567275 C or CN102177144 B).
[0047] In the following examples, general conditions or conditions recommended by the manufacturer are used in test methods.
[0048] The abbreviations in the present disclosure are explained as follows:
XRPD: X-ray Powder Diffraction;
[0049] DSC: Differential Scanning calorimetry;
TGA: Thermal Gravimetric Analysis.
[0050] X-ray powder diffraction pattern in the present disclosure was acquired by a Panalytical Empyrean X-ray powder diffractometer. The parameters of the X-ray powder diffraction of the present disclosure are as follows:
X-ray Reflection: Cu, K.alpha.
[0051] K.alpha.1 (.ANG.): 1.540598; K.alpha.2 (.ANG.): 1.544426 [0052] K.alpha.2/K.alpha.1 intensity ratio: 0.50
Voltage: 45 (kV)
Current: 40 (mA)
[0053] Scanning range: from 3.0 degree to 40.0 degree Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) data in the present disclosure were acquired by a TA Q2000. The parameters of the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) method of the present disclosure were as follows: Heating rate: 10.degree. C./min Purge gas: nitrogen Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) data in the present disclosure are acquired by a TA Q5000. The parameters of the thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) method of the present disclosure were as follow: Heating rate: 10.degree. C./min Purge gas: nitrogen
Example 1
Preparation Method of Form 1:
[0054] 48.1 mg of Ponesimod was added into 0.4 mL of 1, 4-dioxane, then the mixture was filtered to obtain a filtrate. 1.2 mL of n-heptane was added dropwise into the filtrate at room temperature to obtain a suspension, then the suspension was stirred overnight and Form 1 was obtained by centrifugation.
[0055] The XRPD data of Form 1 prepared in this example comprise diffraction peaks listed in Table 1. The XRPD pattern is displayed in FIG. 1. The DSC curve is displayed in FIG. 2. The TGA curve is displayed in FIG. 3.
TABLE-US-00001 TABLE 1 2theta d spacing intensity % 3.90 22.63 3.82 4.33 20.38 4.11 6.83 12.95 19.68 9.25 9.56 8.92 10.83 8.17 33.57 11.33 7.81 48.18 13.07 6.78 18.63 14.55 6.09 50.30 16.28 5.44 30.46 16.95 5.23 12.05 17.69 5.01 33.34 18.10 4.90 100.00 18.62 4.76 21.41 19.54 4.54 13.20 20.02 4.44 20.89 20.89 4.25 15.98 21.39 4.15 15.31 22.37 3.97 15.94 22.74 3.91 26.48 23.56 3.78 27.53 24.20 3.68 15.26 24.86 3.58 10.25 25.04 3.56 9.56 25.96 3.43 21.58 26.24 3.40 18.40 27.36 3.26 13.49 28.06 3.18 5.96 28.61 3.12 7.59 29.16 3.06 9.02 30.16 2.96 4.41 31.36 2.85 3.55 32.26 2.78 9.03 35.32 2.54 2.65
Example 2
Preparation Method of Form 2:
[0056] 399.9 mg of Ponesimod was added into 4.0 mL of ethyl acetate to obtain a suspension. The obtained suspension was stirred at room temperature for 24 hours, and then centrifuged to obtain a solid. The obtained solid was dried under vacuum for 3 hours at room temperature. The obtained solid was Form 2.
[0057] The XRPD data of Form 2 prepared in this example comprise the diffraction peaks listed in Table 2. The XRPD pattern is displayed in FIG. 4. The DSC curve is displayed in FIG. 5. The TGA curve is displayed in FIG. 6.
TABLE-US-00002 TABLE 2 2theta d spacing Intensity % 3.83 23.05 100.00 5.39 16.40 57.99 6.13 14.42 61.47 7.01 12.61 51.80 7.61 11.62 31.18 8.70 10.17 18.02 9.13 9.68 16.66 9.60 9.22 16.67 10.19 8.68 55.67 10.76 8.22 68.96 11.42 7.75 30.04 12.04 7.35 20.31 12.33 7.18 16.82 12.94 6.84 21.97 13.69 6.47 50.85 14.64 6.05 19.98 15.23 5.82 3.84 17.04 5.20 19.88 18.81 4.72 21.25 20.52 4.33 10.78 22.23 4.00 21.07 23.88 3.73 13.89 24.26 3.67 14.97 25.86 3.45 9.12 29.93 2.99 1.31
Example 3
Preparation Method of Form 3:
[0058] 106.8 mg of Ponesimod was added into 2.0 mL of methyl tert-butyl ether to obtain a suspension. The obtained suspension was stirred at 50.degree. C. for 24 hours, and then centrifuged to obtain a solid. The obtained solid was dried under vacuum for 3 hours at room temperature. The obtained solid was Form 3 of Ponesimod.
[0059] The XRPD data of Form 3 prepared in this example comprise the diffraction peaks listed in Table 3. The XRPD pattern is displayed in FIG. 7. The DSC curve is displayed in FIG. 8.
TABLE-US-00003 TABLE 3 2theta d spacing Intensity % 3.04 29.06 44.85 4.11 21.47 48.04 5.57 15.86 68.31 6.22 14.21 100.00 6.80 13.00 35.35 7.12 12.42 34.38 8.24 10.73 22.06 8.63 10.25 27.59 9.37 9.44 23.09 9.77 9.05 29.19 10.19 8.68 46.52 10.84 8.16 65.59 11.20 7.90 48.96 11.72 7.55 19.84 12.22 7.24 88.65 12.81 6.91 18.81 13.42 6.60 55.47 13.65 6.49 34.77 14.28 6.20 10.23 14.90 5.95 10.64 16.28 5.45 41.52 17.49 5.07 9.70 18.88 4.70 21.65 19.11 4.64 26.78 19.49 4.55 12.97 20.46 4.34 30.74 21.17 4.20 10.12 21.89 4.06 23.63 22.62 3.93 12.80 23.52 3.78 10.69 24.39 3.65 16.03 24.62 3.62 14.56 25.13 3.54 7.78 26.19 3.40 6.51 27.26 3.27 4.75
Example 4
Preparation Method of Form 3:
[0060] 149.5 mg of Ponesimod was added into 1.2 mL of ethyl acetate to obtain a mixture. The mixture was heated to 50.degree. C. to obtain a clear solution, and then the solution was cooled to 4.degree. C. for crystallization, centrifuged to obtain a solid. The solid was dried under vacuum for 3 hours at room temperature. The obtained solid was Form 3 of Ponesimod.
[0061] The XRPD data of Form 3 prepared in this example comprise the diffraction peaks listed in Table 4.
TABLE-US-00004 TABLE 4 2theta d spacing Intensity % 5.51 16.03 59.01 6.23 14.19 100.00 6.89 12.82 20.88 8.60 10.28 28.10 9.76 9.06 23.34 10.15 8.71 46.48 10.82 8.18 86.19 11.21 7.89 66.72 12.14 7.29 95.88 13.35 6.63 58.84 16.30 5.44 42.09 18.97 4.68 24.42 20.50 4.33 29.97 21.92 4.06 24.79 24.43 3.64 15.93
Example 5
Stability Assessment of Form 2:
[0062] 20 mg of sample of Form 2 was stored under 25.degree. C./60% RH, 40.degree. C./75% RH for 6 months, and 80.degree. C. for 3 months. The assessment results were shown in Table 5. The XRPD patterns of Form 2 before and after storage were depicted in FIG. 9, which show that Form 2 sample doesn't change under 25.degree. C./60% RH and 40.degree. C./75% RH for 6 months, under 80.degree. C. for 3 months. The results indicate that Form 2 has good physical stability.
TABLE-US-00005 TABLE 5 Stability assessment of Form 2 Initial Form Conditions Storage time Solid Form after storage Form 2 25.degree. C./60% RH 6 months Form 2 (FIG. 9A) (FIG. 9B) Form 2 40.degree. C./75% RH 6 months Form 2 (FIG. 9A) (FIG. 9C) Form 2 80.degree. C. 3 months Form 2 (FIG. 9A) (FIG. 9D)
Example 6
Stability Assessment of Form 3:
[0063] 20 mg of sample of Form 3 was stored under 25.degree. C./60% RH and 40.degree. C./75% RH for 6 months. The assessment results were shown in Table 6. The XRPD patterns of Form 3 before and after storage were depicted in FIG. 10, which show that Form 3 doesn't change under 25.degree. C./60% RH and 40.degree. C./75% RH for 6 months. The results indicate that Form 3 has good physical stability.
TABLE-US-00006 TABLE 6 Stability assessment of Form 3 Crystalline form after Initial form Conditions Storage time storing Form 3 25.degree. C./60% RH 6 months Form 3 (FIG. 10A) (FIG. 10B) Form 3 40.degree. C./75% RH 6 months Form 3 (FIG. 10A) (FIG. 10C)
Example 7
[0064] Solubility assessment of Form 2 in present disclosure and Form A, Form C disclosed in CN102177144B:
[0065] Saturated solution of Form 2 and Form A, Form C disclosed in CN102177144B were prepared in FaSSIF (Fasted state simulated intestinal fluids, pH=6.5), FeSSIF (Fed state simulated intestinal fluids, pH=5.0), SGF (Simulated gastric fluids, pH=1.8), and water. Concentrations in the saturation solutions were measured after 1 hour and 24 hours by HPLC. The data were listed in Table 7.
TABLE-US-00007 TABLE 7 Solubility of Form 2 and Form A, Form C disclosed in CN102177144B FaSSIF FeSSIF SGF H.sub.2O Form Form Form Form Form Form Form Form Form Form Form Form Time A C 2 A C 2 A C 2 A C 2 Solubility 1 h 0.007 0.010 0.017 0.141 0.133 0.996 0.034 0.029 0.097 ND* 0.003 ND (mg/mL) 24 h 0.004 0.003 0.033 0.163 0.149 0.813 0.045 0.024 0.124 ND 0.001 ND *ND: below the LOD of instrument
[0066] The data in Table 7 indicate that the solubility of Form 2 is higher than that of Form A and Form C in FaSSIF, FeSSIF, and SGF, which means Form 2 will have higher bioavailability, which is of great significance to improve the efficacy and safety of Ponesimod and reduce the drug loading.
Example 8
Solubility Assessment of Form 3 and Form A, Form C:
[0067] Form 3 and Form A, Form C were prepared into saturated solution in FaSSIF (Fasted state simulated intestinal fluids, pH=6.5), FeSSIF (Fed state simulated intestinal fluids, pH=5.0) and water. Concentrations in the saturation solutions were measured after 1 hour and 24 hours by HPLC. The results were listed in Table 8.
TABLE-US-00008 TABLE 8 Solubility of Form 3 and Form A, Form C disclosed in CN102177144B. FaSSIF FeSSIF H.sub.2O Form Form From 3 From From From 3 From From From 3 Time A C A C A C Solubility 1 h 0.007 0.010 0.084 0.141 0.133 1.168 ND* 0.003 ND (mg/mL) 24 h 0.004 0.003 0.015 0.163 0.149 0.486 ND 0.001 ND *ND: below the LOD of instrument
[0068] Solubility is one of the key characteristics of a drug, which directly affects in vivo absorption of the drug. Different crystalline forms have remarkable difference in solubility, and will affect in vivo absorption, thus lead to the differences in bioavailability. As a result, clinical safety and efficacy will be affected.
[0069] The data in Table 8 indicate that the solubility of Form 3 is higher than that of Form A and Form C in FaSSIF and FeSSIF, which means Form 3 will have higher bioavailability, which is of great significance to improve the efficacy and safety of Ponesimod and reduce the drug loading.
[0070] The examples described above are only for illustrating the technical concepts and features of the present disclosure, and intended to make those skilled in the art being able to understand the present disclosure and thereby implement it, and should not be concluded to limit the protective scope of this disclosure. Any equivalent variations or modifications according to the spirit of the present disclosure should be covered by the protective scope of the present disclosure.
* * * * *

D00001

D00002

D00003

D00004

D00005

XML
uspto.report is an independent third-party trademark research tool that is not affiliated, endorsed, or sponsored by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) or any other governmental organization. The information provided by uspto.report is based on publicly available data at the time of writing and is intended for informational purposes only.
While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information displayed on this site. The use of this site is at your own risk. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
All official trademark data, including owner information, should be verified by visiting the official USPTO website at www.uspto.gov. This site is not intended to replace professional legal advice and should not be used as a substitute for consulting with a legal professional who is knowledgeable about trademark law.