Copper-zinc Alloy For A Plumbing Fitting And Method For The Production Thereof
SCHROEDER; Thomas ; et al.
U.S. patent application number 14/847566 was filed with the patent office on 2015-12-31 for copper-zinc alloy for a plumbing fitting and method for the production thereof. This patent application is currently assigned to GROHE AG. The applicant listed for this patent is Grohe AG. Invention is credited to Olaf PETZOLDT, Thomas SCHROEDER.
| Application Number | 20150376736 14/847566 |
| Document ID | / |
| Family ID | 48875640 |
| Filed Date | 2015-12-31 |
| United States Patent Application | 20150376736 |
| Kind Code | A1 |
| SCHROEDER; Thomas ; et al. | December 31, 2015 |
COPPER-ZINC ALLOY FOR A PLUMBING FITTING AND METHOD FOR THE PRODUCTION THEREOF
Abstract
A copper-zinc alloy, in particular for providing components for a plumbing fitting. The alloy comprises (in % by weight): between 63.0 and 64.5% Cu, between 33.8 and 36.8% Zn, between 0.0 and 0.20% Pb, between 0.2 and 0.7% Al, between 0.04 and 0.14% As, between 0.0 and 0.3% Fe, between 0.0 and 0.3% Sn, between 0.0 and 0.1% Mn, and residual constituents in respective maximum quantities of 0.02%. A method for producing a cast component is provided that includes a copper-zinc alloy of this type. The copper-zinc alloy and the components produced therewith permit a particularly environmentally-friendly, cost-effective production of plumbing fittings.
| Inventors: | SCHROEDER; Thomas; (Menden, DE) ; PETZOLDT; Olaf; (Wernigerode, DE) | ||||||||||
| Applicant: |
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assignee: | GROHE AG Hemer DE |
||||||||||
| Family ID: | 48875640 | ||||||||||
| Appl. No.: | 14/847566 | ||||||||||
| Filed: | September 8, 2015 |
Related U.S. Patent Documents
| Application Number | Filing Date | Patent Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2013/002907 | Sep 27, 2013 | |||
| 14847566 | ||||
| Current U.S. Class: | 420/480 ; 148/553 |
| Current CPC Class: | E03C 1/04 20130101; C22C 9/04 20130101; E03C 1/021 20130101; C22F 1/08 20130101; F16K 17/00 20130101; F16K 51/00 20130101 |
| International Class: | C22C 9/04 20060101 C22C009/04; E03C 1/02 20060101 E03C001/02; C22F 1/08 20060101 C22F001/08 |
Foreign Application Data
| Date | Code | Application Number |
|---|---|---|
| Mar 7, 2013 | DE | 10 2013 003 817.0 |
Claims
1. A copper-zinc alloy comprising: 63.0 to 64.5 wt % Cu; 33.8 to 36.8 wt % Zn; 0.0 to 0.20 wt % Pb; 0.2 to 0.7 wt % Al; 0.04 to 0.14 wt % As; 0.0 to 0.3 wt % Fe; 0.0 to 0.3 wt % Sn; 0.0 to 0.1 wt % Mn; and residual constituents in maximum quantities of 0.02% each.
2. The copper-zinc alloy according to claim 2, wherein: Cu is 63.5 to 63.8 wt %; Zn is 35.2 to 35.6 wt %; Pb is 0.17 to 0.20 wt %; Al is 0.32 to 0.40 wt %; As is 0.11 to 0.13 wt %; Fe is 0.16 to 0.20 wt %; Sn is 0.0 to 0.20 wt %; and Mn is 0.0 to 0.02 wt %.
3. The copper-zinc alloy according to claim 1, wherein Pb is less than 0.17 wt %.
4. The copper-zinc alloy according to claim 3, wherein Sn is more than 0.2 wt %.
5. The copper-zinc alloy according to claim 1, wherein no Si is included.
6. A use of a copper-zinc alloy according to claim 1 for a plumbing fitting.
7. A plumbing fitting comprising a housing component, which forms at least one outer surface or an inner surface for a water channel, wherein at least the outer surface or the inner surface is formed with the copper-zinc alloy according to claim 1.
8. A method for producing a cast component from a copper-zinc alloy, comprising at least the following steps: providing a copper-zinc alloy according to claim 1; heating the copper-zinc alloy so that it is present in liquid form; casting the copper-zinc alloy into a predetermined shape; cooling the copper-zinc alloy so that it solidifies; heating the solidified copper-zinc alloy to a temperature from 430.degree. C. to 470.degree. C. for a predetermined holding time; and cooling the copper-zinc alloy.
9. The method according to claim 8, wherein the holding time is in the range from 40 minutes to 70 minutes.
Description
[0001] This nonprovisional application is a continuation of International Application No. PCT/EP2013/002907, filed Sep. 27, 2013, and which claims priority to German Patent Application No. 10 2013 003 817.0, filed Mar. 7, 2013, all of which is herein incorporated by reference.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0002] 1. Field of the Invention
[0003] The present invention relates to a copper-zinc alloy (or brass alloy) for a plumbing fitting as well as a method for the production thereof. In particular, relates to a cast alloy, with the aid of which water-conducting components and/or water-contacting components of a plumbing fixture may be produced.
[0004] 2. Description of the Background Art
[0005] When producing components of a plumbing fitting, a wide range of requirements must be taken into account. In general, the material must be suitable for producing the components of a plumbing fitting, which may have, in part, a highly complex design. This applies to good castability or deformability, on the one hand, as well as to machineability in the event that these components must be post-processed with the aid of machining methods. It goes without saying that cost aspects play a key role here.
[0006] The fact that these components are also used for delivering drinking water must also be taken into account. In this regard, different legal requirements exist worldwide, which are intended to ensure a long-lasting use of such components without contaminating the drinking water, in particular with heavy metals.
[0007] One particularly important requirement in this regard is the dezincification resistance, which is determined, in particular, by a material test according to ISO 6509. The material here is immersed in a 75.degree. C. copper chloride bath (CUCl.sub.2) with a concentration of 12.7 grams of CuCl.sub.2 to one liter of water (H.sub.2O) for a period of 24 hours. The depth to which the zinc ions are discharged is then determined. The shallower this dezincification depth, the better suited this material is for delivering drinking water.
[0008] Another requirement is that the different components of a plumbing fitting may preferably be recycled together. For this purpose, it is considered to be advantageous that a copper-zinc alloy of this type has a preferably small concentration of silicon (Si). It may thus be ensured that the alloy may be mixed with the standard brass alloys in the standard production process and thus be recycled.
[0009] Thus, when selecting a suitable material for components of a plumbing fitting, a large number of different objectives are present, which also conflict with each other to some extent.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0010] It is therefore an object of the present invention is to provide a copper-zinc alloy, which at least partially solves the problems illustrated at the outset. In particular, a copper-zinc alloy should be suitable for use in a plumbing fitting. Furthermore, an advantageous plumbing fitting as well as a method for the production thereof are to be provided.
[0011] Further scope of applicability of the present invention will become apparent from the detailed description given hereinafter. However, it should be understood that the detailed description and specific examples, while indicating preferred embodiments of the invention, are given by way of illustration only, since various changes and modifications within the spirit and scope of the invention will become apparent to those skilled in the art from this detailed description.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING
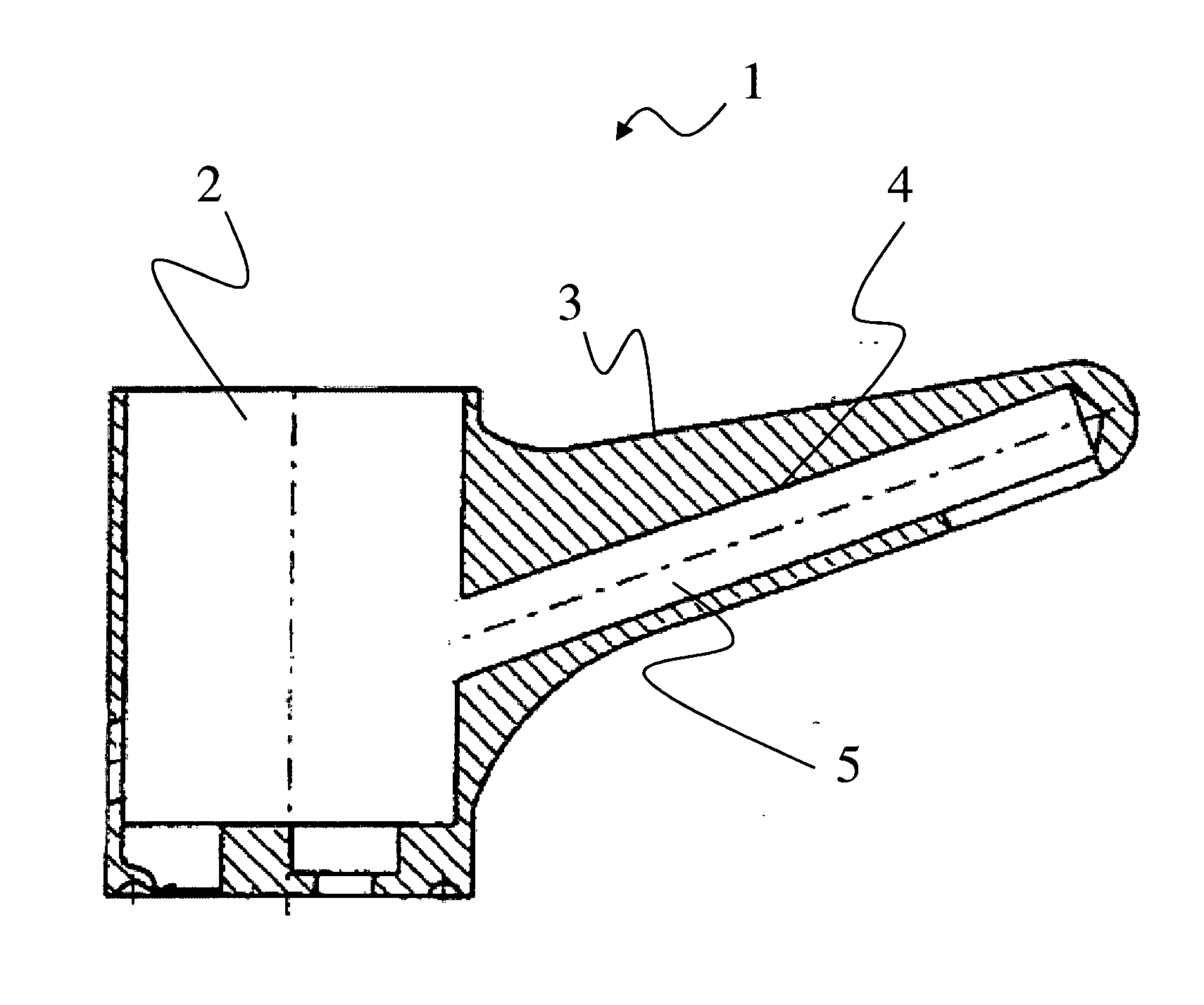
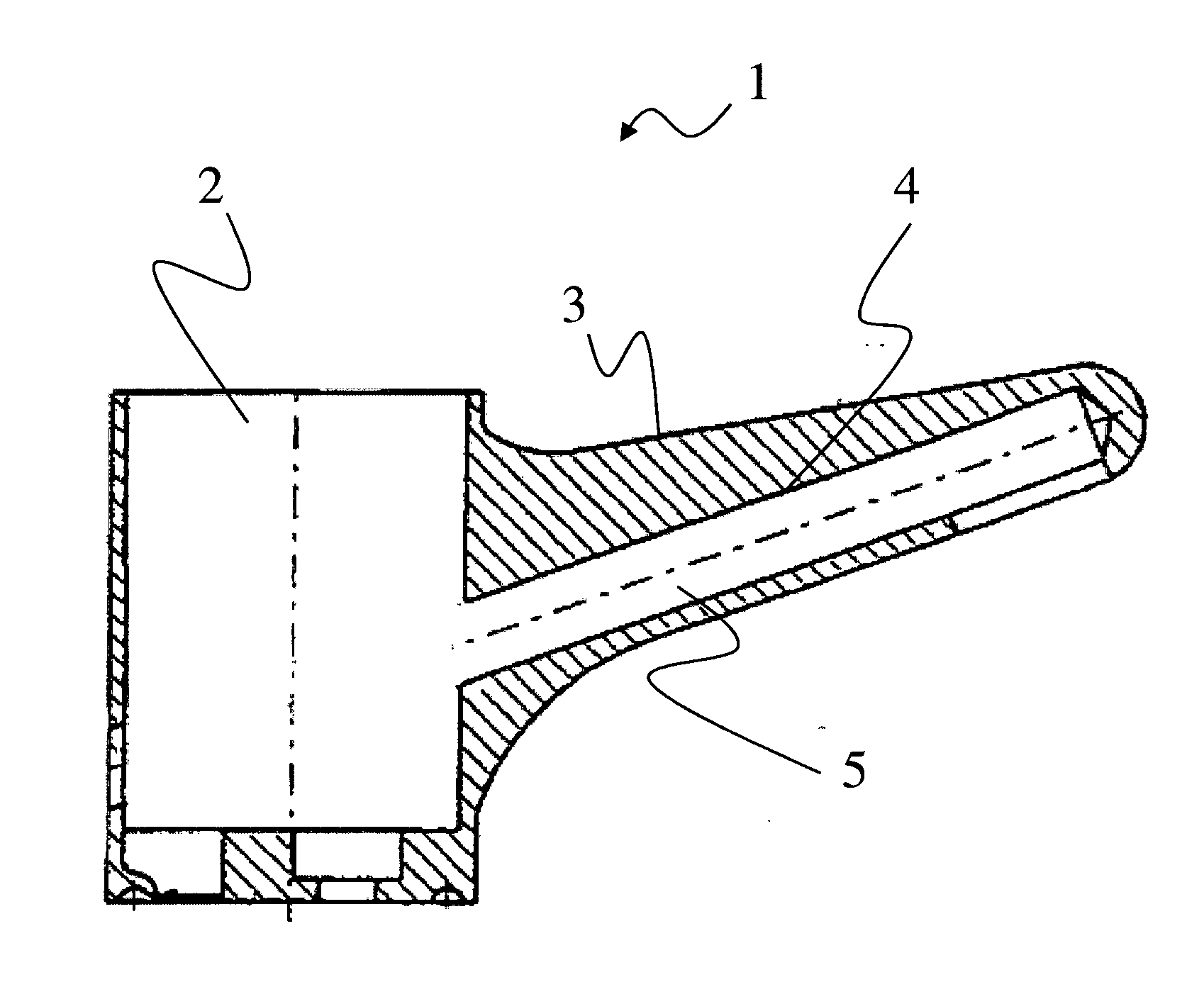
[0012] The present invention will become more fully understood from the detailed description given hereinbelow and the accompanying drawing which is given by way of illustration only, and thus, is not limitive of the present invention, and wherein the sole FIGURE illustrates an example embodiment, showing a cross-sectional view of an adjustment fitting with sealing of the eccentric receiving space.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
[0013] According to an exemplary embodiment of the invention, the copper-zinc alloy comprises: [0014] 63.0 to 64.5 wt % copper (Cu), [0015] 33.8 to 36.8 wt % zinc (Zn), [0016] 0.0 to 0.20 wt % lead (Pb), [0017] 0.20 to 0.70 wt % aluminum (Al), [0018] 0.04 to 0.14 wt % arsenic (As), [0019] 0.0 to 0.30 wt % iron (Fe), [0020] 0.0 to 0.30 wt % tin (Sn), [0021] 0.0 to 0.10 wt % manganese (Mn),
[0022] and residual constituents in maximum quantities of 0.02 wt % each.
[0023] Of the residual constituents, nickel should be emphasized in particular, whose concentration in the alloy is less than 0.02 wt %.
[0024] It should be emphasized that the specified lead content (Pb) of this copper-zinc alloy is very small, or that even no lead is present in the alloy. It should furthermore be noted that the copper content (Cu) is also low compared to known alloys. It should likewise be pointed out that the copper-zinc alloy has only a (negligible) content of silicon (Si). It has surprisingly turned out that this copper-zinc alloy is more cost-effective, on the one hand, due to the composition selected herein, and also has an excellent dezincification resistance, namely to a dezincification depth of less than 200 .mu.m (micrometers), in particular even less than 100 .mu.m.
[0025] The copper-zinc alloy specified here is, in particular, a so-called cast alloy.
[0026] In an exemplary embodiment, the copper-zinc alloy has the following, more precisely specified alloy elements: [0027] 63.0 to 64.5 wt % copper (Cu), [0028] 33.8 to 36.8 wt % zinc (Zn), [0029] 0.017 to 0.20 wt % lead (Pb), [0030] 0.20 to 0.70 wt % aluminum (Al), [0031] 0.04 to 0.14 wt % arsenic (As), [0032] 0.0 to 0.30 wt % iron (Fe), [0033] 0.0 to 0.30 wt % tin (Sn), [0034] 0.0 to 0.10 wt % manganese (Mn),
[0035] and residual constituents in maximum quantities of 0.02 wt % each.
[0036] The copper-zinc alloy exceptionally preferably has the following, more precisely specified alloy elements: [0037] 63.0 to 63.8 wt % Cu, [0038] 35.2 to 35.6 wt % Zn, [0039] 0.17 to 0.20 wt % Pb, [0040] 0.32 to 0.40 wt % Al, [0041] 0.11 to 0.13 wt % As, [0042] 0.16 to 0.20 wt % Fe, [0043] 0.0 to 0.20 wt % Sn, [0044] 0.0 to 0.02 wt % Mn,
[0045] and residual constituents in maximum quantities of 0.02 wt % each.
[0046] With regard to the lead concentration (Pb), it should be noted that this concentration causes an adequate improvement in the machineability of the cast alloy. It is furthermore known that lead has a positive effect on the dezincification resistance. It was determined that, in the specified range, a noteworthy grain-refining effect exists.
[0047] The grain refinement causes the concentration of the less acid-resistant beta brass contained in the brass to be distributed in the dezincification-resistant alpha brass matrix in a fine and isolated, island-shaped manner. It is preferred for the lead concentration to be in a partial range which is close to the upper limit, for example in a range from 0.19 to 0.2 wt %.
[0048] The aluminum (Al) increases the strength of the alpha phase and the beta phase, in particular due to solid-solution hardening, without significantly influencing the hot workability. It furthermore improves the resistance to erosion corrosion as well as the tarnish and weather resistance. Aluminum also increases the strength in order to achieve a high surface quality, especially in cast products.
[0049] In test series, aluminum demonstrated a negative effect on the dezincification resistance. A relatively small aluminum concentration induces a more limited formation of the less acid-resistant beta brass proportionate to surface area. The beta brass solid solution concentration reduced in this way is better distributed in the dezincification-resistant alpha brass matrix in an isolated island-shaped manner. Above the specified upper limit, the dezincification resistance values deteriorated significantly. If the specified lower limit fails to be reached, the physically and economically positive effects of the aluminum are no long extensively used. The aluminum content described for the composition additionally ensures an adequate mold-filling behavior (flowability) of the casting material made of the described copper-zinc alloys. The specified aluminum content furthermore increases the corrosion resistance in slightly alkaline waters and therefore, as a corrosion inhibitor, helps increase the service life.
[0050] In the small amounts specified here, arsenic (As) promotes the fact that the copper zinc alloy having the standard (alpha) phase does not undergo significant zincification. In test series, arsenic also had a positive effect on the characteristic of dezincification resistance. The increased arsenic concentration, compared to the conventional standard brass, causes a lesser formation of the less acid-resistant beta brass proportionate to surface area. One explanation for the positive effects of arsenic on dezincification resistance may be its action as an inhibitor with respect to the chemical attack of the acids used in the dezincification test. The upper limit of 0.14 wt %, or in particular 0.13 wt %, was also selected, in particular, by taking into account the target parameters mentioned at the outset. The lower limit of 0.04 wt %, or in particular 0.11 wt %, is the result of test series. A significant deterioration of the dezincification resistance occurred below this limit. It is preferred for the arsenic concentration to be in a partial range which is close to the upper limit, for example in a range from 0.12 to 0.13 wt %.
[0051] The proposed iron content (Fe) supports, in particular, a grain refinement, due to primarily precipitated iron crystals, and thus improves the mechanical properties of the components. In test series, iron had a positive effect on the characteristic of dezincification resistance. This may be explained by the proven grain-refining effect. The grain refinement causes the iron concentration of the less acid-resistant beta brass contained in the brass to be distributed in the dezincification-resistant alpha brass matrix in a fine and isolated, island-shaped manner. The upper limit of 0.3 wt %, or in particular 0.2 wt %, was set because higher iron values may induce the formation of hard inclusions. The explanation therefor lies in the relatively high melting point of iron. Hard inclusions result in surface defects which are not accepted for surface-mounted fittings. The preferred lower limit of 0.16 wt % is the result of test series. A significant deterioration with regard to dezincification resistance occurred below this limit. It is preferred for the iron concentration to be in a partial range from 0.16 wt % to 0.24 wt %, particularly preferably from 0.18 wt % to 0.20 wt %.
[0052] The tin content (Sn) increases the corrosion resistance (by forming a cover layer), in particular in single-phase (alpha) copper-zinc alloys, and improves, in particular, the strength and/or antifriction properties. The upper limit of 0.3 wt %, in particular 0.2 wt %, was set because, no positive effects on the corrosion resistance could be established beyond this level. The lower limit of 0.0 wt % is the result of test series and the fact that, depending on the input material, very little or no tin may be contained therein. It has furthermore been shown that the addition of tin has a positive influence on the workability of workpieces made from the alloy. It is therefore advantageous if the tin content is at least 0.1 wt %.
[0053] The manganese content proposed here improves the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, in particular, to weather influences or moisture. The upper limit of 0.1 wt %, in particular 0.02 wt %, was set to avoid any problems involving hard inclusions that may occur. This limit was also set on the basis of the content that experience has shown will set in during melting.
[0054] In addition, residual constituents may also be provided, it being possible for these constituents to comprise specific alloy elements as well as (unavoidable) impurities. Each of these residual constituents is permitted with a maximum content of 0.02 wt %. The total quantity of all residual constituents should not exceed, in particular, the value of 0.2 wt %.
[0055] Of the residual constituents, nickel (Ni) should be emphasized, in particular. A nickel content of less than 0.02 wt % makes it possible to minimize a leaching of nickel into the water that is in contact with a workpiece manufactured from the alloy.
[0056] It is clear that the copper-zinc alloy having the content ranges specified here should be selected in such a way that the total quantity of the alloy constituents results in 100 wt %.
[0057] According to exemplary embodiment with respect to the specification of an alloy specified above, which has a concentration of 0.17 to 0.2 wt % Pb, the following composition is proposed for the copper-zinc alloy: [0058] 63.0 to 64.5 wt % Cu, [0059] 33.8 to 36.8 wt % Zn, [0060] less than 0.17 wt % Pb, [0061] 0.2 to 0.7 wt % Al, [0062] 0.04 to 0.14 wt % As, [0063] 0.0 to 0.3 wt % Fe, [0064] 0.0 to 0.3 wt % Sn, [0065] 0.0 to 0.1 wt % Mn,
[0066] and residual constituents in maximum quantities of 0.02% each.
[0067] The copper-zinc alloy particularly preferably has the following composition according to the other design variant: [0068] 63.0 to 64.5 wt % Cu, [0069] 33.8 to 36.8 wt % Zn, [0070] less than 0.17 wt % Pb, [0071] 0.2 to 0.7 wt % Al, [0072] 0.04 to 0.14 wt % As, [0073] 0.0 to 0.3 wt % Fe, [0074] more than 0.2 wt % to a maximum of 0.3 wt % Sn, [0075] 0.0 to 0.1 wt % Mn,
[0076] and residual constituents in maximum quantities of 0.02% each.
[0077] With regard to the constituents Cu, Zn, Al, As, Fe, Sn and Mn, the relationships described above for the alloy having 0.17 to 0.2 wt % Pb also apply to this alloy, which has less than 0.17 wt % Pb.
[0078] The Pb concentration (as described above) serves the purpose of achieving a grain refinement of the copper-zinc alloy and, in particular, of improving the machineability of the alloy as well as improving the workability of workpieces made from the alloy.
[0079] It has surprisingly turned out that the material may also be produced with a lead content of less than 0.17 wt %. It is preferably preferred for the lead content to be even smaller than 0.169 wt % or even smaller than 0.165 wt % and is exceptionally preferably even below 0.1 wt %. According to the RoHS electronic regulation (Directive 2002/95/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council dated Jan. 27, 2003 on limiting the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment) and various national requirements (e.g., in Sweden), a material is considered to be lead-free if the lead content thereof is less than 0.1 wt %. If necessary, the lead content may be, in particular, at least 0.07 wt %.
[0080] The tin content is particularly important to the design variant of the alloy having a reduced lead content. The preferred composition of the other design variant of the alloy having less than 0.17 wt % lead therefore has a tin content of more than 0.2 wt %. The tin content improves the corrosion resistance and machineability of the alloy. The reduced lead content of less than 0.17 wt % compared to the design variant having a lead content of 0.17 wt % to 0.2 wt %, may be at least partially compensated for by an increased tin content, comparatively good results being achievable with regard to the addressed properties or effects of the alloy. The tin content is therefore preferably more than 0.2 wt %. The tin content is particularly preferably even more than 0.21 wt %.
[0081] For both of the alloys described here, the leaching of lead into water that is in contact with workpieces produced from the alloy drops significantly below the predetermined limit values for lead leaching in the approval test for alloys (leaching test according to DIN EN 15664-1 for material approval--so-called Positive List of the 4 Member States). In this test, a material is placed in a solution, the solution acting upon the material for a predetermined (comparatively long) period of time. This period may be, for example, 26 weeks. The amount of alloy constituents that the workpiece has released into the solution is subsequently measured.
[0082] Tests are known for the dezincification resistance of alloys for brass plumbing fittings, in which the alloy is introduced into a solution for a predetermined period of time, and the depth to which a dezincification of the material has taken place is tested. One example of this is the test according to GSO 481.1.110 (Australian Standard 2345-2006). In this test, a sample of the alloy is stored in a test solution containing copper chloride at a temperature of 75.degree. C. for 24 hours. Grindings are then prepared, and the dezincification depth is optically measured under the microscope. The dezincification depth may be an average of no more than 100 .mu.m (micrometers) at 25 measuring points on the sample. These requirements apply to both the specified alloys having a lead content of 0.17 wt % to 0.2 wt % as well as to the alloys having a lead content of less than 0.17 wt %.
[0083] According to an embodiment, it is proposed that the copper-zinc alloy contains no silicon (Si).
[0084] In addition to cost advantages, this results in the fact that this silicon-free alloy may possibly be recycled together with other copper-zinc alloys after use. Due to the fact that the alloy is silicon-free, effects caused by hard inclusions and local precipitates, in particular, are avoidable, which may occur during melting of the alloy.
[0085] The proposed copper-zinc alloy is used, in particular, for a plumbing fitting. In particular, in this area, water-conducting components and/or components exposed to water, may be provided with a copper-zinc alloy of this type. The components may be, in particular, cast components. Examples of components of this type are housing components, rings, sleeves and the like.
[0086] Accordingly, it is also proposed that a plumbing fitting, which includes a housing component that forms at least one outer surface or which comprises an inner surface for a water channel, is designed in such a way that at least the outer surface or the inner surface is formed with the aid of the copper-zinc alloy. The surfaces of the housing component which are moistened by water and/or which conduct water are addressed hereby. It is also possible that the outer surface as well as the inner surface of the housing component are formed with the aid of the copper-zinc alloy, for example, if the housing component is cast as a single piece. Irrespective thereof, it is possible to also provide a protective layer on the outer surface and/or the inner surface, in particular with regard to the visual design and/or the additional improvement of the corrosion protection.
[0087] A method is furthermore proposed for producing a cast component from a copper-zinc alloy, comprising at least the following steps: [0088] providing a copper-zinc alloy according to the invention, [0089] heating the copper-zinc alloy so that it is present in liquid form, [0090] casting the copper-zinc alloy into a predetermined shape, [0091] cooling the copper-zinc alloy so that it solidifies, [0092] heating the solidified copper-zinc alloy to a temperature from 430.degree. C. to 470.degree. C. for a predetermined holding time, [0093] cooling the copper-zinc alloy.
[0094] In particular, a casting method is specified hereby, wherein the cast component is subsequently subjected to another heat treatment.
[0095] The holding time is exceptionally preferably in a range from 40 minutes to 70 minutes, exceptionally preferably in a range from 50 minutes to 65 minutes.
[0096] Using the subsequent heat treatment proposed herein, a structural change, in particular, is achieved, in which a large part of the beta brass present in the cast part is transformed into dezincification-resistant alpha brass. The described heat treatment is advantageous, in particular, if the specified copper-zinc alloy having less than 0.17 wt % Pb is used. Due to the described heat treatment, a grain refinement of the copper-zinc alloy may be achieved, in particular, which results in an improved machineability and an improved dezincification resistance. The described heat treatment therefore facilitates a reduction in the lead content while maintaining the same machineability and dezincification resistance.
[0097] To illustrate the invention, three examples of specific copper-zinc alloys are specified below. The materials CuZn21Si3P and MS63 are also discussed as comparison examples, on the basis of which the differences from the copper-zinc alloy according to the invention are illustrated.
Exemplary Embodiment 1
[0098] 63.60 wt % Cu; 35.50 wt % Zn; 0.177 wt % Pb;
[0099] 0.382 wt % Al; 0.128 wt % As; 0.187 wt % Fe;
[0100] 0.017 wt % Sn; 0.001 wt % Mn;
[0101] 0.008 wt % residual constituents
Exemplary Embodiment 2
[0102] 63.29 wt % Cu; 35.57 wt % Zn; 0.168 wt % Pb;
[0103] 0.459 wt % Al; 0.135 wt % As; 0.163 wt % Fe;
[0104] 0.212 wt % Sn; 0.001 wt % Mn;
[0105] 0.002 wt % residual constituents
Exemplary Embodiment 3
[0106] 63.38 wt % Cu; 35.51 wt % Zn; 0.148 wt % Pb;
[0107] 0.433 wt % Al; 0.125 wt % As; 0.164 wt % Fe;
[0108] 0.239 wt % Sn; 0.001 wt % Mn;
[0109] The specified examples are characterized by an excellent dezincification resistance, a composition being simultaneously present, which may be easily recycled with other brass components. In particular, the copper-zinc alloy according to exemplary embodiment 2 is suitable to be further processed using the described method for producing a cast component. Due to the described heat treatment, properties of the cast component may be achieved, in which it was previously assumed that these properties were achievable only with the aid of increased lead contents above 0.2 wt %, particularly with regard to the machineability and the dezincification resistance properties of the cast component.
[0110] Comparison Materials:
[0111] CuZn21Si3P:
[0112] This alloy has a very high copper content (approximately 76 wt %) and is therefore very expensive. The equally high silicon content of approximately 4 wt % results in enormous problems when mixed with conventional alloys; in particular, the danger of inclusion-comprising silicon oxide arises. The recyclable material must therefore be strictly separated, and only input materials of one type may be used. In practice, a foundry must used either separate furnaces or crucible melting furnaces which have removable inserts for mixtures of CuZn21Si3P and other materials.
[0113] MS 63:
[0114] This brass has a lead content of up to 1.6 wt % and may therefore not be classified as lead-free brass.
[0115] One preferred area of application, to which the invention is, however, not to be limited, is illustrated in the attached FIG. 1. The FIGURE shows a housing component 2, formed in a single piece, for a plumbing fitting. Housing component 2 forms an outer surface 3, which is visible, for example, to the operator. Housing component 2 furthermore forms an inner surface 4, with the aid of which water channel 5 is formed. Housing component 2 is exceptionally preferably a cast component made of the copper-zinc alloy according to the invention.
[0116] The copper-zinc alloy as well as components produced therewith allow a particularly environmentally friendly and cost-effective provision of plumbing fittings. In particular, the copper-zinc alloy and the cast component produced from the copper-zinc alloy meet all of the currently known hygiene requirements, in particular with regard to heavy metal content and heavy metal leaching, corrosion resistance and dezincification resistance.
[0117] The invention being thus described, it will be obvious that the same may be varied in many ways. Such variations are not to be regarded as a departure from the spirit and scope of the invention, and all such modifications as would be obvious to one skilled in the art are to be included within the scope of the following claims.
* * * * *
D00000

D00001

XML
uspto.report is an independent third-party trademark research tool that is not affiliated, endorsed, or sponsored by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) or any other governmental organization. The information provided by uspto.report is based on publicly available data at the time of writing and is intended for informational purposes only.
While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the accuracy, completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information displayed on this site. The use of this site is at your own risk. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
All official trademark data, including owner information, should be verified by visiting the official USPTO website at www.uspto.gov. This site is not intended to replace professional legal advice and should not be used as a substitute for consulting with a legal professional who is knowledgeable about trademark law.